1. PROTEIN MODIFICATION 1.1 What are posttranslational
... amino acids are broken down via different pathways and mechanisms. However, the first step in the catabolism of all 20 amino acids is the same: deamination that is catalyzed by an aminotransferase, which is dependent upon the cofactor pyridoxalphosphate (PLP). In the first part of the deamination re ...
... amino acids are broken down via different pathways and mechanisms. However, the first step in the catabolism of all 20 amino acids is the same: deamination that is catalyzed by an aminotransferase, which is dependent upon the cofactor pyridoxalphosphate (PLP). In the first part of the deamination re ...
Valine Mydrogenase from Streptmzyces fiadipe
... Valine dehydrogenase (VDH ; EC 1.4.1.8) activity was detected in a cell-free extract of Streptomycesfiadk in which it was thought to be a mgulatory enzyme involved in biosynthesis of n-butyrate, a buiiding unit of the oligoketideantibiotictylosin ( b u r a et al., 1983). Inhibition of VDH synthesisa ...
... Valine dehydrogenase (VDH ; EC 1.4.1.8) activity was detected in a cell-free extract of Streptomycesfiadk in which it was thought to be a mgulatory enzyme involved in biosynthesis of n-butyrate, a buiiding unit of the oligoketideantibiotictylosin ( b u r a et al., 1983). Inhibition of VDH synthesisa ...
Nadine Noelting
... superfamily. This is roughly located between amino acids 120 and 420. The mutations associated with my gene are found in this conserved domain. The family consists of nonheme, iron (II)- dependent enzymes, including phenylalanine hydroxylase, eukaryotic tyrosine hydroxylase, and eukaryotic tryptopha ...
... superfamily. This is roughly located between amino acids 120 and 420. The mutations associated with my gene are found in this conserved domain. The family consists of nonheme, iron (II)- dependent enzymes, including phenylalanine hydroxylase, eukaryotic tyrosine hydroxylase, and eukaryotic tryptopha ...
1 - u.arizona.edu
... lactate dehydrogenase; this occurs in liver where pyruvate is the metabolized to glucose (gluconeogenesis: pyruvate carboxylated oxaloacetate via pyruvate carboxylase) - when pyruvate used for energy production or fatty acid biosynthesis pyruvate undergoes oxidative decarboxylation to acetyl CoA ...
... lactate dehydrogenase; this occurs in liver where pyruvate is the metabolized to glucose (gluconeogenesis: pyruvate carboxylated oxaloacetate via pyruvate carboxylase) - when pyruvate used for energy production or fatty acid biosynthesis pyruvate undergoes oxidative decarboxylation to acetyl CoA ...
Oxidative Phosphorylation accompanying Oxidation of
... lowered and respiration is inhibited when the concentration of the fatty acid in the incubating medium is raised (to 5-10mM); octanoate is a more potent uncoupler than either hexanoate or butyrate. 4. Serum albumin and carnitine, either singly or in combination, protect the mitochondria from the eff ...
... lowered and respiration is inhibited when the concentration of the fatty acid in the incubating medium is raised (to 5-10mM); octanoate is a more potent uncoupler than either hexanoate or butyrate. 4. Serum albumin and carnitine, either singly or in combination, protect the mitochondria from the eff ...
File
... two G3P but 4 ATP are made while rearranging them into pyruvate; therefore, glycolysis has a net production of 2 ATP ...
... two G3P but 4 ATP are made while rearranging them into pyruvate; therefore, glycolysis has a net production of 2 ATP ...
Homeostatic Control of Metabolism
... Insulin Increases Glucose Transport • Required for resting skeletal muscle and adipose tissue • Moves GLUT-4 transporters to cell membrane • Exercising skeletal muscle does not require insulin for glucose uptake • In liver cells, indirect influence on glucose ...
... Insulin Increases Glucose Transport • Required for resting skeletal muscle and adipose tissue • Moves GLUT-4 transporters to cell membrane • Exercising skeletal muscle does not require insulin for glucose uptake • In liver cells, indirect influence on glucose ...
Chapter 3 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... that are insoluble in water. • Fats and oils are well-known lipids used for energy storage and other purposes. • Phospholipids are components of the membranes that surround cells. • Steroids, which have a different structure from most lipids, are used as hormones and for other purposes. ...
... that are insoluble in water. • Fats and oils are well-known lipids used for energy storage and other purposes. • Phospholipids are components of the membranes that surround cells. • Steroids, which have a different structure from most lipids, are used as hormones and for other purposes. ...
Syllabus for GUTS lecture on Amino Acids
... At physiological pH (7.4) both the amino group (a basic functional group) and the carboxylate group (acidic functional group) are ionized. At this pH amino acids are dipolar ions (contains oppositely charged groups but the overall charge on the molecule is 0). The degree of ionization of acids and b ...
... At physiological pH (7.4) both the amino group (a basic functional group) and the carboxylate group (acidic functional group) are ionized. At this pH amino acids are dipolar ions (contains oppositely charged groups but the overall charge on the molecule is 0). The degree of ionization of acids and b ...
Cell Energyrespiration
... keep only a small amount of ATP on hand. • Cells can regenerate ATP as needed by using the energy stored in foods like glucose. • The energy stored in glucose by photosynthesis is released by cellular respiration and repackaged into the energy of ATP. ...
... keep only a small amount of ATP on hand. • Cells can regenerate ATP as needed by using the energy stored in foods like glucose. • The energy stored in glucose by photosynthesis is released by cellular respiration and repackaged into the energy of ATP. ...
