CHAPTER 6
... storing large amounts of triacylglycerols prior to flight – These birds are often 70% fat by weight when migration begins (compared with values of 30% and less for nonmigratory birds) ...
... storing large amounts of triacylglycerols prior to flight – These birds are often 70% fat by weight when migration begins (compared with values of 30% and less for nonmigratory birds) ...
I LEARN AT HOME ASSIGNMENT 4 Macromolecule Review
... Organic molecules have four common characteristics. First, they are all carbon based, meaning they all contain carbon. They are formed from just a few elements which join together to form small molecules which join together, or bond, to form large molecules. The third characteristic of all orga ...
... Organic molecules have four common characteristics. First, they are all carbon based, meaning they all contain carbon. They are formed from just a few elements which join together to form small molecules which join together, or bond, to form large molecules. The third characteristic of all orga ...
PDF File
... prokaryotes and eukaryotes (2– 8). It is likely, therefore, that active extrusion systems play a crucial role in the cellular defense mechanism against incoming noxious compounds in many living organisms. It is of great interest and importance, therefore, to analyze the mechanism by which such unive ...
... prokaryotes and eukaryotes (2– 8). It is likely, therefore, that active extrusion systems play a crucial role in the cellular defense mechanism against incoming noxious compounds in many living organisms. It is of great interest and importance, therefore, to analyze the mechanism by which such unive ...
Controlling reaction specificity in pyridoxal phosphate
... Claisen condensation, and others on substrates containing an amino group, most commonly α-amino acids. The wide variety of reactions catalyzed by PLP enzymes is enabled by the ability of the covalent aldimine intermediate formed between substrate and PLP to stabilize carbanionic intermediates at Cα ...
... Claisen condensation, and others on substrates containing an amino group, most commonly α-amino acids. The wide variety of reactions catalyzed by PLP enzymes is enabled by the ability of the covalent aldimine intermediate formed between substrate and PLP to stabilize carbanionic intermediates at Cα ...
A “random steady state” model for the pyruvate dehydrogenase and
... organized into an octahedral symmetry (figure 1B). This can be pictured as a cube with 3 E2s occupying each of its eight vertices. Each vertex of the cube has three neighboring vertices. The E2 core of PDH can accommodate up to 24 dimers of either E1 alone or E3 alone (3 dimers of E1 or E3 at each v ...
... organized into an octahedral symmetry (figure 1B). This can be pictured as a cube with 3 E2s occupying each of its eight vertices. Each vertex of the cube has three neighboring vertices. The E2 core of PDH can accommodate up to 24 dimers of either E1 alone or E3 alone (3 dimers of E1 or E3 at each v ...
Biochimie
... acid in the Kennedy pathway. In mammals, four homologous isoforms of GPAT, each the product of a separate gene, catalyze this reaction, two of them residing in the ER [39 and references therein]. All four isoforms are thought to be able to initiate glycerolipid biosynthesis and at least three of the ...
... acid in the Kennedy pathway. In mammals, four homologous isoforms of GPAT, each the product of a separate gene, catalyze this reaction, two of them residing in the ER [39 and references therein]. All four isoforms are thought to be able to initiate glycerolipid biosynthesis and at least three of the ...
W+-Retail-summary
... amino acid: soothes. •Anti-age Illuminating agent: Combination of rabdosia Rubescens + Siegesbeckia: Action on collagen synthesis Action on Skin Chromophores(Hemoglob in, Melanin, Collagen) ...
... amino acid: soothes. •Anti-age Illuminating agent: Combination of rabdosia Rubescens + Siegesbeckia: Action on collagen synthesis Action on Skin Chromophores(Hemoglob in, Melanin, Collagen) ...
CHAPTER 11 Mechanism of Enzyme Action
... - Can act as enzymes *chemical teeth” to take over chemical reactions that cannot be performed by amino acid side chains… - Required in diet of organisms - for example metal ions, Cu2+, Fe3+, Zn2+ toxicity, Cd2+ and Hg2+ can replace Zn and inactivate the enzyme - organic molecules, coenzymes, ca ...
... - Can act as enzymes *chemical teeth” to take over chemical reactions that cannot be performed by amino acid side chains… - Required in diet of organisms - for example metal ions, Cu2+, Fe3+, Zn2+ toxicity, Cd2+ and Hg2+ can replace Zn and inactivate the enzyme - organic molecules, coenzymes, ca ...
