Oct. 5, 2015 Cells - AP Biology Study Guide
... 3. Contrast the general features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 4. Be able to distinguish the organelles and structures typical of eukaryotic plant and animal cells. 5. Describe the nucleus of eukaryotes with respect to structure and function. 6. Describe the organelles associated with the end ...
... 3. Contrast the general features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 4. Be able to distinguish the organelles and structures typical of eukaryotic plant and animal cells. 5. Describe the nucleus of eukaryotes with respect to structure and function. 6. Describe the organelles associated with the end ...
Matter in Ecosystems Part 2
... c. Made of a “phospholipid bilayer” d. Phospholipids have non-polar, hydrophobic (water hating) ends that stick together and polar, hydrophilic (water loving) ends ...
... c. Made of a “phospholipid bilayer” d. Phospholipids have non-polar, hydrophobic (water hating) ends that stick together and polar, hydrophilic (water loving) ends ...
Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Cell
... bridges in peptidoglycan Lysozyme-enzyme-tears, saliva, mucus Breaks the bond between sugar molecules. Gram- more resistant – outer membrane Gram+ more sensitive – peptidoglycan is exposed to the environment ...
... bridges in peptidoglycan Lysozyme-enzyme-tears, saliva, mucus Breaks the bond between sugar molecules. Gram- more resistant – outer membrane Gram+ more sensitive – peptidoglycan is exposed to the environment ...
Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Cell
... bridges in peptidoglycan Lysozyme-enzyme-tears, saliva, mucus Breaks the bond between sugar molecules. Gram- more resistant – outer membrane Gram+ more sensitive – peptidoglycan is exposed to the environment ...
... bridges in peptidoglycan Lysozyme-enzyme-tears, saliva, mucus Breaks the bond between sugar molecules. Gram- more resistant – outer membrane Gram+ more sensitive – peptidoglycan is exposed to the environment ...
Document
... 28. Cross a homozygous tall parent with a pure breeding short parent. What is the probability of having an offspring that is SHORT? 29. In a cross between heterozygous parents RrTt X RrTt, what is the probability of having an offspring that is wrinkled and tall? ...
... 28. Cross a homozygous tall parent with a pure breeding short parent. What is the probability of having an offspring that is SHORT? 29. In a cross between heterozygous parents RrTt X RrTt, what is the probability of having an offspring that is wrinkled and tall? ...
File
... 14. A system of folded membranes in which proteins, lipids, and other materialsare made is the ______________________. 15. Two forms of endoplasmic reticulum are and ______________________. ...
... 14. A system of folded membranes in which proteins, lipids, and other materialsare made is the ______________________. 15. Two forms of endoplasmic reticulum are and ______________________. ...
Chapter 5 Cell Membrane
... nonpolar hydrophobic tail • Hydrogen bonds form between the phospholipid "heads" and the watery environment inside and outside of the cell Hydrophobic interactions force the "tails" to face inward Phospholipids are not bonded to each other, which makes the double layer fluid • Cholesterol embedded i ...
... nonpolar hydrophobic tail • Hydrogen bonds form between the phospholipid "heads" and the watery environment inside and outside of the cell Hydrophobic interactions force the "tails" to face inward Phospholipids are not bonded to each other, which makes the double layer fluid • Cholesterol embedded i ...
Plasma Membranes - cellsinactionEDF4402
... Moving molecules or ions against a concentration gradient (one way) Energy required – high numbers mitochondria Occurs in intestines to absorb as much of the nutrient molecules as possible Occurs in cells to keep high K+ inside and high Na+ outside, and to expel metabolism wastes (eg H+) Plants also ...
... Moving molecules or ions against a concentration gradient (one way) Energy required – high numbers mitochondria Occurs in intestines to absorb as much of the nutrient molecules as possible Occurs in cells to keep high K+ inside and high Na+ outside, and to expel metabolism wastes (eg H+) Plants also ...
Organelle Notes
... Questions/Main Ideas: Nucleus Contains the cell’s DNA Control center of cell, the cell’s brain Ribosomes ...
... Questions/Main Ideas: Nucleus Contains the cell’s DNA Control center of cell, the cell’s brain Ribosomes ...
Prokaryote and Eukaryote organelle vocabulary 1. Cell
... 1. Cell- is the basic structural, functional and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and are often called the "building blocks of life". 2. cell theory- is one of the basic principles of biology. Credit for the formulat ...
... 1. Cell- is the basic structural, functional and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and are often called the "building blocks of life". 2. cell theory- is one of the basic principles of biology. Credit for the formulat ...
PARTS OF THE CELL CELL ORGANELLES
... NUCLEUS: controls most cell processes and contains DNA (code for all proteins and other molecules made by cells) ...
... NUCLEUS: controls most cell processes and contains DNA (code for all proteins and other molecules made by cells) ...
Bacterial Cell Walls Contain Peptidoglycans
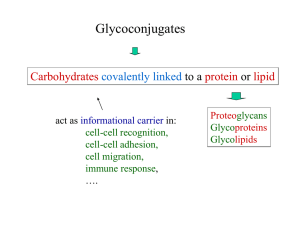
... • Others are not dependent on glycans • Some are glycan-dependent in one cell type but not in another • Some glycosylation sites are more important than others – Aid in certain sorting events • In later secretory pathway of glycoproteins in Golgi – Structural features of glycans act as destination l ...
