Word
... D) Is used by chylomicrons to bind cholesterol to lipid soluble vitamins and facilitate their transport E) Transfers cholesterol to an acyl chain on a phospholipid to facilitate its packaging into low density lipoproteins. ...
... D) Is used by chylomicrons to bind cholesterol to lipid soluble vitamins and facilitate their transport E) Transfers cholesterol to an acyl chain on a phospholipid to facilitate its packaging into low density lipoproteins. ...
1st exam
... 5) In the fasting state when glucose is in short supply, the liver can convert fatty acids released from adipose tissue into _______________________ 6) In the muscle the enzyme ______________ phosphorylates fructose to _______________ 7) Hypoglycaemia is a clinical condition which occur when glucose ...
... 5) In the fasting state when glucose is in short supply, the liver can convert fatty acids released from adipose tissue into _______________________ 6) In the muscle the enzyme ______________ phosphorylates fructose to _______________ 7) Hypoglycaemia is a clinical condition which occur when glucose ...
Exam #2 BMB 514 – Medical Biochemistry 10/10/11
... 28) Which of the following statements is correct? A) Triacylglycerols (TAG) and phospholipids are synthesized by branches from a common intermediate. B) ATP is used for activation in the salvage pathway of phospholipid synthesis. C) Serine is a source used to create the backbone of phospholipids and ...
... 28) Which of the following statements is correct? A) Triacylglycerols (TAG) and phospholipids are synthesized by branches from a common intermediate. B) ATP is used for activation in the salvage pathway of phospholipid synthesis. C) Serine is a source used to create the backbone of phospholipids and ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... A polysaccharide is a macromolecule consisting of repeating units of simple sugars, usually glucose. Thousands of units are typically present in a single molecule. Starch, the typical form of carbohydrate used for energy storage in plants, is a polymer consisting of a-glucose subunits. When energy i ...
... A polysaccharide is a macromolecule consisting of repeating units of simple sugars, usually glucose. Thousands of units are typically present in a single molecule. Starch, the typical form of carbohydrate used for energy storage in plants, is a polymer consisting of a-glucose subunits. When energy i ...
full_ppt_ch19
... • Contain one or more double C=C bonds • Nonlinear chains do not allow molecules to pack closely • Few interactions between chains • Lower melting points than saturated – Melting points increase with chain length – And decrease with number of double bonds ...
... • Contain one or more double C=C bonds • Nonlinear chains do not allow molecules to pack closely • Few interactions between chains • Lower melting points than saturated – Melting points increase with chain length – And decrease with number of double bonds ...
Learning Objectives
... Know how pyruvate dehydrogenase complex works (cofactors involved, mechanism, regulation) Know net reaction Know where ATP, CO2, FADH2 and NADH are made Know ultimate # ATP formed Stereospecificity of aconitase, fumarase ...
... Know how pyruvate dehydrogenase complex works (cofactors involved, mechanism, regulation) Know net reaction Know where ATP, CO2, FADH2 and NADH are made Know ultimate # ATP formed Stereospecificity of aconitase, fumarase ...
Basic organic chemistry of important macromolecules (Lecture 11-12)
... 1. Organic molecules Organic molecules are those that: 1) formed by the actions of living things; and/or 2) have a carbon backbone. Carbon has four electrons in outer shell, and can bond with up to four other atoms (usually H, O, N, or another C). Since carbon can make covalent bonds with another ca ...
... 1. Organic molecules Organic molecules are those that: 1) formed by the actions of living things; and/or 2) have a carbon backbone. Carbon has four electrons in outer shell, and can bond with up to four other atoms (usually H, O, N, or another C). Since carbon can make covalent bonds with another ca ...
Chapter Outline
... b. Fat provides insulation and energy storage in animals. c. Phospholipids form plasma membranes and steroids are important cell messengers. d. Waxes have protective functions in many organisms. A. Triglycerides: Long-Term Energy Storage 1. Fats and oils contain two molecular units: glycerol and fat ...
... b. Fat provides insulation and energy storage in animals. c. Phospholipids form plasma membranes and steroids are important cell messengers. d. Waxes have protective functions in many organisms. A. Triglycerides: Long-Term Energy Storage 1. Fats and oils contain two molecular units: glycerol and fat ...
