PP Ch_ 2-3 Modified - Maria Regina High School
... Enzymes are substrate specific (One enzyme for a particular reaction will not work with substrates from another particular reaction) Because of the specific fit, the ES Complex is called a LOCK AND KEY COMPLEX ...
... Enzymes are substrate specific (One enzyme for a particular reaction will not work with substrates from another particular reaction) Because of the specific fit, the ES Complex is called a LOCK AND KEY COMPLEX ...
Fatty acids: Review
... is oxidized depends on where the double bond ends up after several of the C-2 fragments have been removed by normal β-oxidation -As the oxidation machinery chews off 2-carbon fragments, it nibbles down to one of two possible situations depending on whether the first double bond started out at an eve ...
... is oxidized depends on where the double bond ends up after several of the C-2 fragments have been removed by normal β-oxidation -As the oxidation machinery chews off 2-carbon fragments, it nibbles down to one of two possible situations depending on whether the first double bond started out at an eve ...
Chapter 3 - Haiku Learning
... b) phospholipids: two fatty acids joined to glycerol ( cell membrane) c) wax: long fatty acid chain joined to a long alcohol chain 3. Steroids: four fused carbon rings with different functional groups a) Examples: testosterone and cholesterol Lipids ...
... b) phospholipids: two fatty acids joined to glycerol ( cell membrane) c) wax: long fatty acid chain joined to a long alcohol chain 3. Steroids: four fused carbon rings with different functional groups a) Examples: testosterone and cholesterol Lipids ...
Ch 3 organic molecules
... Concept 5.3: Lipids are a diverse group of hydrophobic molecules • Lipids are the one class of large biological molecules that do not form polymers • The unifying feature of lipids is having little or no affinity for water – Hydro …? ...
... Concept 5.3: Lipids are a diverse group of hydrophobic molecules • Lipids are the one class of large biological molecules that do not form polymers • The unifying feature of lipids is having little or no affinity for water – Hydro …? ...
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE DEPARTMENT OF BIOCHEMISTRY ADVANCED PLACEMENT TEST (SAMPLE)
... A. Metalloenzyme uses metal for activity. B. A lipoprotein contains lipid covalently linked to the protein. C. A glycoprotein contains glycogen covalently linked to the protein. D. A hemoprotein contains iron. E. A flavoprotein contains flavin dinucleotide. ...
... A. Metalloenzyme uses metal for activity. B. A lipoprotein contains lipid covalently linked to the protein. C. A glycoprotein contains glycogen covalently linked to the protein. D. A hemoprotein contains iron. E. A flavoprotein contains flavin dinucleotide. ...
Secondary Metabolites and Building Blocks
... Are plentiful and diverse in plant-based foods May be more prevalent or unique to certain genus, species, and similar compounds occur within genuses and families Often have vital functions in the source • attractants for propagation of species • defense against predators • signaling May have useful ...
... Are plentiful and diverse in plant-based foods May be more prevalent or unique to certain genus, species, and similar compounds occur within genuses and families Often have vital functions in the source • attractants for propagation of species • defense against predators • signaling May have useful ...
4.1_Proteins_Amino_Acids_2011
... chain. The peptide bond is planar (gray shading) and does not permit rotation. By contrast, rotation can occur about the Cα–C bond, whose angle of rotation is called psi (ψ), and about the N–Cα bond, whose angle of rotation is called phi (ϕ). By convention, an R group is often used to denote an amin ...
... chain. The peptide bond is planar (gray shading) and does not permit rotation. By contrast, rotation can occur about the Cα–C bond, whose angle of rotation is called psi (ψ), and about the N–Cα bond, whose angle of rotation is called phi (ϕ). By convention, an R group is often used to denote an amin ...
CH 3 Notes
... a) two ends of the chain are very different b) hydrophilic: water loving c) hydrophobic: water fearing 2. Complex lipid examples a) triglyceride: three molecules of fatty acid joined to glycerol (animal fat) ...
... a) two ends of the chain are very different b) hydrophilic: water loving c) hydrophobic: water fearing 2. Complex lipid examples a) triglyceride: three molecules of fatty acid joined to glycerol (animal fat) ...
Chapter 30: Final Questions
... a chemical group for such an interaction. These amino acids might be those for which you would look in your enzyme structure. C). Denote which residue in your enzyme that you might change by site-directed mutagenesis to investigate the fidelity of this enzyme. Which kinetic constant would you expect ...