Coenzyme A and Acyl Carrier Protein
... acids can enter mitochondria without carnitine transport but they must be still activated before βoxidation can occur. Similarly, peroxisomes in animal cells have a distinct fatty acid β-oxidation system with a separate set of enzymes, including as many as three acyl-CoA oxidases. The acyl-CoA oxida ...
... acids can enter mitochondria without carnitine transport but they must be still activated before βoxidation can occur. Similarly, peroxisomes in animal cells have a distinct fatty acid β-oxidation system with a separate set of enzymes, including as many as three acyl-CoA oxidases. The acyl-CoA oxida ...
Liver glycogen constitutes a reserve of glucose for the
... The reserve is not large. In fact, the reserve is virtually exhausted in 24 hours. In such an animal the continuing requirement for glucose is satisfied by gluconeogenesis, which is the synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors: lactate, propionate, glycerol, pyruvate, gluconeogenic amin ...
... The reserve is not large. In fact, the reserve is virtually exhausted in 24 hours. In such an animal the continuing requirement for glucose is satisfied by gluconeogenesis, which is the synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors: lactate, propionate, glycerol, pyruvate, gluconeogenic amin ...
Chapter 25 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... carbon atom are called _______ amino acids. Amino acids are coupled together by amide linkages called ____________ bonds. Relatively short chains of amino acids are called ___________. Only twenty amino acids are abundantly found in proteins, all of which are ___ amino acids, except for ____________ ...
... carbon atom are called _______ amino acids. Amino acids are coupled together by amide linkages called ____________ bonds. Relatively short chains of amino acids are called ___________. Only twenty amino acids are abundantly found in proteins, all of which are ___ amino acids, except for ____________ ...
Essentiality and damage in metabolic networks
... number 2, 4, 6 and 10) are involved in the production of chorismate, which is an important link to the biosynthesis of aromatic aminoacids, folate and ubiquinone. The enzyme with the highest damage, ribose-phosphate-pyrophosphokinase, generates phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate, which is the initial comp ...
... number 2, 4, 6 and 10) are involved in the production of chorismate, which is an important link to the biosynthesis of aromatic aminoacids, folate and ubiquinone. The enzyme with the highest damage, ribose-phosphate-pyrophosphokinase, generates phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate, which is the initial comp ...
Creatine kinase: The reactive cysteine is required for synergism but
... C278N. Thus, Cys278 probably provides a negative charge which is directly or indirectly involved in maximizing C K activity. Under near-optimal conditions in the reverse reaction, mutants C278G and C278S showed about an 1l-fold increase inKm(PCr),but only 1.7- and 2.8-fold reductions in V-, respecti ...
... C278N. Thus, Cys278 probably provides a negative charge which is directly or indirectly involved in maximizing C K activity. Under near-optimal conditions in the reverse reaction, mutants C278G and C278S showed about an 1l-fold increase inKm(PCr),but only 1.7- and 2.8-fold reductions in V-, respecti ...
L-Carnitine in human metabolism
... Finally the acyl-CoA is conveyed to the betaoxidation and fragmented in chains containing two Carbons (acetyl-CoA), which subsequently enter in the Krebs cycle, the Electron Transport Chain, with the final result of energy production (ATP). ...
... Finally the acyl-CoA is conveyed to the betaoxidation and fragmented in chains containing two Carbons (acetyl-CoA), which subsequently enter in the Krebs cycle, the Electron Transport Chain, with the final result of energy production (ATP). ...
1 Analysis of Polyphenoloxidase Enzyme Activity from Potato Extract
... and all their metabolic intermediates. Enzymes are able to perform their functions by binding to reactants in a very specific manner, straining them to increase their reactivity and providing the chemical environment necessary to allow the reaction to proceed quickly and efficiently. The rate at whi ...
... and all their metabolic intermediates. Enzymes are able to perform their functions by binding to reactants in a very specific manner, straining them to increase their reactivity and providing the chemical environment necessary to allow the reaction to proceed quickly and efficiently. The rate at whi ...
Down-regulation of acetolactate synthase compromises Ol
... rar1-suppressor (rsp) mutants, in which the level of threonine (Thr) was highly elevated [11]. The rsp1 mutant carries a mutation in the aspartate kinase2 gene [11], which catalyzes the first step in the aspartate-derived amino acid pathway. The rsp2 mutant contains a loss-of-function allele of dihy ...
