a Disulfide Bridge DataBase for the predictive analysis of cysteine
... [4] Neves Petersen Maria Teresa, Johnson Per Harald and Petersen Steffen B., Amino acid neighbours and detailed conformational analysis of cysteines in proteins, Protein Engineering, vol 12, no. 7, pp 535-548, 1999. [5] Hyunsoo Kim and Haesun Park, Protein secondary structure prediction based on an ...
... [4] Neves Petersen Maria Teresa, Johnson Per Harald and Petersen Steffen B., Amino acid neighbours and detailed conformational analysis of cysteines in proteins, Protein Engineering, vol 12, no. 7, pp 535-548, 1999. [5] Hyunsoo Kim and Haesun Park, Protein secondary structure prediction based on an ...
File
... in the Nucleotide Biosynthetic Pathways The first set of agents includes compounds that inhibit glutamine amidotransferases. Recall that glutamine is a nitrogen donor in at least half a dozen separate reactions in nucleotide biosynthesis. The binding sites for glutamine and the mechanism by which NH ...
... in the Nucleotide Biosynthetic Pathways The first set of agents includes compounds that inhibit glutamine amidotransferases. Recall that glutamine is a nitrogen donor in at least half a dozen separate reactions in nucleotide biosynthesis. The binding sites for glutamine and the mechanism by which NH ...
CWI Learning List for ANAT 111
... 1. Differentiate between an organic molecule and an inorganic molecule. 2. Describe the general chemical composition of biomolecules. 3. Define a monomer and polymer. 4. Describe the role of water in both dehydration and hydrolysis reactions in altering biomolecules. 5. Describe the general characte ...
... 1. Differentiate between an organic molecule and an inorganic molecule. 2. Describe the general chemical composition of biomolecules. 3. Define a monomer and polymer. 4. Describe the role of water in both dehydration and hydrolysis reactions in altering biomolecules. 5. Describe the general characte ...
Cellular Respiration
... The phosphorylated sugar has an electrical charge preventing it from leaving the cell, due the impermeability of the cell membrane to ions. In step three another molecule of ATP is used up, and another phosphate group is added to the sugar. In step four the molecule is split into two three-carbon su ...
... The phosphorylated sugar has an electrical charge preventing it from leaving the cell, due the impermeability of the cell membrane to ions. In step three another molecule of ATP is used up, and another phosphate group is added to the sugar. In step four the molecule is split into two three-carbon su ...
Spermatogenesis-preventing substance - Development
... extracted from the testes of hCG-treated (3 days after hCG injection) (+) and untreated (–) eels. First strand of cDNA was synthesised with reverse transcriptase from 5 µg of each poly(A)+ RNA using an oligo (dT) primer. The second strand of cDNA was synthesised with RNase H and E. coli DNA polymera ...
... extracted from the testes of hCG-treated (3 days after hCG injection) (+) and untreated (–) eels. First strand of cDNA was synthesised with reverse transcriptase from 5 µg of each poly(A)+ RNA using an oligo (dT) primer. The second strand of cDNA was synthesised with RNase H and E. coli DNA polymera ...
Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, Peroxisomes - Beck-Shop
... of ATP synthase and three of the four electron transfer complexes. Nuclear genes encode most of the protein subunits of these complexes, but mitochondrial genes are responsible for a few key subunits. Bacteria and mitochondria share homologous proteins for the key steps in oxidative phosphorylation ...
... of ATP synthase and three of the four electron transfer complexes. Nuclear genes encode most of the protein subunits of these complexes, but mitochondrial genes are responsible for a few key subunits. Bacteria and mitochondria share homologous proteins for the key steps in oxidative phosphorylation ...
Polyunsaturated fatty acids stimulate hepatic UCP
... this hypothesis. UCP-2, like UCP-1, has been shown to be able to dissipate the proton gradient when overexpressed in yeast or reconstituted in vesicles with coenzyme Q (12, 13, 16). Also, there is indirect evidence in primary hepatocytes suggesting that UCP-2 is capable of dissipating the mitochondr ...
... this hypothesis. UCP-2, like UCP-1, has been shown to be able to dissipate the proton gradient when overexpressed in yeast or reconstituted in vesicles with coenzyme Q (12, 13, 16). Also, there is indirect evidence in primary hepatocytes suggesting that UCP-2 is capable of dissipating the mitochondr ...
Mitochondrium
... inner membrane of Mch. Other point of the inner membrane of Mch. is impermeable for H+ and OH-. ...
... inner membrane of Mch. Other point of the inner membrane of Mch. is impermeable for H+ and OH-. ...
INOTROPIC AGENTS - Dr Ted Williams
... primary plug also acts as a ‘net’ to catch the procoagulants and serves as a catalytic surface for clot formation ...
