Summary of Additional A-level Paper 2 content - A
... I can describe a nucleotide as made up from a phosphate ion bonded to 2-deoxyribose which is in turn bonded to one of the four bases adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine (structures given in the Chemistry data booklet), that a single strand of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a polymer of nucleotide ...
... I can describe a nucleotide as made up from a phosphate ion bonded to 2-deoxyribose which is in turn bonded to one of the four bases adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine (structures given in the Chemistry data booklet), that a single strand of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a polymer of nucleotide ...
Biochemistry Chapter 6
... • Monomers = amino acids • There are 20 types of amino acids. • We produce 10 of the 20! ...
... • Monomers = amino acids • There are 20 types of amino acids. • We produce 10 of the 20! ...
Protein Synthesis
... This is a diagram of tRNA. Remember this contains the base uracil just like mRNA. Notice the amino acid attached to the upper part of the tRNA molecule. This amino acid will become a part of the polypeptide chain that will make up the protein. Also notice the dark green bottom section. There are 3- ...
... This is a diagram of tRNA. Remember this contains the base uracil just like mRNA. Notice the amino acid attached to the upper part of the tRNA molecule. This amino acid will become a part of the polypeptide chain that will make up the protein. Also notice the dark green bottom section. There are 3- ...
Amino Acids Interp Guide
... Why is this test important? Amino acids are the building blocks that make up protein in all bodily tissues, including bone, muscles, ligaments, tendons, nails, hair, glands and organs. Amino acids are also the basic constituents of all hormones, enzymes and neurotransmitters. Assessment of amino aci ...
... Why is this test important? Amino acids are the building blocks that make up protein in all bodily tissues, including bone, muscles, ligaments, tendons, nails, hair, glands and organs. Amino acids are also the basic constituents of all hormones, enzymes and neurotransmitters. Assessment of amino aci ...
pogil
... between atoms represents a bond between them. Double bonds exist which would be represented by two lines (=). The diagrams are sometimes simplified by leaving out the central carbon symbol instead showing only the outer atoms and bonds (this can be seen in the two versions of a nucleotide). 13. The ...
... between atoms represents a bond between them. Double bonds exist which would be represented by two lines (=). The diagrams are sometimes simplified by leaving out the central carbon symbol instead showing only the outer atoms and bonds (this can be seen in the two versions of a nucleotide). 13. The ...
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
... production of eighteen ATP molecules, and the two molecules of FADH2 produce four ATP molecules, for a total of 22. The total is therefore the two ATP molecules produced directly plus the 22 molecules formed through the electron transport chain, which ...
... production of eighteen ATP molecules, and the two molecules of FADH2 produce four ATP molecules, for a total of 22. The total is therefore the two ATP molecules produced directly plus the 22 molecules formed through the electron transport chain, which ...
Nutrients - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... cooling of body during cold weather or sweating when their core temperature gets too hot. Homeostasis allows an organism to remain in balance with its environment. If homeostasis is not maintained, it can harm or kill the organism. ...
... cooling of body during cold weather or sweating when their core temperature gets too hot. Homeostasis allows an organism to remain in balance with its environment. If homeostasis is not maintained, it can harm or kill the organism. ...
008 Chapter 08 Metabolism: Energy Enzymes and Regulation 1
... C. Enzymes are highly specific for the substrates they react with and catalyze only one or a limited set of possible reactions with those substrates. D. all of the choices 4. The energy required to bring the substrates of a reaction together in the correct way to reach the transition state is called ...
... C. Enzymes are highly specific for the substrates they react with and catalyze only one or a limited set of possible reactions with those substrates. D. all of the choices 4. The energy required to bring the substrates of a reaction together in the correct way to reach the transition state is called ...
Carbon Compounds
... This is a single nucleotide that carries energy in cells. – This is the “currency” of cells. – When food molecules (glucose) are broken down inside of cells (cell respiration), some of the energy in the molecules is stored temporarily in ATP. – Some of this energy is used by cell. All cells need a s ...
... This is a single nucleotide that carries energy in cells. – This is the “currency” of cells. – When food molecules (glucose) are broken down inside of cells (cell respiration), some of the energy in the molecules is stored temporarily in ATP. – Some of this energy is used by cell. All cells need a s ...
Overview: The Molecules of Life
... If the fatty acid has one or more carbon-carbon double bonds formed by the removal of hydrogen atoms from the carbon skeleton, then the molecule is an unsaturated fatty acid. A saturated fatty acid is a straight chain, but an unsaturated fatty acid has a kink wherever there is a double bond. Fats ma ...
... If the fatty acid has one or more carbon-carbon double bonds formed by the removal of hydrogen atoms from the carbon skeleton, then the molecule is an unsaturated fatty acid. A saturated fatty acid is a straight chain, but an unsaturated fatty acid has a kink wherever there is a double bond. Fats ma ...
Amylase
... How will enzyme activity compare when incubated at O o C and 37 o C? 2. Denaturization of Enzymes How will enzyme activity be altered if the enzyme is denatured by boiling? ...
... How will enzyme activity compare when incubated at O o C and 37 o C? 2. Denaturization of Enzymes How will enzyme activity be altered if the enzyme is denatured by boiling? ...
Yeast Impact on Wine Composition: Overview
... Increased solubility of aroma compound (less volatile) Creates “ethanol pockets” areas of enhanced solubility Affects physical interactions with other wine components Decreases perception? Converted to aldehydes during aging ...
... Increased solubility of aroma compound (less volatile) Creates “ethanol pockets” areas of enhanced solubility Affects physical interactions with other wine components Decreases perception? Converted to aldehydes during aging ...
