Chapter 08
... Cell-cell recognition: Some glycoproteins act as identification tags that are recognized by other cells. Attachment to ECM: The cytoskeleton may be bound to membrane proteins to maintain the size/shape of the cell. Lipid Bilayer Permeability: The hydrophobic core of the membrane prefers not to allow ...
... Cell-cell recognition: Some glycoproteins act as identification tags that are recognized by other cells. Attachment to ECM: The cytoskeleton may be bound to membrane proteins to maintain the size/shape of the cell. Lipid Bilayer Permeability: The hydrophobic core of the membrane prefers not to allow ...
Hyper/Hypo/Isotonic Solutions
... the process of taking materials into a cell by forming vesicles around the substance pinocytosis: pin: to drink cells taking in substances dissolved in water phagocytosis: phag: to eat cells taking in large particles ...
... the process of taking materials into a cell by forming vesicles around the substance pinocytosis: pin: to drink cells taking in substances dissolved in water phagocytosis: phag: to eat cells taking in large particles ...
PASSIVE TRANSPORT
... Phospholipid membranes are semi-permeable, meaning that some substances can travel across them but others cannot The size and polarity of a molecule helps determine whether it can move across a membrane easily, with assistance or not at all Passive Transport the movement of materials across a cell m ...
... Phospholipid membranes are semi-permeable, meaning that some substances can travel across them but others cannot The size and polarity of a molecule helps determine whether it can move across a membrane easily, with assistance or not at all Passive Transport the movement of materials across a cell m ...
Cell Size
... membrane. • As the cell gets larger, its volume increases faster than its surface area. So as a cell grows its surface area to volume ratio decreases. • At some point the cell’s volume becomes too large for its surface area to supply it with raw materials. ...
... membrane. • As the cell gets larger, its volume increases faster than its surface area. So as a cell grows its surface area to volume ratio decreases. • At some point the cell’s volume becomes too large for its surface area to supply it with raw materials. ...
Concept Covered: Cell Internal Organiza8on
... 1. Basic eukaryotic cell structure consists of an outer membrane, cytoplasm filled with organelles and a nucleus. Describe and give the function of each of the following: ...
... 1. Basic eukaryotic cell structure consists of an outer membrane, cytoplasm filled with organelles and a nucleus. Describe and give the function of each of the following: ...
Passive and Active Transport Internet Assignment
... Scroll back to the top of your web page and look at the upper right side menu Click on “Active Transport” 22. What is active transport? 23. Which membrane molecules do most of the work in active transport? 24. Membrane proteins are very __________________, meaning that they are designed to move ...
... Scroll back to the top of your web page and look at the upper right side menu Click on “Active Transport” 22. What is active transport? 23. Which membrane molecules do most of the work in active transport? 24. Membrane proteins are very __________________, meaning that they are designed to move ...
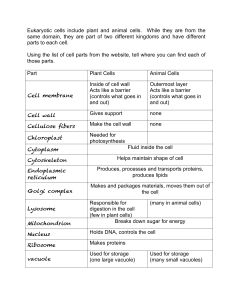
Cell membrane Cell wall Cellulose fibers Chloroplast Cytoplasm
... (controls what goes in and out) ...
... (controls what goes in and out) ...
Plant Cell - Effingham County Schools
... •Leucoplasts store starch and other molecules for the cell. Many in potato cells. Process - Storage ...
... •Leucoplasts store starch and other molecules for the cell. Many in potato cells. Process - Storage ...
Carbohydrates and Lipids - Washington State University
... superior to carbohydrates as a form of energy storage, especially for organisms that move around (e.g., animals rather than plants.) ...
... superior to carbohydrates as a form of energy storage, especially for organisms that move around (e.g., animals rather than plants.) ...
Study guide
... 4. What is the major difference between a prokaryote and a eukaryote? 5. What does the cytoplasm include? 6. What feature(s) allow eukaryotes to be much larger than prokaryotes? 7. Be able to describe both the basic structure and the functions of each of the major organelles discussed in class/text. ...
... 4. What is the major difference between a prokaryote and a eukaryote? 5. What does the cytoplasm include? 6. What feature(s) allow eukaryotes to be much larger than prokaryotes? 7. Be able to describe both the basic structure and the functions of each of the major organelles discussed in class/text. ...
Sec.3 and 4 Notes - Revere Local Schools
... Carbohydrate- an organic rich molecule. There are 2 forms, simple carbs which are sugars (monosaccharides) and made of only one molecule and complex carbs are two or more molecules in chains (polysaccharides). The main function of a carbohydrate is as the primary energy source for organisms. Plants ...
... Carbohydrate- an organic rich molecule. There are 2 forms, simple carbs which are sugars (monosaccharides) and made of only one molecule and complex carbs are two or more molecules in chains (polysaccharides). The main function of a carbohydrate is as the primary energy source for organisms. Plants ...
A View of the cells: Cell parts and organelles
... site of protein synthesis, suspends all of the organelles in the cell (like Jell-O or a factory) control center of the cell, contains the directions to make proteins (like a boss or the president) makes ribosomes (like a factory machine) ...
... site of protein synthesis, suspends all of the organelles in the cell (like Jell-O or a factory) control center of the cell, contains the directions to make proteins (like a boss or the president) makes ribosomes (like a factory machine) ...
The Cell Membrane
... to others. Permeable means “allowing passage,” and impermeable means “not allowing passage.” The cell membrane plays an important role in keeping harmful substances out of the cell and in removing wastes. Because it allows only certain substances to pass through it, we call the cell membrane a selec ...
... to others. Permeable means “allowing passage,” and impermeable means “not allowing passage.” The cell membrane plays an important role in keeping harmful substances out of the cell and in removing wastes. Because it allows only certain substances to pass through it, we call the cell membrane a selec ...
Plasma Membrane Notes (7.2)
... the cell and its environment Allows ____________ ____________ the cell Allows ____________ to ____________ the cell ...
... the cell and its environment Allows ____________ ____________ the cell Allows ____________ to ____________ the cell ...
Cell Organelles
... • Ribosomes are non-membrane-bound organelles in the nucleus where proteins are ...
... • Ribosomes are non-membrane-bound organelles in the nucleus where proteins are ...
Unit 5 SCA Review Sheet
... green color of plants. I am found only in plants. __________________________________________________ 3. I hold in cytoplasm and protect all of the organelles. I am made up of a semi-permeable membrane, which allows some things to pass in and out of the cell. _________________________________________ ...
... green color of plants. I am found only in plants. __________________________________________________ 3. I hold in cytoplasm and protect all of the organelles. I am made up of a semi-permeable membrane, which allows some things to pass in and out of the cell. _________________________________________ ...
Types of Passive Transport
... What must cells take in to survive? ________________________________________________________ What part of the cell allows it to take in nutrients and water? ____________________________________ Does it have another name? What is the cell membrane made of? ____________________________________________ ...
... What must cells take in to survive? ________________________________________________________ What part of the cell allows it to take in nutrients and water? ____________________________________ Does it have another name? What is the cell membrane made of? ____________________________________________ ...
1b Unit 3 Cell transport notes
... two types of transport movement of water across a membrane movement of substances across a membrane part of the cell that regulates what goes in and out movement assisted with channel proteins. two components of the cell membrane ...
... two types of transport movement of water across a membrane movement of substances across a membrane part of the cell that regulates what goes in and out movement assisted with channel proteins. two components of the cell membrane ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.