Lecture 24: the genetic code
... function of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, encoded by a domain that is distinct from the domain for aminoacylation. If they are not cleared, genetic code ambiguity is introduced (that is, a given codon in the messenger RNA will specify incorporation of more than one amino acid, resulting in the product ...
... function of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, encoded by a domain that is distinct from the domain for aminoacylation. If they are not cleared, genetic code ambiguity is introduced (that is, a given codon in the messenger RNA will specify incorporation of more than one amino acid, resulting in the product ...
FES 100 - Introduction to Forest Biology Exam 1: 100 points October
... What are three, clear characteristics that can distinguish between something that is living ...
... What are three, clear characteristics that can distinguish between something that is living ...
Secretory Protein mRNA Finds Another Way Out
... It turns out that mRNAs that encode many secretory proteins do indeed have additional functions, as Alexander Palazzo, Tom Rapoport, and their colleagues report in a new study. While many proteins are created and destroyed within the same cell, others are secreted. One property that differentiates s ...
... It turns out that mRNAs that encode many secretory proteins do indeed have additional functions, as Alexander Palazzo, Tom Rapoport, and their colleagues report in a new study. While many proteins are created and destroyed within the same cell, others are secreted. One property that differentiates s ...
(pt=2) What is an acid?
... What are three, clear characteristics that can distinguish between something that is living or ...
... What are three, clear characteristics that can distinguish between something that is living or ...
Crystal Structure and Functional Analysis of Glyceraldehyde
... OsGAPDH shows homotetramer form and each subunit could be seperated to three domains: NAD-binding domain, catalytic domain and S-loop domain. NAD+ bind to OsGAPDH by hydrogen bonds directly and intermediated by water. Some residues form positive grooves to attract sulfate molecules which are used to ...
... OsGAPDH shows homotetramer form and each subunit could be seperated to three domains: NAD-binding domain, catalytic domain and S-loop domain. NAD+ bind to OsGAPDH by hydrogen bonds directly and intermediated by water. Some residues form positive grooves to attract sulfate molecules which are used to ...
Protein synthesis 2015 TranscritpionTranslation.notebook
... Protein synthesis 2015 TranscritpionTranslation.notebook ...
... Protein synthesis 2015 TranscritpionTranslation.notebook ...
Document
... Draw a water molecule (structural) and state why it is considered a polar molecule. Why are valence electrons essential for life? Identify two internal environmental factors that directly influence the rate of enzyme action. Explain how an enzyme can have its shape changed/altered (into abnormal str ...
... Draw a water molecule (structural) and state why it is considered a polar molecule. Why are valence electrons essential for life? Identify two internal environmental factors that directly influence the rate of enzyme action. Explain how an enzyme can have its shape changed/altered (into abnormal str ...
Cellular Respiration
... • The mitochondria are the engines of our cells where sugar is burned for fuel and the exhaust is CO2 and H2O. ...
... • The mitochondria are the engines of our cells where sugar is burned for fuel and the exhaust is CO2 and H2O. ...
Chapter14
... • Remember, living things are at steady state, not equilibrium • J(flux of metabolite) = vf - vr – Rate of flux for irreversible step if rate of forward rxn – Slowest step usually controls flux of a pathway – Sometimes multiple enzymes control flux of pathway ...
... • Remember, living things are at steady state, not equilibrium • J(flux of metabolite) = vf - vr – Rate of flux for irreversible step if rate of forward rxn – Slowest step usually controls flux of a pathway – Sometimes multiple enzymes control flux of pathway ...
Homework Solutions
... Silk produced by a silkworm is a protein with a high glycine and alanine content. This makes the silk fiber strong because it has regions of -pleated sheet and regions of -helix. The -pleated sheet regions are almost fully extended and their highly ordered three-dimension ...
... Silk produced by a silkworm is a protein with a high glycine and alanine content. This makes the silk fiber strong because it has regions of -pleated sheet and regions of -helix. The -pleated sheet regions are almost fully extended and their highly ordered three-dimension ...
A1982NC82400001
... Tissue cell cultures grew in free gas ex- HeLa cell line, revealed that the essential change with the atmosphere when the bicar- amino acids could be incorporated in media bonate buffer was replaced by the free base at much higher concentrations and that he amino acids, especially L-arginine. Glycol ...
... Tissue cell cultures grew in free gas ex- HeLa cell line, revealed that the essential change with the atmosphere when the bicar- amino acids could be incorporated in media bonate buffer was replaced by the free base at much higher concentrations and that he amino acids, especially L-arginine. Glycol ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... circle and move outward! • UCG = Serine • CAC = • GGU = • UAA = There are 64 codons but only 20 amino acids. So, different codons can code for the same amino acid. ...
... circle and move outward! • UCG = Serine • CAC = • GGU = • UAA = There are 64 codons but only 20 amino acids. So, different codons can code for the same amino acid. ...
Measurement of Enzymes and Their Clinical Significance
... • IUB standardized these as international units (IU) – IU: the amount of enzyme that will convert one micromole of substrate per minute in an assay system – Expressed as units per liter or U/L – Conditions: pH, temperature, substrate,activators ...
... • IUB standardized these as international units (IU) – IU: the amount of enzyme that will convert one micromole of substrate per minute in an assay system – Expressed as units per liter or U/L – Conditions: pH, temperature, substrate,activators ...