2nd Nine Weeks Exam Review Unit 5
... A. Trp—Thr changed to Ser—Gly B. Trp—Thr changed to Ser—Pro C. hr—Cys changed to Ser—Pro D. No change in amino acids would occur. DNA can be changed by UV radiation. If the sun damages skin cells what is most likely to occur? A. A somatic mutation that will not affect offspring. B. A somatic mutatio ...
... A. Trp—Thr changed to Ser—Gly B. Trp—Thr changed to Ser—Pro C. hr—Cys changed to Ser—Pro D. No change in amino acids would occur. DNA can be changed by UV radiation. If the sun damages skin cells what is most likely to occur? A. A somatic mutation that will not affect offspring. B. A somatic mutatio ...
Enzymes and Temperature
... ranges of pH. Changes in pH result in excess H+ or OH- ions. These disrupt the bonds in the enzymes structure. This changes the shape of the active site. This means that an enzyme-substrate complex cannot form. The proteases pepsin and trypsin are both produced by cells in an inactive form. The acid ...
... ranges of pH. Changes in pH result in excess H+ or OH- ions. These disrupt the bonds in the enzymes structure. This changes the shape of the active site. This means that an enzyme-substrate complex cannot form. The proteases pepsin and trypsin are both produced by cells in an inactive form. The acid ...
4. Transcription in Detail
... _____________ that adds the appropriate amino acid is aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (20 different enzymes) ...
... _____________ that adds the appropriate amino acid is aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (20 different enzymes) ...
Recent Advances in Directed Protein Evolution
... Increased activity/selectivity Expand substrate scope Develop novel biological tools Probe mechanism and structure Improve upon rational design Understand natural protein evolution ...
... Increased activity/selectivity Expand substrate scope Develop novel biological tools Probe mechanism and structure Improve upon rational design Understand natural protein evolution ...
Name
... 25) a) True b) False: If both glycolysis and gluconeogenesis occurred in the same cell at the same time a futile cycle would occur. Allosteric regulation helps prevent this. 26) For eukaryotic cells glycolysis occurs in the ______and the tricarboxylic acid cycle occurs in the ______. a) Mitochondria ...
... 25) a) True b) False: If both glycolysis and gluconeogenesis occurred in the same cell at the same time a futile cycle would occur. Allosteric regulation helps prevent this. 26) For eukaryotic cells glycolysis occurs in the ______and the tricarboxylic acid cycle occurs in the ______. a) Mitochondria ...
Cell Bio/Physio Lecture 6 Objectives Sunday, August 14, 2011 11:41
... Naming begins with the N-terminus Peptides are named using the 3 letter abbreviations, whereas protein sequences use the 1 letter code Proteins go by common names, rather than by chemical names. ...
... Naming begins with the N-terminus Peptides are named using the 3 letter abbreviations, whereas protein sequences use the 1 letter code Proteins go by common names, rather than by chemical names. ...
Document
... imported into others. A non-Darwinian mechanism, it adds a new twist to evolution by mutation and natural selection. Lynn Margulis proposed endosymbiosis in the 1960s, initially rejected by most, but now accepted as the origin of complexity in eukaryotes from ...
... imported into others. A non-Darwinian mechanism, it adds a new twist to evolution by mutation and natural selection. Lynn Margulis proposed endosymbiosis in the 1960s, initially rejected by most, but now accepted as the origin of complexity in eukaryotes from ...
ENZYME STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... very difficult problem that has not yet been solved. Most enzymes are much larger than the substrates they act on, and only a small portion of the enzyme (around 2–4 amino acids) is directly involved in catalysis. The region that contains these catalytic residues, binds the substrate, and then carri ...
... very difficult problem that has not yet been solved. Most enzymes are much larger than the substrates they act on, and only a small portion of the enzyme (around 2–4 amino acids) is directly involved in catalysis. The region that contains these catalytic residues, binds the substrate, and then carri ...
Molecular biology for bioinformatics
... DNA (and RNA) are polymer sequences composed of a small number of chemically similar compounds. The individual units are called nucleotides, each made up of three distinct parts: a cyclic base a, c, g or t (or u, respectively), a cyclic sugar deoxyribose (or ribose, respectively), and a phosphate gr ...
... DNA (and RNA) are polymer sequences composed of a small number of chemically similar compounds. The individual units are called nucleotides, each made up of three distinct parts: a cyclic base a, c, g or t (or u, respectively), a cyclic sugar deoxyribose (or ribose, respectively), and a phosphate gr ...
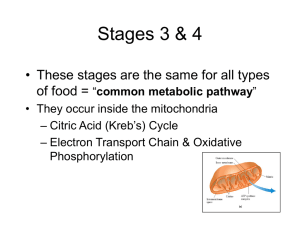
the Four Stages of Biochemical Energy Production
... Citric acid cycle – For every glucose, two acetyl groups enter the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) • Each two-carbon acetyl group combines with a fourcarbon compound • Two CO2 molecules are removed (why is this important?) • Energy captured as 1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2 form from each acetyl group ...
... Citric acid cycle – For every glucose, two acetyl groups enter the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) • Each two-carbon acetyl group combines with a fourcarbon compound • Two CO2 molecules are removed (why is this important?) • Energy captured as 1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2 form from each acetyl group ...
handout nucleic acids and DNA replication
... molecules is the base sequence. Therefore, the sequence of bases in DNA must determine the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. The length of DNA that codes for a polypeptide chain is called a gene and it can be thousands of nucleotides long. The code cannot be as simple as 1 base codin ...
... molecules is the base sequence. Therefore, the sequence of bases in DNA must determine the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. The length of DNA that codes for a polypeptide chain is called a gene and it can be thousands of nucleotides long. The code cannot be as simple as 1 base codin ...