Lecture-Lipid Metabolism - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... Not enough insulin, tissues cannot take up glc efficiently from blood to use as fuel or store as fat Malonyl CoA (fatty acid biosynthesis) not formed, so carnitine acyltransferase I not inhibited Fatty acids enter mitochondria to be degraded to acetyl CoA (which cannot go to TCA because cycle interm ...
... Not enough insulin, tissues cannot take up glc efficiently from blood to use as fuel or store as fat Malonyl CoA (fatty acid biosynthesis) not formed, so carnitine acyltransferase I not inhibited Fatty acids enter mitochondria to be degraded to acetyl CoA (which cannot go to TCA because cycle interm ...
CHEM 210(Biochemistry)
... biochemistry of pH and buffers. Structure and function of enzymes including enzyme kinetics and glycogen synthesis and degradation, and insulin and glycogenesis. DNA replication, transcription, translation, protein synthesis by RNA molecules and regulation of gene expression. Cell membrane structure ...
... biochemistry of pH and buffers. Structure and function of enzymes including enzyme kinetics and glycogen synthesis and degradation, and insulin and glycogenesis. DNA replication, transcription, translation, protein synthesis by RNA molecules and regulation of gene expression. Cell membrane structure ...
Lecture notes Chapters 10
... Saponification: Natural soap are sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids. They are prepared from a blend of tallow and coconut oils (triglyceride). Triglycerides are triesters of glycerol. The solid fats are melted with steam, and the water insoluble triglyceride layer that forms on the top is remo ...
... Saponification: Natural soap are sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids. They are prepared from a blend of tallow and coconut oils (triglyceride). Triglycerides are triesters of glycerol. The solid fats are melted with steam, and the water insoluble triglyceride layer that forms on the top is remo ...
A1984SZ47200001
... homocystine to cystathionine. Since then, to examine the children and was impressed three genetically determined enzyme deby the similarity and unusual nature of their fects are now known in the remethylation symptoms, i.e., mental retardation, fits, ec- pathway from homocystine to methamine. topia ...
... homocystine to cystathionine. Since then, to examine the children and was impressed three genetically determined enzyme deby the similarity and unusual nature of their fects are now known in the remethylation symptoms, i.e., mental retardation, fits, ec- pathway from homocystine to methamine. topia ...
Describe in simple terms the chemical nature of sugars, proteins
... When the pH level varies from the normal range, the carbonic acid-bicarbonate system allows the body to automatically balance out the pH level. It converts the strong acids and bases to weak acids and bases. ...
... When the pH level varies from the normal range, the carbonic acid-bicarbonate system allows the body to automatically balance out the pH level. It converts the strong acids and bases to weak acids and bases. ...
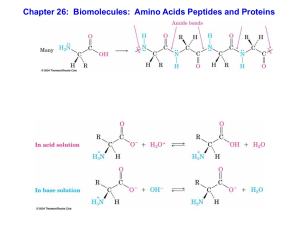
Chapter 26: Biomolecules: Amino Acids Peptides and Proteins
... Draw Fisher diagrams of L-Alanine (R = CH3) and L-cysteine (R = CH2-SH) and assign stereochemistry as R or S ...
... Draw Fisher diagrams of L-Alanine (R = CH3) and L-cysteine (R = CH2-SH) and assign stereochemistry as R or S ...
BOROUGH OF MANHATTAN COMMUNITY COLLEGE City
... Plagiarism is the presentation of someone else’s ideas, words or artistic, scientific, or technical work as one’s own creation. Using the idea or work of another is permissible only when the original author is identified. Paraphrasing and summarizing, as well as direct quotations, require citations ...
... Plagiarism is the presentation of someone else’s ideas, words or artistic, scientific, or technical work as one’s own creation. Using the idea or work of another is permissible only when the original author is identified. Paraphrasing and summarizing, as well as direct quotations, require citations ...
Objectives_Set1
... Be able to trace a single carbon atom through glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. Practice, start with glucose, keep track of carbons 1 through 6 all the way through glycolysis, the PDH complex and the citric acid cycle. ...
... Be able to trace a single carbon atom through glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. Practice, start with glucose, keep track of carbons 1 through 6 all the way through glycolysis, the PDH complex and the citric acid cycle. ...
