06 Salts of carboxylic acids,saturated amino acids of aliphatic series
... Proteins are biosynthesized from α-amino acids, and when proteins are hydrolyzed, amino acids are obtained. Some very complex (conjugated) proteins yield other hydrolysis products in addition to amino acids. α-Amino acids are commonly characterized with the generalized structure: ...
... Proteins are biosynthesized from α-amino acids, and when proteins are hydrolyzed, amino acids are obtained. Some very complex (conjugated) proteins yield other hydrolysis products in addition to amino acids. α-Amino acids are commonly characterized with the generalized structure: ...
Characterization and Cloning of the Chlorophyll
... Enzymatic removal of the methoxycarbonyl group of pheophorbide (Pheid) a in chlorophyll degradation was investigated in cotyledons of radish (Raphanus sativus). The enzyme pheophorbidase (PPD) catalyzes the conversion of Pheid a to a precursor of pyropheophorbide (PyroPheid), C-132-carboxylPyroPheid ...
... Enzymatic removal of the methoxycarbonyl group of pheophorbide (Pheid) a in chlorophyll degradation was investigated in cotyledons of radish (Raphanus sativus). The enzyme pheophorbidase (PPD) catalyzes the conversion of Pheid a to a precursor of pyropheophorbide (PyroPheid), C-132-carboxylPyroPheid ...
Uric acid estimation in plasma
... Absence of HGPRT is cause of Lesch-Nyhan syndrome This increase may be due to PRPP feed-forward activation of de novo pathways the rate of purine synthesis is increased about 200X Symptoms are gouty arthritis due to uric acid accumulation and severe neurological malfunctions including mental retarda ...
... Absence of HGPRT is cause of Lesch-Nyhan syndrome This increase may be due to PRPP feed-forward activation of de novo pathways the rate of purine synthesis is increased about 200X Symptoms are gouty arthritis due to uric acid accumulation and severe neurological malfunctions including mental retarda ...
100 Pectin is a complex polysaccharide consisting mainly of
... The isolated bacteria were identified based on staining, biochemical tests and molecular characterization by sequencing the 16S rRNA gene. The genomic DNA of the isolated bacteria was isolated using single step kit method and the isolated genomic DNA was tested for purity by gel electrophoresis and ...
... The isolated bacteria were identified based on staining, biochemical tests and molecular characterization by sequencing the 16S rRNA gene. The genomic DNA of the isolated bacteria was isolated using single step kit method and the isolated genomic DNA was tested for purity by gel electrophoresis and ...
General and Organic Chemistry: Theory content HT 2016
... F&F ch. 18.1.-18.4A only ”Reaction of amines and alkyl halides”, 18.4B, 18.5, 18.6, 18.8, 25.1, 25.2 (except ”Gabriel phtalimide synthesis”), 25.3B, 25.3C, 25.5, 25.7 before A. Key concepts amines: Nomenclature . Hybridization . Preparation 1) from halides, 2) by reducing a) nitro-compounds, b) nitr ...
... F&F ch. 18.1.-18.4A only ”Reaction of amines and alkyl halides”, 18.4B, 18.5, 18.6, 18.8, 25.1, 25.2 (except ”Gabriel phtalimide synthesis”), 25.3B, 25.3C, 25.5, 25.7 before A. Key concepts amines: Nomenclature . Hybridization . Preparation 1) from halides, 2) by reducing a) nitro-compounds, b) nitr ...
Overview of Protein Structure • The three
... among chemical polymers in that they adopt one folded conformation in solution. Steric repulsion between neighboring amino acids partially restricts the number of conformations accessible to a peptide chain. Weak noncovalent interactions among neighboring residues in the folded state determine the n ...
... among chemical polymers in that they adopt one folded conformation in solution. Steric repulsion between neighboring amino acids partially restricts the number of conformations accessible to a peptide chain. Weak noncovalent interactions among neighboring residues in the folded state determine the n ...
Bio-Organic Chemistry will Page | 1
... biological fluids. There will be more applications of UV-Vis spectroscopy in CHEM 122 and 220. Infra-Red (IR) Spectroscopy IR energy is long wavelength (hence low energy) light below visible red in the spectrum. It is the same as what you feel in your toaster and what you [don't] see in your toaster ...
... biological fluids. There will be more applications of UV-Vis spectroscopy in CHEM 122 and 220. Infra-Red (IR) Spectroscopy IR energy is long wavelength (hence low energy) light below visible red in the spectrum. It is the same as what you feel in your toaster and what you [don't] see in your toaster ...
Genes and Enzymes in Man
... determing phenylketonuria and have a partial deficiency of the It is now generally believed that genes exert their effects by enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase, and this, of course, is only 1 directing the synthesis of enzymes and other proteins. There example out of many. A few cases are also known ...
... determing phenylketonuria and have a partial deficiency of the It is now generally believed that genes exert their effects by enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase, and this, of course, is only 1 directing the synthesis of enzymes and other proteins. There example out of many. A few cases are also known ...
