I LEARN AT HOME ASSIGNMENT 4 Macromolecule Review
... Organic molecules have four common characteristics. First, they are all carbon based, meaning they all contain carbon. They are formed from just a few elements which join together to form small molecules which join together, or bond, to form large molecules. The third characteristic of all orga ...
... Organic molecules have four common characteristics. First, they are all carbon based, meaning they all contain carbon. They are formed from just a few elements which join together to form small molecules which join together, or bond, to form large molecules. The third characteristic of all orga ...
I LEARN AT HOME ASSIGNMENT 4 Macromolecule Review
... Organic molecules have four common characteristics. First, they are all carbon based, meaning they all contain carbon. They are formed from just a few elements which join together to form small molecules which join together, or bond, to form large molecules. The third characteristic of all orga ...
... Organic molecules have four common characteristics. First, they are all carbon based, meaning they all contain carbon. They are formed from just a few elements which join together to form small molecules which join together, or bond, to form large molecules. The third characteristic of all orga ...
The Urea Cycle - LSU School of Medicine
... Summary of the Urea Cycle * The urea cycle consists of five reactions: two mitochondrial and three cytosolic. * The cycle converts two amino groups, one from NH4+ and one from Asp, and a carbon atom from CO2. to the relatively nontoxic excretion product urea. * Requires four "high-energy" phosphate ...
... Summary of the Urea Cycle * The urea cycle consists of five reactions: two mitochondrial and three cytosolic. * The cycle converts two amino groups, one from NH4+ and one from Asp, and a carbon atom from CO2. to the relatively nontoxic excretion product urea. * Requires four "high-energy" phosphate ...
Further Details of Mechanism
... • The cycle is a mechanism for oxidizing acetyl CoA to CO2 by NAD+ and Q • The cycle itself is not a pathway for a net degradation of any cycle intermediates • Cycle intermediates can be shared with other pathways, which may lead to a resupply or net decrease in cycle intermediates ...
... • The cycle is a mechanism for oxidizing acetyl CoA to CO2 by NAD+ and Q • The cycle itself is not a pathway for a net degradation of any cycle intermediates • Cycle intermediates can be shared with other pathways, which may lead to a resupply or net decrease in cycle intermediates ...
Mitochondrial NRG - Designs for Health
... Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations by Devlin 6th Edition: ISBN: 0471678082 Food and Nutrients in Disease Management by Ingrid Kohlstadt. CRC Press ISNB: 978-1-4200-6762-0 Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high calorie diet. Baur JA et al. Nature. 2006 Nov 16;444( ...
... Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations by Devlin 6th Edition: ISBN: 0471678082 Food and Nutrients in Disease Management by Ingrid Kohlstadt. CRC Press ISNB: 978-1-4200-6762-0 Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high calorie diet. Baur JA et al. Nature. 2006 Nov 16;444( ...
Chapter 2
... oxygen. In contrast to carbohydrates, the ratio of oxygen to carbon and hydrogen is much lower. Lipids are the primary building block of membranes, and are also essential for energy storage and other cellular functions. ...
... oxygen. In contrast to carbohydrates, the ratio of oxygen to carbon and hydrogen is much lower. Lipids are the primary building block of membranes, and are also essential for energy storage and other cellular functions. ...
6-APA - Teknologi Industri Pertanian
... Kg quantity product/g cells Acrylic acid is not produced Fewer process steps are involved Much more environmental friendly Nitto Chemical Industry: 6,000 tons annually ...
... Kg quantity product/g cells Acrylic acid is not produced Fewer process steps are involved Much more environmental friendly Nitto Chemical Industry: 6,000 tons annually ...
4. Microbial Products
... Excessive pigment formation in D. salina is achieved by numerous stress factors like high temperature, lack of nitrogen and phosphate but excess of carbon, high light intensity, and high salt concentration, the latter two having the highest impact. ...
... Excessive pigment formation in D. salina is achieved by numerous stress factors like high temperature, lack of nitrogen and phosphate but excess of carbon, high light intensity, and high salt concentration, the latter two having the highest impact. ...
... 50% yield with >98% regioselectivity by reaction of the corresponding free sugar with ethyl L-lactate in the presence of 10% water. Compounds 2a and 2b were further converted to 4a and 4b, respectively, via reaction with pyruvate catalyzed by sialic acid aldolase. Compounds 3a and 3b were deoxygenat ...