Sec_2_3 Carbon Compunds
... group (-NH2) on one end and a carboxyl group (-COOH) on the other end ...
... group (-NH2) on one end and a carboxyl group (-COOH) on the other end ...
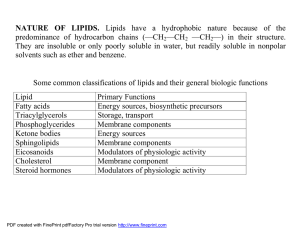
NATURE OF LIPIDS. Lipids have a hydrophobic nature because of
... a. Ketone bodies are synthesized in liver mitochondria and released into the blood for use as metabolic fuel by other tissues. The liver does not use ketone bodies. b. Levels of synthesis are high when the rate of fatty acid oxidation is high and carbohydrate utilization is low. This occurs during f ...
... a. Ketone bodies are synthesized in liver mitochondria and released into the blood for use as metabolic fuel by other tissues. The liver does not use ketone bodies. b. Levels of synthesis are high when the rate of fatty acid oxidation is high and carbohydrate utilization is low. This occurs during f ...
Acetyl-CoA
... catalyzed by enoyl-ACP reductase (ER), producing a saturated acyl on ACP (butyryl-ACP) 丁酰-ACP ...
... catalyzed by enoyl-ACP reductase (ER), producing a saturated acyl on ACP (butyryl-ACP) 丁酰-ACP ...
Amino Acids and Healthy Muscle - SEA
... promotion of our body muscles. In particular, the Branched Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) which cannot be produced in our living body are called “essential amino acids”. Human beings should take BCAAs (valine, leucine and isoleucine) through meal (and / or supplement if needed) in considering the balance ...
... promotion of our body muscles. In particular, the Branched Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) which cannot be produced in our living body are called “essential amino acids”. Human beings should take BCAAs (valine, leucine and isoleucine) through meal (and / or supplement if needed) in considering the balance ...
lec32_F2015
... CoA is a central intermediate Anabolic role: TCA cycle provides starting material for fats and amino acids. Note: carbohydrates cannot be synthesized from acetyl-CoA by humans. PyruvateAcetyl CoA is one way! In contrast to glycolysis, none of the intermediates are phosphorylated; but all are ei ...
... CoA is a central intermediate Anabolic role: TCA cycle provides starting material for fats and amino acids. Note: carbohydrates cannot be synthesized from acetyl-CoA by humans. PyruvateAcetyl CoA is one way! In contrast to glycolysis, none of the intermediates are phosphorylated; but all are ei ...
Lecture_Notes_Ch 19
... • Contain one or more double C=C bonds • Nonlinear chains do not allow molecules to pack closely • Few interactions between chains • Lower melting points than saturated – Melting points increase with chain length – And decrease with number of double bonds ...
... • Contain one or more double C=C bonds • Nonlinear chains do not allow molecules to pack closely • Few interactions between chains • Lower melting points than saturated – Melting points increase with chain length – And decrease with number of double bonds ...
bottom-up-methodology
... Example Bottom-Up Metabolic Model Construction Process 1. The Basics Starting from glucose-6-phosphate in a glycolytic organism: # sanity check that one reaction can happen FRUCTOSE-6-P[CCO-CYTOSOL] # complete glycolysis and get to pyruvate (alanine, serine, glycerol-3P) PYRUVATE[CCO-CYTOSOL] # reac ...
... Example Bottom-Up Metabolic Model Construction Process 1. The Basics Starting from glucose-6-phosphate in a glycolytic organism: # sanity check that one reaction can happen FRUCTOSE-6-P[CCO-CYTOSOL] # complete glycolysis and get to pyruvate (alanine, serine, glycerol-3P) PYRUVATE[CCO-CYTOSOL] # reac ...
lecture notes-metabolism pathways-web
... degrading a compound into smaller and simpler products and generating energy. Glucose to CO2, and H2O, protein to amino acids. - Anabolism: the synthesis of more complex compounds and requires energy. Synthesis of glycan (polysaccharide), DNA, RNA, and lipid. ...
... degrading a compound into smaller and simpler products and generating energy. Glucose to CO2, and H2O, protein to amino acids. - Anabolism: the synthesis of more complex compounds and requires energy. Synthesis of glycan (polysaccharide), DNA, RNA, and lipid. ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.