Protein Synthesis - BLI-Research-SynBio-2016-session-2
... RNA polymerase- complex of enzymes with 2 functions: • Unwind DNA sequence • Produce primary transcript by stringing together the chain of RNA nucleotides ...
... RNA polymerase- complex of enzymes with 2 functions: • Unwind DNA sequence • Produce primary transcript by stringing together the chain of RNA nucleotides ...
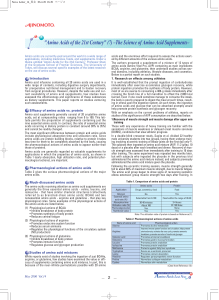
Amino acids in the human placental intervillous space
... intervillous space. The amino acid composition of this plasma has been compared with that of the simultaneously sampled blood from the maternal vein and the umbilical cord. Six mothers of 1 6 1 9 weeks gestation were subjected to foetoscopy and foetal blood sampling prior to termination of pregnancy ...
... intervillous space. The amino acid composition of this plasma has been compared with that of the simultaneously sampled blood from the maternal vein and the umbilical cord. Six mothers of 1 6 1 9 weeks gestation were subjected to foetoscopy and foetal blood sampling prior to termination of pregnancy ...
Lecture 7
... – The sugars composing nucleotides are derived from either the pentose phosphate pathway or the Entner-Doudoroff pathway. – Carbon and nitrogen atoms from certain amino acids form the backbones of the purines and pyrimidines ...
... – The sugars composing nucleotides are derived from either the pentose phosphate pathway or the Entner-Doudoroff pathway. – Carbon and nitrogen atoms from certain amino acids form the backbones of the purines and pyrimidines ...
BCH 405 – REGULATION OF METABOLIC PROCESSES
... modulator is said to be a +ve effector or allosteric activator whereas when the modulator diminishes the binding of substrate, it is called a –ve effector or allosteric inhibitor, +ve effectors increase the number of binding sites for substrate whereas –ve effectors decrease the number of binding si ...
... modulator is said to be a +ve effector or allosteric activator whereas when the modulator diminishes the binding of substrate, it is called a –ve effector or allosteric inhibitor, +ve effectors increase the number of binding sites for substrate whereas –ve effectors decrease the number of binding si ...
The Citric Acid Cycle
... Acetyl-CoA + 3NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi + 2 H2O 2CO2 +3NADH + FADH2 + GTP + CoA + 3H+ • Carbons of acetyl groups in acetyl-CoA are oxidized to CO2 • Electrons from this process reduce NAD+ and FAD • One GTP is formed per cycle, this can be converted to ATP • Intermediates in the cycle are not depleted ...
... Acetyl-CoA + 3NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi + 2 H2O 2CO2 +3NADH + FADH2 + GTP + CoA + 3H+ • Carbons of acetyl groups in acetyl-CoA are oxidized to CO2 • Electrons from this process reduce NAD+ and FAD • One GTP is formed per cycle, this can be converted to ATP • Intermediates in the cycle are not depleted ...
AASK National Framework
... dual coloring scheme — a colored band at the base of each sidechain indicates chemical properties while embedded colored balls in the model show atomic structure. Understanding protein structure begins with this unique combination of structure and chemical properties of the amino acid sidechains. Th ...
... dual coloring scheme — a colored band at the base of each sidechain indicates chemical properties while embedded colored balls in the model show atomic structure. Understanding protein structure begins with this unique combination of structure and chemical properties of the amino acid sidechains. Th ...
Protein Synthesis
... 1. Messenger RNA goes to the ribosome-template (pattern) is formed on the ribosome. 2. Transfer RNA previously made by DNA and sent to the cytoplasm goes to be sure it matches the RNA pattern on the ribosome. 3. If it matches correctly then Transfer RNA goes and picks up its amino acid in the cytopl ...
... 1. Messenger RNA goes to the ribosome-template (pattern) is formed on the ribosome. 2. Transfer RNA previously made by DNA and sent to the cytoplasm goes to be sure it matches the RNA pattern on the ribosome. 3. If it matches correctly then Transfer RNA goes and picks up its amino acid in the cytopl ...
HMT Newsletter - Human Metabolome Technologies
... Breast Cancer Stem Cell Maintenance and Lung Metastasis Samanta D., et al., Cancer Research, 76, pp. 4430-4442. ...
... Breast Cancer Stem Cell Maintenance and Lung Metastasis Samanta D., et al., Cancer Research, 76, pp. 4430-4442. ...
Certificate of Analysis (CoA) Recombinant Human Cardiotrophin-1
... Description: CT-1 is a member of the IL-6 family of cytokines which also includes LIF, CNTF, OSM (Oncostatin M), IL-11, IL-6 and possibly NNT-1/BSF-3. CT-1 is a pleiotropic cytokine which is expressed in various tissues including the adult heart, skeletal muscle, ovary, colon, prostate and fetal lun ...
... Description: CT-1 is a member of the IL-6 family of cytokines which also includes LIF, CNTF, OSM (Oncostatin M), IL-11, IL-6 and possibly NNT-1/BSF-3. CT-1 is a pleiotropic cytokine which is expressed in various tissues including the adult heart, skeletal muscle, ovary, colon, prostate and fetal lun ...
chapter2 questions
... acidic or basic. What is the primary function of carbohydrates such as monosaccharides and disaccharides? Storing the genetic information of the human body Catalyzing chemical reactions Serving as the main structural components of cell membranes Serving as an important energy source Helping to break ...