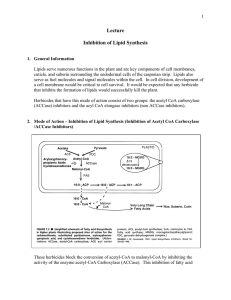
Lecture Inhibition of Lipid Synthesis
... 11. General Comments – Inhibition of Lipid Synthesis (Inhibition of Elongases / non ACCase Inhibitors) The details of the precise mode of action of the thiocarbamates is not truly known and the symptoms of the family may vary among herbicides. One of the more well known thiocarbamates is EPTC, a che ...
... 11. General Comments – Inhibition of Lipid Synthesis (Inhibition of Elongases / non ACCase Inhibitors) The details of the precise mode of action of the thiocarbamates is not truly known and the symptoms of the family may vary among herbicides. One of the more well known thiocarbamates is EPTC, a che ...
labmuscle
... because H+ are produced during the breakdown of glucose, thus increasing the number of H+ and causing the carbonate-carbonate acid equilibrium to shift towards more acidic.CO2 is also produced during the breakdown of glucose and is lost through exhalation. One method of decreasing acid build up is b ...
... because H+ are produced during the breakdown of glucose, thus increasing the number of H+ and causing the carbonate-carbonate acid equilibrium to shift towards more acidic.CO2 is also produced during the breakdown of glucose and is lost through exhalation. One method of decreasing acid build up is b ...
2 395G Exam 3 11 Dec 2002 First calculate ∆E
... this step is regulated by light. ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate + CO2 + H20 ‡ 2 3-phosphoglycerate (RUBISCO reaction) Regulation is indirectly by light: Enzyme is allosteric and is stimulated by 3 different changes: 1) Increase in pH. When chloroplasts are illuminated, protons transported from stroma to ...
... this step is regulated by light. ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate + CO2 + H20 ‡ 2 3-phosphoglycerate (RUBISCO reaction) Regulation is indirectly by light: Enzyme is allosteric and is stimulated by 3 different changes: 1) Increase in pH. When chloroplasts are illuminated, protons transported from stroma to ...
Supplemental notes in pdf
... body. However, unlike the liver that contains 10% glycogen by weight, individual muscle groups contain only ~1% glycogen by weight. Therefore, glycogen stores in any one muscle group become depleted when muscle contraction continues beyond about an hour. As glucose levels decline, the muscle tissue ...
... body. However, unlike the liver that contains 10% glycogen by weight, individual muscle groups contain only ~1% glycogen by weight. Therefore, glycogen stores in any one muscle group become depleted when muscle contraction continues beyond about an hour. As glucose levels decline, the muscle tissue ...
... 3. (8 pts) Please do one of the following two choices: Choice A: Briefly describe the chemical structure of bacterial cell walls. Choice B: Compare and contrast the chemical structure of cellulose to glycogen (or starch). What is the normal biochemical role of cellulose and glycogen? Choice A: Linea ...
Lecture 11 We started to discuss alkaloids possessing pipyridine
... In the past they were studying enolate alkaloids originated from ornithine, lysine, and aspartic acid (aliphatic a.a), with time this aspartic acid has been excluded from titles , and the text books included alkaloids originated from nicotinic acid or alkaloids containing pyridine –pipyridine, but w ...
... In the past they were studying enolate alkaloids originated from ornithine, lysine, and aspartic acid (aliphatic a.a), with time this aspartic acid has been excluded from titles , and the text books included alkaloids originated from nicotinic acid or alkaloids containing pyridine –pipyridine, but w ...
Chapter 27 Reproductive Endocrinology
... electrons pass to lower E molecules electrons in O2 have lowest E O2 ...
... electrons pass to lower E molecules electrons in O2 have lowest E O2 ...
B-Vitamins
... • Vitamins do not provide the body with fuel for energy • However, they can work as coenzymes • Assist enzymes with release of energy • Without coenzyme, an enzyme cannot function ...
... • Vitamins do not provide the body with fuel for energy • However, they can work as coenzymes • Assist enzymes with release of energy • Without coenzyme, an enzyme cannot function ...
removal of amino gp from glutamate to release ammonia Other
... 3. Metabolic break down of carbon skeleton to generate common intermediates that can be catabolized to CO2 or used in anabolic pathways to be stored as glucose or fat. ...
... 3. Metabolic break down of carbon skeleton to generate common intermediates that can be catabolized to CO2 or used in anabolic pathways to be stored as glucose or fat. ...
Metabolism
... Enzymes work by bending their substrates in such a way that the bonds to be broken are stressed and the substrate molecule resembles the transition state. This makes them more amenable to reaction with other molecules. Enzymes function by lowering the barriers that block a particular reaction. Put ...
... Enzymes work by bending their substrates in such a way that the bonds to be broken are stressed and the substrate molecule resembles the transition state. This makes them more amenable to reaction with other molecules. Enzymes function by lowering the barriers that block a particular reaction. Put ...
Evidence for the absence of amino acid isomerization in microwave
... the differences between the various products are hardly significant. The exception is the higher isomerization rate of Val, Ile in UHT milk, and Asp in formula C. Evidence for such an influence of the nature of the protein on the hydrolysis-induced isomerization of particular amino acid residues has ...
... the differences between the various products are hardly significant. The exception is the higher isomerization rate of Val, Ile in UHT milk, and Asp in formula C. Evidence for such an influence of the nature of the protein on the hydrolysis-induced isomerization of particular amino acid residues has ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.