File
... Dairy products such as milk contain a sugar called lactose. Lactose is a disaccharide (meaning “two sugars”) that is composed of the two simple sugars Glucose and Galactose. Some people are “lactose intolerant,” meaning that their digestive system cannot break down the Lactose sugar into these simpl ...
... Dairy products such as milk contain a sugar called lactose. Lactose is a disaccharide (meaning “two sugars”) that is composed of the two simple sugars Glucose and Galactose. Some people are “lactose intolerant,” meaning that their digestive system cannot break down the Lactose sugar into these simpl ...
CHAPTER 6
... polysaccharides are constructed from appropriate building blocks via the pathways of anabolism • The building blocks (amino acid, nucleotides, sugars, and fatty acids) can be generated from metabolites • Some pathways serve both in catabolism and anabolism –citric acid cycle- Such pathways are amphi ...
... polysaccharides are constructed from appropriate building blocks via the pathways of anabolism • The building blocks (amino acid, nucleotides, sugars, and fatty acids) can be generated from metabolites • Some pathways serve both in catabolism and anabolism –citric acid cycle- Such pathways are amphi ...
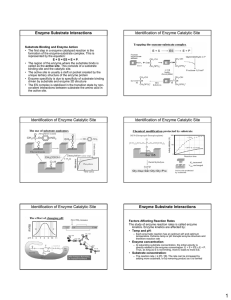
Enzyme Substrate Interactions Identification of Enzyme Catalytic Site
... If enzyme just binds substrate then there will be no further reaction ...
... If enzyme just binds substrate then there will be no further reaction ...
Chapter 7
... Gluconeogenesis • glucose can be formed by body tissues from noncarbohydrate metabolites, including lipids, amino acids. • Glucogenic amino acids such as nonessential amino acids and several of essential (arginine, methionine, cystine, histidine, threonine, tryptophane, valine.) • The amino acids u ...
... Gluconeogenesis • glucose can be formed by body tissues from noncarbohydrate metabolites, including lipids, amino acids. • Glucogenic amino acids such as nonessential amino acids and several of essential (arginine, methionine, cystine, histidine, threonine, tryptophane, valine.) • The amino acids u ...
Digestive Enzymes - Goshen Cancer Survivor Network
... Curcumin, which is the source of the yellow/gold color in turmeric (Curcuma longa) also possesses enzymatic activity. The anti-inflammatory properties have been found to equal the effects of some of the more traditional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDS) in acute conditions. It is ...
... Curcumin, which is the source of the yellow/gold color in turmeric (Curcuma longa) also possesses enzymatic activity. The anti-inflammatory properties have been found to equal the effects of some of the more traditional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDS) in acute conditions. It is ...
nucleic acid - Notes-for-all
... They are thus referred to as: polypeptides. There are 20 different amino acids Proteins form different shapes, based upon the order that the amino acids are strung together. ...
... They are thus referred to as: polypeptides. There are 20 different amino acids Proteins form different shapes, based upon the order that the amino acids are strung together. ...
Word
... points were recorded every 30 minutes. For growth in presence of 20 different amino acids, cells ...
... points were recorded every 30 minutes. For growth in presence of 20 different amino acids, cells ...
Kinetics of Enzyme-Catalyzed Reactions
... The effects of KI are best observed in Lineweaver-Burk plots. Probably the best known reversible inhibitors are competitive inhibitors, which always bind at the catalytic or active site of the enzyme. Most drugs that alter enzyme activity are of this type. Competitive inhibitors are especially attra ...
... The effects of KI are best observed in Lineweaver-Burk plots. Probably the best known reversible inhibitors are competitive inhibitors, which always bind at the catalytic or active site of the enzyme. Most drugs that alter enzyme activity are of this type. Competitive inhibitors are especially attra ...
DOC
... reduced form that carries the electrons and protons. Electron Transport and Chemiosmosis occur in the mitochondria. The electrons are passed through the electron transport chain, a series of enzymes that transport electrons. The electrons eventually end up on oxygen, which is the terminal electron a ...
... reduced form that carries the electrons and protons. Electron Transport and Chemiosmosis occur in the mitochondria. The electrons are passed through the electron transport chain, a series of enzymes that transport electrons. The electrons eventually end up on oxygen, which is the terminal electron a ...
Energy Conversion Pathways 1. Substrate level phosphorylation
... 28. a) The radioactive carbon became incorporated into all of the cycle intermediates at atom positions that could only be explained by products also serving as substrates. The metabolism of oxaloacetate in one round of the cycle produces a different radioactively labeled product depending on the nu ...
... 28. a) The radioactive carbon became incorporated into all of the cycle intermediates at atom positions that could only be explained by products also serving as substrates. The metabolism of oxaloacetate in one round of the cycle produces a different radioactively labeled product depending on the nu ...