... acidic or basic. What is the primary function of carbohydrates such as monosaccharides and disaccharides? Storing the genetic information of the human body Catalyzing chemical reactions Serving as the main structural components of cell membranes Serving as an important energy source Helping to break ...
"Amino Acids of the 21st Century" (7) –The
... "Amino Acids of the 21st Century" (7) –The Science of Amino Acid Supplements– acids and the enormous effort required to assess the actions exerted by different amounts of the various amino acids. The authors prepared a supplement of a mixture of 12 types of amino acids (Amino Vital Pro, AVP) contain ...
... "Amino Acids of the 21st Century" (7) –The Science of Amino Acid Supplements– acids and the enormous effort required to assess the actions exerted by different amounts of the various amino acids. The authors prepared a supplement of a mixture of 12 types of amino acids (Amino Vital Pro, AVP) contain ...
Conversion of amino acids to specialized products
... Introduction of iron (as Fe2+) occurs spontaneously but the rate is enhanced by ferrochelatase. This enzyme like ALA is also inhibited by lead. ...
... Introduction of iron (as Fe2+) occurs spontaneously but the rate is enhanced by ferrochelatase. This enzyme like ALA is also inhibited by lead. ...
CH 5
... Even a slight change in primary structure can affect a protein’s conformation and ability to function. The substitution of one amino acid (valine) for the normal one (glutamic acid) at a particular position in the primary structure of hemoglobin, the protein that carries oxygen in red blood cells, ...
... Even a slight change in primary structure can affect a protein’s conformation and ability to function. The substitution of one amino acid (valine) for the normal one (glutamic acid) at a particular position in the primary structure of hemoglobin, the protein that carries oxygen in red blood cells, ...
Ch 2 - Biochemistry
... High heat capacity – absorbs and releases large amounts of heat before changing temperature ...
... High heat capacity – absorbs and releases large amounts of heat before changing temperature ...
Understanding the origin and organization of
... A (exchanges • Coenzyme electrons for phosphates through sulfur intermediate) ...
... A (exchanges • Coenzyme electrons for phosphates through sulfur intermediate) ...
Metabolic engineering Synthetic Biology
... Mmosquito-borne infectious disease of humans and other animals caused by protists (a type of microorganism) of the genus Plasmodium. It begins with a bite from an infected female Anopheles mosquito, which introduces the protists through saliva into the circulatory system. A motile infective form (ca ...
... Mmosquito-borne infectious disease of humans and other animals caused by protists (a type of microorganism) of the genus Plasmodium. It begins with a bite from an infected female Anopheles mosquito, which introduces the protists through saliva into the circulatory system. A motile infective form (ca ...
Data/hora: 16/04/2017 16:28:45 Provedor de dados: 36 País: Brazil
... Resumo: An ion chromatography procedure, employing an IonPac AC15 concentrator column was used to investigate on line preconcentration for the simultaneous determination of inorganic anions and organic acids in river water. Twelve organic acids and nine inorganic anions were separated without any in ...
... Resumo: An ion chromatography procedure, employing an IonPac AC15 concentrator column was used to investigate on line preconcentration for the simultaneous determination of inorganic anions and organic acids in river water. Twelve organic acids and nine inorganic anions were separated without any in ...
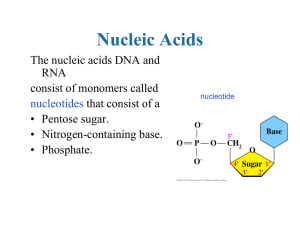
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis: Power Point presentation
... DNA Secondary Structure Double Helix ...
... DNA Secondary Structure Double Helix ...
Final Exam Revision Answers 2009
... (PFK) and fructose –1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase)? A. AMP stimulates PFK and inhibits FBPase. B. Fructose2,6 bisphosphate inhibits PFK and activates FBPase. C. Acetyl-CoA inhibits PFK and activates FBPase.` D. Citrate stimulates PFK and inhibits FBPase. E. NADPH activates PFK and inhibits FBPase. 38. ...
... (PFK) and fructose –1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase)? A. AMP stimulates PFK and inhibits FBPase. B. Fructose2,6 bisphosphate inhibits PFK and activates FBPase. C. Acetyl-CoA inhibits PFK and activates FBPase.` D. Citrate stimulates PFK and inhibits FBPase. E. NADPH activates PFK and inhibits FBPase. 38. ...
Transcription - Lake Station Community Schools
... -this is pre-mRNA it needs further processing before it can be translated ...
... -this is pre-mRNA it needs further processing before it can be translated ...
Lecture 24: the genetic code
... function of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, encoded by a domain that is distinct from the domain for aminoacylation. If they are not cleared, genetic code ambiguity is introduced (that is, a given codon in the messenger RNA will specify incorporation of more than one amino acid, resulting in the product ...
... function of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, encoded by a domain that is distinct from the domain for aminoacylation. If they are not cleared, genetic code ambiguity is introduced (that is, a given codon in the messenger RNA will specify incorporation of more than one amino acid, resulting in the product ...