Biochemistry II, Test One
... (c) The primary role of ATP is to drive nitrogen fixation through the hydrolysis of PPi. (d) Nitrogen fixation occurs only in prokaryotes. (e) The final electron acceptor in this process in N2. 9. In nucleotide metabolism, all of the following are true except: Answer: D A. The committed step in puri ...
... (c) The primary role of ATP is to drive nitrogen fixation through the hydrolysis of PPi. (d) Nitrogen fixation occurs only in prokaryotes. (e) The final electron acceptor in this process in N2. 9. In nucleotide metabolism, all of the following are true except: Answer: D A. The committed step in puri ...
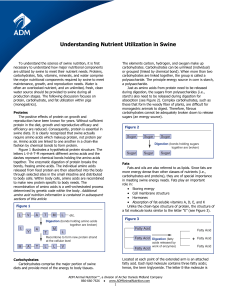
Nutrient Utilization in Swine
... Most information normally discusses excess nitrogen excretion as a result of overfeeding protein. However, deficiencies in one or more essential amino acids can also result in excess nitrogen excretion. To understand this process, one needs to have a basic understanding of how protein is formed. The ...
... Most information normally discusses excess nitrogen excretion as a result of overfeeding protein. However, deficiencies in one or more essential amino acids can also result in excess nitrogen excretion. To understand this process, one needs to have a basic understanding of how protein is formed. The ...
Model answer Class: B.Pharm V Semester Subject: Pharmaceutical
... especially synthetic organic chemistry, and pharmacology and various other biological specialties, where they are involved with design, chemical synthesis and development for market of pharmaceutical agents, or bio-active molecules (drugs). Example of any drugs like Aspirin, Propanolol ii) ...
... especially synthetic organic chemistry, and pharmacology and various other biological specialties, where they are involved with design, chemical synthesis and development for market of pharmaceutical agents, or bio-active molecules (drugs). Example of any drugs like Aspirin, Propanolol ii) ...
Are nonessential amino acids not so redundant for Chinese hamster
... by utilizing experimental depletion of individual essential amino acids in a variety of mammalian cell lines commonly used in scientific research [14–17] . However, cellular responses to depletion of amino acids commonly classified as ‘nonessential’ and especially in CHO cell lines commonly used for ...
... by utilizing experimental depletion of individual essential amino acids in a variety of mammalian cell lines commonly used in scientific research [14–17] . However, cellular responses to depletion of amino acids commonly classified as ‘nonessential’ and especially in CHO cell lines commonly used for ...
Amino Acids: An Introduction to Their Structure, Functions and
... Turkey and milk have high levels of trp. There seems to be some controversy as to whether or not there is enough trp in milk (especially warm milk) to render a person drowsy so that they will fall asleep when it is difficult for them to do so without assistance. In recent times, ...
... Turkey and milk have high levels of trp. There seems to be some controversy as to whether or not there is enough trp in milk (especially warm milk) to render a person drowsy so that they will fall asleep when it is difficult for them to do so without assistance. In recent times, ...
Biochemistry-lab-identifying
... composed of smaller N-H groups known as amino acids. Food sources for protein include beef, poultry, fish, and green vegetables. These amino acid chains inside a protein are called a peptide chain. Amino acids are like the individual Lego bricks that fit together to build a bigger structure. Therefo ...
... composed of smaller N-H groups known as amino acids. Food sources for protein include beef, poultry, fish, and green vegetables. These amino acid chains inside a protein are called a peptide chain. Amino acids are like the individual Lego bricks that fit together to build a bigger structure. Therefo ...
carbonyl carbons
... bond. The four atoms which define f are (1) the carbonyl carbonn-1, (2) the nitrogenn, (3) the a-carbonn, and (4) the carbonyl carbonn. – Psi rotation, y: the rotation of the leading polypeptide about the C"-C (carbonyl) bond. The four atoms which define y (1) the nitrogenn, (2) the alpha carbonn, ( ...
... bond. The four atoms which define f are (1) the carbonyl carbonn-1, (2) the nitrogenn, (3) the a-carbonn, and (4) the carbonyl carbonn. – Psi rotation, y: the rotation of the leading polypeptide about the C"-C (carbonyl) bond. The four atoms which define y (1) the nitrogenn, (2) the alpha carbonn, ( ...
Lecture 24 – PDF
... 1) Initiation complex forms: complex includes 30S (40S) ribosomal subunit, a messenger RNA (mRNA), several initiation factors (proteins), and an initiating tRNA (tRNA i ). 2) The 50S (60S) subunit positions tRNA i into the P site. 3) Initiation in prokaryotes: a) tRNA i f-Met -- Initiator tRNA that ...
... 1) Initiation complex forms: complex includes 30S (40S) ribosomal subunit, a messenger RNA (mRNA), several initiation factors (proteins), and an initiating tRNA (tRNA i ). 2) The 50S (60S) subunit positions tRNA i into the P site. 3) Initiation in prokaryotes: a) tRNA i f-Met -- Initiator tRNA that ...
1 Pioneer Junior College 9647/9746 H2 Chemistry Banding Lecture
... Compound P has the molecular formula C5H12O. When P is heated with acidified potassium dichromate (VI), the solution remains orange, when P is reacted with excess concentrated sulfuric acid at 180oC, a mixture of two isomers, Q and R, is ...
... Compound P has the molecular formula C5H12O. When P is heated with acidified potassium dichromate (VI), the solution remains orange, when P is reacted with excess concentrated sulfuric acid at 180oC, a mixture of two isomers, Q and R, is ...