... primary plug also acts as a ‘net’ to catch the procoagulants and serves as a catalytic surface for clot formation ...
Changes of cellular redox homeostasis and protein - LINK
... which can be easily oxidized, and provide a large redox buffer capacity for the cell. Gluthationylation, i.e. thiol-disulfide exchange between a cysteine residue in a protein and the oxidized form of glutathione (GSSG) occurs in oxidative stress. This process serves as a redox-dependent regulator of ...
... which can be easily oxidized, and provide a large redox buffer capacity for the cell. Gluthationylation, i.e. thiol-disulfide exchange between a cysteine residue in a protein and the oxidized form of glutathione (GSSG) occurs in oxidative stress. This process serves as a redox-dependent regulator of ...
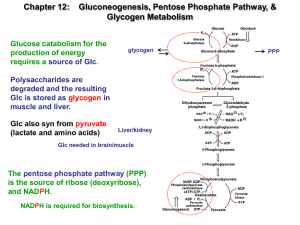
Lecture 17 Glycolysis (continued) Recap Phases: priming: glucose
... Glucose is metabolized in a series of 10 reactions to pyruvate Glycolysis provides the cell (cytoplasm) with 2 mol ATP/glucose Glycolysis also provides cytoplasm with 2 mol NADH/glucose In the absence of O2, NADH is oxidized by reduction of pyruvate In the presence of O2, NADH is oxidized in the mit ...
... Glucose is metabolized in a series of 10 reactions to pyruvate Glycolysis provides the cell (cytoplasm) with 2 mol ATP/glucose Glycolysis also provides cytoplasm with 2 mol NADH/glucose In the absence of O2, NADH is oxidized by reduction of pyruvate In the presence of O2, NADH is oxidized in the mit ...
Genome-Based Metabolic Mapping and C Flux
... CoenzymeA; AH, acetaldehyde; AKG, a-ketoglutarate; Cit, citrate; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; E4P, erythrose-4phosphate; EtOH, ethanol; F6P, fructose-6-phosphate; FBP, fructose-1,6-bisphosphate; Fum, fumarate; G3P, glucose-3-phosphate; G6P, glucose-6-phosphate; Glx, glyoxylate; Go3P, glycerol-3 ...
... CoenzymeA; AH, acetaldehyde; AKG, a-ketoglutarate; Cit, citrate; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; E4P, erythrose-4phosphate; EtOH, ethanol; F6P, fructose-6-phosphate; FBP, fructose-1,6-bisphosphate; Fum, fumarate; G3P, glucose-3-phosphate; G6P, glucose-6-phosphate; Glx, glyoxylate; Go3P, glycerol-3 ...
Cyclic AMP-Mediated Inhibition of Cell Growth Requires the Small G
... cell types (8, 19, 60, 64) through multiple mechanisms (37), including the regulation of the levels of critical cell cycle proteins (108) including cyclin D1 (50, 58) and p27kip1 (110). ERKs are activated by growth factors through consecutive cascades of tyrosine and serine/threonine phosphorylation ...
... cell types (8, 19, 60, 64) through multiple mechanisms (37), including the regulation of the levels of critical cell cycle proteins (108) including cyclin D1 (50, 58) and p27kip1 (110). ERKs are activated by growth factors through consecutive cascades of tyrosine and serine/threonine phosphorylation ...
Fatty Acid Catabolism
... D) Lysophospholipid CoA. 2. There are four steps in the β-oxidation pathway. Some reaction types are listed below. Give the proper reaction types in the order that they occur in the β-oxidation pathway. ...
... D) Lysophospholipid CoA. 2. There are four steps in the β-oxidation pathway. Some reaction types are listed below. Give the proper reaction types in the order that they occur in the β-oxidation pathway. ...
Substitutions and Deletions in the Cytoplasmic
... Because phosphorylation of tyrosine residues in one or both Y-x-x-L sequences may be involved in the activation of intracellular signaling events, wild-type and mutant transfectants were also examined for induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of FcyRIIA (Fig 3). COS-l cell transfectants were stimula ...
... Because phosphorylation of tyrosine residues in one or both Y-x-x-L sequences may be involved in the activation of intracellular signaling events, wild-type and mutant transfectants were also examined for induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of FcyRIIA (Fig 3). COS-l cell transfectants were stimula ...
An overview of Metabolism - Harford Community College
... • To survive cells need to make ATP. • For ATP synthesis the following are required: – oxygen – nutrients/vitamins – mitochondria – enzymes ...
... • To survive cells need to make ATP. • For ATP synthesis the following are required: – oxygen – nutrients/vitamins – mitochondria – enzymes ...