... rar1-suppressor (rsp) mutants, in which the level of threonine (Thr) was highly elevated [11]. The rsp1 mutant carries a mutation in the aspartate kinase2 gene [11], which catalyzes the first step in the aspartate-derived amino acid pathway. The rsp2 mutant contains a loss-of-function allele of dihy ...
Altering substrate specificity of catechol 2,3
... conserved region in the active site containing two histidine residues, one glutamate and two molecules of water as Fe2+ ligands (Huang et al., 2010; Wojcieszyńska et al., 2011). The catalytic mechanism starts with bidentate binding of the substrate as catecholate monoanion to the active-site metal w ...
... conserved region in the active site containing two histidine residues, one glutamate and two molecules of water as Fe2+ ligands (Huang et al., 2010; Wojcieszyńska et al., 2011). The catalytic mechanism starts with bidentate binding of the substrate as catecholate monoanion to the active-site metal w ...
Consortium for Educational Communication
... altering the equilibrium between the reactants and the products. Although, the rate at which the chemical equilibrium is established is enhanced. The enzymes affect only the rate and not the direction. They can accelerate the reaction in either direction. Many enzymes which are required for the synt ...
... altering the equilibrium between the reactants and the products. Although, the rate at which the chemical equilibrium is established is enhanced. The enzymes affect only the rate and not the direction. They can accelerate the reaction in either direction. Many enzymes which are required for the synt ...
Codon Dictionary Worksheet
... So, if the mRNA codon is UUU, what tRNA anticodon is complementary? (Answer: AAA) If the mRNA codon is UAC, what tRNA anticodon is complementary? (Answer #4 below) If the mRNA codon is GGU, what tRNA anticodon is complementary? (Answer #5 below) If the tRNA anticodon is UAC, with which mRNA codon do ...
... So, if the mRNA codon is UUU, what tRNA anticodon is complementary? (Answer: AAA) If the mRNA codon is UAC, what tRNA anticodon is complementary? (Answer #4 below) If the mRNA codon is GGU, what tRNA anticodon is complementary? (Answer #5 below) If the tRNA anticodon is UAC, with which mRNA codon do ...
University of Groningen Mutants and homologs of
... activating the hydroxyl group of Serβ1, which is the nucleophile in the first processing step [53-55] (Figure 3). If this water is forced out by mutating Pheβ177 to proline, the hydroxyl group is not positioned correctly and processing is inhibited [55]. In the nondeficient enzyme, the formed interm ...
... activating the hydroxyl group of Serβ1, which is the nucleophile in the first processing step [53-55] (Figure 3). If this water is forced out by mutating Pheβ177 to proline, the hydroxyl group is not positioned correctly and processing is inhibited [55]. In the nondeficient enzyme, the formed interm ...
Gibbs Free Energy Changes for the Glycolytic Enzymes
... uptake of fuel molecules such as glucose. Phosphorylated glucose is no longer recognized by the glucose transport system and is therefore trapped in the cell. There is no transport system for phosphorylated glucose. The glucose transporter is a passive transporter. Converting glucose to G6P depletes ...
... uptake of fuel molecules such as glucose. Phosphorylated glucose is no longer recognized by the glucose transport system and is therefore trapped in the cell. There is no transport system for phosphorylated glucose. The glucose transporter is a passive transporter. Converting glucose to G6P depletes ...
Introduction to Winemaking Part 2: Must Additions
... • Each form reacts differently based on its own specific chemistry. ...
... • Each form reacts differently based on its own specific chemistry. ...
ATP
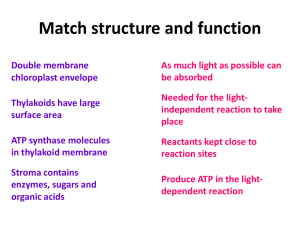
... 1.3.4 Light Independent • CO2 diffuses into the stroma • Combines with a 5C acceptor RuBP – uses enzyme • RuBP has become carboxylated – carboxyl group • Produces 2 x 3C molecule – glycerate 3-phosphate ...
... 1.3.4 Light Independent • CO2 diffuses into the stroma • Combines with a 5C acceptor RuBP – uses enzyme • RuBP has become carboxylated – carboxyl group • Produces 2 x 3C molecule – glycerate 3-phosphate ...
Chapter 3 - Slothnet
... Optical isomers occur when a carbon atom has four different atoms or groups attached to it (an asymmetric carbon). ...
... Optical isomers occur when a carbon atom has four different atoms or groups attached to it (an asymmetric carbon). ...