... • Others are not dependent on glycans • Some are glycan-dependent in one cell type but not in another • Some glycosylation sites are more important than others – Aid in certain sorting events • In later secretory pathway of glycoproteins in Golgi – Structural features of glycans act as destination l ...
Cell City Worksheet – high school
... the cell. The ribosomes are the ______________________________ which manufacture proteins. Draw the rough ER with a ribosome. 6. 6. Smooth E.R. ____________ ribosomes. It acts as a __________________________ throughout the cytoplasm. It runs from the cell membrane to the nuclear ________________ and ...
... the cell. The ribosomes are the ______________________________ which manufacture proteins. Draw the rough ER with a ribosome. 6. 6. Smooth E.R. ____________ ribosomes. It acts as a __________________________ throughout the cytoplasm. It runs from the cell membrane to the nuclear ________________ and ...
Transport Across Cell Membrane
... the tails face each other forming a hydrophobic barrier which keeps water dissolved contents inside. Proteins may be Intrinsic – embedded in the lipid double layer and Extrinsic associated outside the lipid double layer. Proteins are gate keepers of cell and make the cell membrane selectively permea ...
... the tails face each other forming a hydrophobic barrier which keeps water dissolved contents inside. Proteins may be Intrinsic – embedded in the lipid double layer and Extrinsic associated outside the lipid double layer. Proteins are gate keepers of cell and make the cell membrane selectively permea ...
Biology- ch. 7
... • Cells are the basic units of structure and organization in living things • New cells are produced from existing cells with cells passing copies of their genetic material down to their daughter cells ...
... • Cells are the basic units of structure and organization in living things • New cells are produced from existing cells with cells passing copies of their genetic material down to their daughter cells ...
Slide 1
... occupying the majority of the cell volume (up to ~90%). Can be one large one or many small ones ...
... occupying the majority of the cell volume (up to ~90%). Can be one large one or many small ones ...
BIOLOGY 1 TEST REVIEW SHEET
... 3. Know how to find the total magnification of the low power objective (4x) and high power objective (10x) ...
... 3. Know how to find the total magnification of the low power objective (4x) and high power objective (10x) ...
MEMBRANES Fluid mosaic of phopholipid bilayer, cholesterol
... MEMBRANES Fluid mosaic of phopholipid bilayer, cholesterol, protein Singer – Nicolson Fluid Mosaic Model, 1970’s Selectively permeable Allows some substances, and not others, to pass Built in EM System ...
... MEMBRANES Fluid mosaic of phopholipid bilayer, cholesterol, protein Singer – Nicolson Fluid Mosaic Model, 1970’s Selectively permeable Allows some substances, and not others, to pass Built in EM System ...
Cell Processes Study Guide OL Answer Key
... Endocytosis brings large particles into cells. Particle comes in contact with membrane, membrane wraps around the particle and pinches off creating a vesicle. ...
... Endocytosis brings large particles into cells. Particle comes in contact with membrane, membrane wraps around the particle and pinches off creating a vesicle. ...
Other types of transport
... • Your nerve cells have lots of protein pumps to move ions across the cell membrane. • This is how signals travel through your nervous system. ...
... • Your nerve cells have lots of protein pumps to move ions across the cell membrane. • This is how signals travel through your nervous system. ...
Cell organelles ppt
... Site of protein synthesis Found attached to rough ER or floating free in cytosol Produced in a part of the nucleus called the nucleolus That looks familiar…what is a polypeptide? ...
... Site of protein synthesis Found attached to rough ER or floating free in cytosol Produced in a part of the nucleus called the nucleolus That looks familiar…what is a polypeptide? ...
Note taking guide
... Membrane-bound sac found in plant and animal cells that’s used for storage. It has a variety of functions, including playing a role in intracellular digestion and the release of cell waste. A plant cell has single large central vacuole; animal cells have varying numbers and sizes. ...
... Membrane-bound sac found in plant and animal cells that’s used for storage. It has a variety of functions, including playing a role in intracellular digestion and the release of cell waste. A plant cell has single large central vacuole; animal cells have varying numbers and sizes. ...
No Slide Title - Biology Junction
... This happens to a carrier molecule when it binds with the molecule it’s moving ...
... This happens to a carrier molecule when it binds with the molecule it’s moving ...
Ch 4 quiz - TESADVBiology
... ____ 7.Which of the following is NOT part of the cell theory? a.All living things are made of one or more cells. b.All cells contain the same organelles. c.Cells are the basic units of structure and function in organisms. d.All cells arise from existing cells. ____ 8.As a cell becomes smaller, its s ...
... ____ 7.Which of the following is NOT part of the cell theory? a.All living things are made of one or more cells. b.All cells contain the same organelles. c.Cells are the basic units of structure and function in organisms. d.All cells arise from existing cells. ____ 8.As a cell becomes smaller, its s ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.