... a chemical group for such an interaction. These amino acids might be those for which you would look in your enzyme structure. C). Denote which residue in your enzyme that you might change by site-directed mutagenesis to investigate the fidelity of this enzyme. Which kinetic constant would you expect ...
Sugar
... However, further research on the trans fatty acids found in partially hydrogenated oils took many by surprise (C&EN, Sept. 22, 2003, page 33). Trans fatty acids, though unsaturated, were found to also increase LDL ("bad" cholesterol) levels in the blood. In the U.S., the Food & Drug Administration w ...
... However, further research on the trans fatty acids found in partially hydrogenated oils took many by surprise (C&EN, Sept. 22, 2003, page 33). Trans fatty acids, though unsaturated, were found to also increase LDL ("bad" cholesterol) levels in the blood. In the U.S., the Food & Drug Administration w ...
Unit 1: Biology Review
... there are simply more bonds to break. You can form complex carbs through dehydration synthesis/reactions, removing water, and binding simpler mono/disaccharides. To break down the carbs, your body uses hydrolysis reactions to add water, and separate larger saccharides. Lipids are primarily used for ...
... there are simply more bonds to break. You can form complex carbs through dehydration synthesis/reactions, removing water, and binding simpler mono/disaccharides. To break down the carbs, your body uses hydrolysis reactions to add water, and separate larger saccharides. Lipids are primarily used for ...
Ch. 2 - The Chemistry of Life
... Monosaccharides—simple sugars ex: glucose C6H12O6 Disaccharides—two simple sugars joined by dehydration synthesis ex: maltose C12H22O11 Polysaccharides—long-branching chains of linked simple sugars ex: starch and glycogen ...
... Monosaccharides—simple sugars ex: glucose C6H12O6 Disaccharides—two simple sugars joined by dehydration synthesis ex: maltose C12H22O11 Polysaccharides—long-branching chains of linked simple sugars ex: starch and glycogen ...
Serine Proteases Teaching Exercises
... a. Find examples of arginine, lysine, glutamic acid and aspartic acid (not that these two acidic amino acids are hard to distinguish from one another). Notice the distribution of charged amino acids. What significance might this distribution have in terms of function? b. Find examples of asparagine/ ...
... a. Find examples of arginine, lysine, glutamic acid and aspartic acid (not that these two acidic amino acids are hard to distinguish from one another). Notice the distribution of charged amino acids. What significance might this distribution have in terms of function? b. Find examples of asparagine/ ...
Metabolic engineering Synthetic Biology
... cases can progress to coma or death. Only female mosquitoes feed on blood; The females of the Anopheles genus of mos quito prefer to feed at night ...
... cases can progress to coma or death. Only female mosquitoes feed on blood; The females of the Anopheles genus of mos quito prefer to feed at night ...
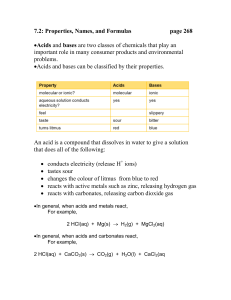
7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas page 268 •Acids and bases
... 7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas ...
... 7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas ...
U4L21 fuel oxidation - The University of Sydney
... • TCA cycle, Citric Acid cycle • Substrate is acetyl CoA – Fatty acid oxidation and/or glucose oxidation ...
... • TCA cycle, Citric Acid cycle • Substrate is acetyl CoA – Fatty acid oxidation and/or glucose oxidation ...
Syllabus Notes - Southwest High School
... 2.1.2 State that a variety of other elements are needed by living organisms including nitrogen, calcium, phosphorus, iron and sodium. 2.1.3 State one role for each of the elements mentioned in 2.1.2. (leave room) N protein, and nucleic acids (DNA), makes stuff POLAR. Ca bones and muscle contract ...
... 2.1.2 State that a variety of other elements are needed by living organisms including nitrogen, calcium, phosphorus, iron and sodium. 2.1.3 State one role for each of the elements mentioned in 2.1.2. (leave room) N protein, and nucleic acids (DNA), makes stuff POLAR. Ca bones and muscle contract ...