Cellular Respiration Part 3
... is the 1st molecule formed in the cycle • Called the Krebs Cycle after Hans Krebs – the researcher who discovered it • Occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria • Involves 2 electron carriers – NADH and FADH2 • The cycle oxidizes organic fuel derived from pyruvate, generating 1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FAD ...
... is the 1st molecule formed in the cycle • Called the Krebs Cycle after Hans Krebs – the researcher who discovered it • Occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria • Involves 2 electron carriers – NADH and FADH2 • The cycle oxidizes organic fuel derived from pyruvate, generating 1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FAD ...
Cell Respiration Notes (Honors)
... Takes place in the mitochondria of the cell (in the matrix). The pyruvate from glycolysis is slightly modified before the citric acid cycle begins. These new molecules are broken down to form ATP and CO2. One ATP per cycle is produced, two cycles occur per glucose molecule – therefore 2 ATP’s are ...
... Takes place in the mitochondria of the cell (in the matrix). The pyruvate from glycolysis is slightly modified before the citric acid cycle begins. These new molecules are broken down to form ATP and CO2. One ATP per cycle is produced, two cycles occur per glucose molecule – therefore 2 ATP’s are ...
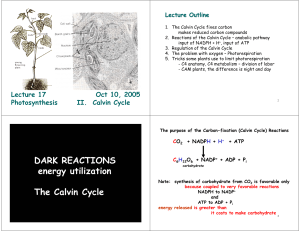
DARK REACTIONS energy utilization The Calvin Cycle
... accumulate malate to high concentration in central vacuole use sugar oxidation/catabolism to power (NADH and ATP) carbon fixation DAY Perform “light” reactions during the day mostly cyclic e- flow to produce ATP (low O2) decarboxylate malate to yield CO2 and NADPH + H+ perform C3 reactions (Calvin C ...
... accumulate malate to high concentration in central vacuole use sugar oxidation/catabolism to power (NADH and ATP) carbon fixation DAY Perform “light” reactions during the day mostly cyclic e- flow to produce ATP (low O2) decarboxylate malate to yield CO2 and NADPH + H+ perform C3 reactions (Calvin C ...
Monomers are the
... Q: What monomer are complex carbohydrates made out of? A: simple carbohydrates = sugars = monosaccharides Q: What do the names of all carbohydrates end with? A: “- ose” Q: Compare and contrast starch and cellulose. ...
... Q: What monomer are complex carbohydrates made out of? A: simple carbohydrates = sugars = monosaccharides Q: What do the names of all carbohydrates end with? A: “- ose” Q: Compare and contrast starch and cellulose. ...
Understanding fatty acid synthesis in developing - Shachar
... reducing equivalents in the form of NADH and NADPH. It was proposed that, in isolated plastids from heterotrophic tissues, reducing power could be generated via the conversion of imported malate into acetyl CoA; one mole of NADPH is liberated during the reaction catalyzed by plastidic NADP-dependent ...
... reducing equivalents in the form of NADH and NADPH. It was proposed that, in isolated plastids from heterotrophic tissues, reducing power could be generated via the conversion of imported malate into acetyl CoA; one mole of NADPH is liberated during the reaction catalyzed by plastidic NADP-dependent ...
AKA TCA CYCLE, KREB`S CYCLE
... •a number of amino acids are made from TCA cycle intermediates 2. Reactions that replenish TCA cycle intermediates: •pyruvate carboxylase reaction ...
... •a number of amino acids are made from TCA cycle intermediates 2. Reactions that replenish TCA cycle intermediates: •pyruvate carboxylase reaction ...
Fermentation and Cellular Respiration
... molecules, but the pathway does not stop there. Instead, the pyruvic acids serve as final electron acceptors, the two molecules of NADH+H+ are oxidized to NAD and the two pyruvic acid molecules are converted into lactic acid molecules. Homofermentative – Organisms that yield lactic acid as the only ...
... molecules, but the pathway does not stop there. Instead, the pyruvic acids serve as final electron acceptors, the two molecules of NADH+H+ are oxidized to NAD and the two pyruvic acid molecules are converted into lactic acid molecules. Homofermentative – Organisms that yield lactic acid as the only ...