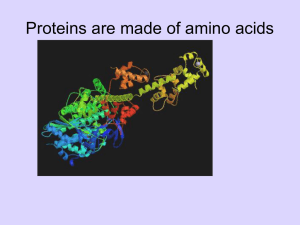
Proteins are made of subunits called amino acids and are
... COLOR and LABEL the parts of a nucleotide --- sugar (5-sided)-green, phosphate group (round)yellow, and nitrogen base (6-sided)-blue. ATP used for cellular energy is a high energy nucleotide with three phosphate groups. Color code the ATP and LABEL THE PHOSPHATES. ...
... COLOR and LABEL the parts of a nucleotide --- sugar (5-sided)-green, phosphate group (round)yellow, and nitrogen base (6-sided)-blue. ATP used for cellular energy is a high energy nucleotide with three phosphate groups. Color code the ATP and LABEL THE PHOSPHATES. ...
biochem ch 23 [2-9
... Fatty acid oxidation can be restricted by mitochondrial CoASH pool size; acetyl CoASH must enter TCA cycle or another metabolic pathway to regenerate CoASH required for formation of fatty acyl-CoA derivative from fatty acyl carnitine CPTI inhibited by malonyl-CoA synthesized in cytosol by acetyl ...
... Fatty acid oxidation can be restricted by mitochondrial CoASH pool size; acetyl CoASH must enter TCA cycle or another metabolic pathway to regenerate CoASH required for formation of fatty acyl-CoA derivative from fatty acyl carnitine CPTI inhibited by malonyl-CoA synthesized in cytosol by acetyl ...
Metabolism of fatty acids in tissues and organs of the ruminants
... increases with the mobilization of fat from adipose tissue [Hocquette and Bauchart 1999]. A secondary source of LCFA in the liver is the hydrolysis of circulating triglycerides. Long-chain fatty acids are subjected to esterification or oxidation in the liver - distribution between these two pathways ...
... increases with the mobilization of fat from adipose tissue [Hocquette and Bauchart 1999]. A secondary source of LCFA in the liver is the hydrolysis of circulating triglycerides. Long-chain fatty acids are subjected to esterification or oxidation in the liver - distribution between these two pathways ...
Exam-2 review
... physical properties associated with each. Do fatty acids primarily occur as free fatty acids? - 7. Understand the different effects that SFA's, MUFA's and PUFA's have on LDL and HDL levels in the blood and how this translates into dietary guidelines for increasing or decreasing these in the diet. - ...
... physical properties associated with each. Do fatty acids primarily occur as free fatty acids? - 7. Understand the different effects that SFA's, MUFA's and PUFA's have on LDL and HDL levels in the blood and how this translates into dietary guidelines for increasing or decreasing these in the diet. - ...
Nutrition - Athens Academy
... A. The primary role of carbohydrates is to serve as an energy source. B. Carbohydrates include sugars, starches, and amino acids. C. Maltose is a complex carbohydrate. D. Sucrose is the primary source of energy for most cells. E. Most carbohydrates come from animal products. ...
... A. The primary role of carbohydrates is to serve as an energy source. B. Carbohydrates include sugars, starches, and amino acids. C. Maltose is a complex carbohydrate. D. Sucrose is the primary source of energy for most cells. E. Most carbohydrates come from animal products. ...
Energy Metabolism and water vitamins
... short supply ☻ Removes from circulation amino acids that are present in excess of need and converts them to p other amino acids ☻ Removes ammonia from the blood and converts it to urea to be sent to the kidneys for excretion ☻ Makes other nitrogen containing compounds the body needs – such as base u ...
... short supply ☻ Removes from circulation amino acids that are present in excess of need and converts them to p other amino acids ☻ Removes ammonia from the blood and converts it to urea to be sent to the kidneys for excretion ☻ Makes other nitrogen containing compounds the body needs – such as base u ...
Chapter 19: Lipids
... people of Greenland, suggest that relationships between direct triglyceride intake and risk factors for disease involve more than simply the total amount of triglycerides taken in. Effect of high Fructose Corn Syrup (HFCS) on the Obesity and LDL bad fats in the blood stream Recent studies indicate O ...
... people of Greenland, suggest that relationships between direct triglyceride intake and risk factors for disease involve more than simply the total amount of triglycerides taken in. Effect of high Fructose Corn Syrup (HFCS) on the Obesity and LDL bad fats in the blood stream Recent studies indicate O ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.