Lecture 17: Nitrogen metabolism
... • Glutamate level is representative of cell’s ammonia level, as the one of the first steps of amino acid degradation is transamination to glutamate. • Carbamoyl‐P synthetase is also regulated by covalent modification – inactivation of specific lysine residue. However the details of this mechanism ...
... • Glutamate level is representative of cell’s ammonia level, as the one of the first steps of amino acid degradation is transamination to glutamate. • Carbamoyl‐P synthetase is also regulated by covalent modification – inactivation of specific lysine residue. However the details of this mechanism ...
3 | biological macromolecules
... smaller organic molecules. There are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids); each is an important cell component and performs a wide array of functions. Combined, these molecules make up the majority of a cell’s dry mass (recall that wate ...
... smaller organic molecules. There are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids); each is an important cell component and performs a wide array of functions. Combined, these molecules make up the majority of a cell’s dry mass (recall that wate ...
Kofaktörler - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... groups (fatty acids) are made wmore water soluble w/CoA attached ...
... groups (fatty acids) are made wmore water soluble w/CoA attached ...
Amino acid and protein
... residues form a colored chelate complex with cupric ions (Cu2+) in an alkaline environment containing sodium potassium tartrate. Single amino acids and dipeptides do not give the biuret reaction, but tripeptides and larger polypeptides or proteins will react to produce the light blue to violet com ...
... residues form a colored chelate complex with cupric ions (Cu2+) in an alkaline environment containing sodium potassium tartrate. Single amino acids and dipeptides do not give the biuret reaction, but tripeptides and larger polypeptides or proteins will react to produce the light blue to violet com ...
Untitled
... surface that is exposed. Since biological lipids are amphipathic, they arrange themselves so that the polar head group is in contact with water, but their hydrophobic tails are buried – this arrangement minimizes the exposure of hydrophobic surface. Lipids with two fatty acid tails (like those found ...
... surface that is exposed. Since biological lipids are amphipathic, they arrange themselves so that the polar head group is in contact with water, but their hydrophobic tails are buried – this arrangement minimizes the exposure of hydrophobic surface. Lipids with two fatty acid tails (like those found ...
Experimentally testing the hypothesis of a limited amino acid
... proteins that express biological functions. The modern genetic code, which encodes the standard 20 amino acids (and the termination signal) using 64 triplet codons, is shared by all of the extant organisms on the earth with a few exceptions. Therefore, the genetic code is thought to have been establ ...
... proteins that express biological functions. The modern genetic code, which encodes the standard 20 amino acids (and the termination signal) using 64 triplet codons, is shared by all of the extant organisms on the earth with a few exceptions. Therefore, the genetic code is thought to have been establ ...
Amino acid and protein
... residues form a colored chelate complex with cupric ions (Cu2+) in an alkaline environment containing sodium potassium tartrate. Single amino acids and dipeptides do not give the biuret reaction, but tripeptides and larger polypeptides or proteins will react to produce the light blue to violet com ...
... residues form a colored chelate complex with cupric ions (Cu2+) in an alkaline environment containing sodium potassium tartrate. Single amino acids and dipeptides do not give the biuret reaction, but tripeptides and larger polypeptides or proteins will react to produce the light blue to violet com ...
Methods of industrial production
... additives. The reason is that typical animal feed, like soybean meal for pigs is poor in some essential amino acids like methionine and lysine. pigs, is poor in some essential amino acids, like methionine and lysine ...
... additives. The reason is that typical animal feed, like soybean meal for pigs is poor in some essential amino acids like methionine and lysine. pigs, is poor in some essential amino acids, like methionine and lysine ...
Algae triglycerides
... include, but are not limited to, neutral lipids, polar lipids, wax esters, sterols and hydrocarbons, as well as prenyl derivatives such as tocopherols, carotenoids, terpenes, quinones and phytylated pyrrole derivatives such as the chlorophylls. Under optimal conditions of growth, algae synthesize fa ...
... include, but are not limited to, neutral lipids, polar lipids, wax esters, sterols and hydrocarbons, as well as prenyl derivatives such as tocopherols, carotenoids, terpenes, quinones and phytylated pyrrole derivatives such as the chlorophylls. Under optimal conditions of growth, algae synthesize fa ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.