Cellular Transport - St. John the Baptist Diocesan High School
... The “water-fearing” lipid tails face each other on the inside of the membrane ...
... The “water-fearing” lipid tails face each other on the inside of the membrane ...
CELLS : the Structural and Functional Units of All Life Forms
... Need to match supply with demand and import with export, energy amts and pollution also need to be considered IT is more EFFICIENT to have many, small cells than fewer large cells. ...
... Need to match supply with demand and import with export, energy amts and pollution also need to be considered IT is more EFFICIENT to have many, small cells than fewer large cells. ...
The Function of Organelles
... ATP Most of cell’s ATP made here Animal cells can’t make own food so we need these to break down sugar for energy ...
... ATP Most of cell’s ATP made here Animal cells can’t make own food so we need these to break down sugar for energy ...
Animal Cell Diagram
... These small organelles contain chemicals that break down food particles and worn-out cell parts. ...
... These small organelles contain chemicals that break down food particles and worn-out cell parts. ...
animal cells
... cell membrane - the thin layer of protein and fat that surrounds the cell. The cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing some substances to pass into the cell and blocking others. centrosome - (also called the "microtubule organizing center") a small body located near the nucleus - it has a dense cen ...
... cell membrane - the thin layer of protein and fat that surrounds the cell. The cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing some substances to pass into the cell and blocking others. centrosome - (also called the "microtubule organizing center") a small body located near the nucleus - it has a dense cen ...
Chapter 8: CELL MEMBRANE
... “GLYCO” = carbohydrate, so: *glycoprotein = protein w/ carbo chain *glycolipid = lipid w/ carbo chain ...
... “GLYCO” = carbohydrate, so: *glycoprotein = protein w/ carbo chain *glycolipid = lipid w/ carbo chain ...
Chapter 8: CELL MEMBRANE
... “GLYCO” = carbohydrate, so: *glycoprotein = protein w/ carbo chain *glycolipid = lipid w/ carbo chain ...
... “GLYCO” = carbohydrate, so: *glycoprotein = protein w/ carbo chain *glycolipid = lipid w/ carbo chain ...
Unit A Notes #1 Cell Intro - Mr. Lesiuk
... heads sticking out, with Hydrophobic (water fearing) fatty acid tails sticking in. ...
... heads sticking out, with Hydrophobic (water fearing) fatty acid tails sticking in. ...
organelles - La Paz Wiki
... break down molecules into smaller ones that can be used. • If a lysosome breaks open inside the cell, it dissolves the cell itself! ...
... break down molecules into smaller ones that can be used. • If a lysosome breaks open inside the cell, it dissolves the cell itself! ...
Transport Across Plasma Membrane
... NA or hydrogen ions to move other chemicals b. How does secondary active transport maintain low calcium concentrations in the cytosol and/or absorption of nutrients into cell? In many cells antiporters move calcium out of the cell while sodium flows in. This maintains the low calcium concentration i ...
... NA or hydrogen ions to move other chemicals b. How does secondary active transport maintain low calcium concentrations in the cytosol and/or absorption of nutrients into cell? In many cells antiporters move calcium out of the cell while sodium flows in. This maintains the low calcium concentration i ...
CELL ORGANELLES
... • Transports newly made proteins to other parts of the cell, or even out of the cell • Divides the cytoplasm into reaction areas • As it grows, it pushes out and inward to form the cell / nuclear membrane ...
... • Transports newly made proteins to other parts of the cell, or even out of the cell • Divides the cytoplasm into reaction areas • As it grows, it pushes out and inward to form the cell / nuclear membrane ...
I. CYTOPLASM A. The cytoplasm is thick! B. It contains nucleoid
... 3. Multiple sugar chains are ___________________ by amino acids ...
... 3. Multiple sugar chains are ___________________ by amino acids ...
Group 3
... selectively permeable membrane (high to low concentration) 1 Factor that controls osmosis: concentration gradient-unequal distribution of particles #3: water diffusing across a selectively permeable membrane the number of sugar molecules did not change on each side of the membrane but the number of ...
... selectively permeable membrane (high to low concentration) 1 Factor that controls osmosis: concentration gradient-unequal distribution of particles #3: water diffusing across a selectively permeable membrane the number of sugar molecules did not change on each side of the membrane but the number of ...
Cell Organelles
... Types of Cells Prokaryotic Prokaryotes are very simple cells Probably first to inhabit the earth. Prokaryotic cells do not contain a membrane bound nucleus. Bacteria are prokaryotes. DNA of bacteria is circular. ...
... Types of Cells Prokaryotic Prokaryotes are very simple cells Probably first to inhabit the earth. Prokaryotic cells do not contain a membrane bound nucleus. Bacteria are prokaryotes. DNA of bacteria is circular. ...
Document
... a. It breaks down sugar to produce energy. b. It makes proteins. c. It breaks down toxic materials. d.It stores material used to make ribosomes. 13. The site of cellular respiration is the ______________________. 14. Energy produced in mitochondria is stored in a substance called _______________. CH ...
... a. It breaks down sugar to produce energy. b. It makes proteins. c. It breaks down toxic materials. d.It stores material used to make ribosomes. 13. The site of cellular respiration is the ______________________. 14. Energy produced in mitochondria is stored in a substance called _______________. CH ...
8.3 Cell surface area
... slow, the cell won’t get what it needs fast enough and will be inefficient and could die. ...
... slow, the cell won’t get what it needs fast enough and will be inefficient and could die. ...
Chapter 7 A tour of the Cell
... “sort” proteins into different vesicles Adds and removes monomers of sugar (small subunits) from glycoproteins Dispatches vesicles w/glyco-proteins for shipping (trans side) ...
... “sort” proteins into different vesicles Adds and removes monomers of sugar (small subunits) from glycoproteins Dispatches vesicles w/glyco-proteins for shipping (trans side) ...
Chapter 7 A tour of the Cell
... “sort” proteins into different vesicles Adds and removes monomers of sugar (small subunits) from glycoproteins Dispatches vesicles w/glyco-proteins for shipping (trans side) ...
... “sort” proteins into different vesicles Adds and removes monomers of sugar (small subunits) from glycoproteins Dispatches vesicles w/glyco-proteins for shipping (trans side) ...
HW#17: Diffusion Loops
... transport particles? What would happen to the organism if many of its cells were damaged in this way? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ...
... transport particles? What would happen to the organism if many of its cells were damaged in this way? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ...
Sponge Bob
... • The jellyfish are like the Golgi body because there are organized and they make jelly. ...
... • The jellyfish are like the Golgi body because there are organized and they make jelly. ...
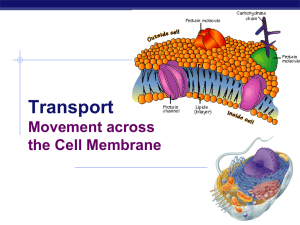
Chapter 8. Movement across the Membrane
... Membrane Proteins Proteins determine most of membrane’s specific functions ...
... Membrane Proteins Proteins determine most of membrane’s specific functions ...
Chapter 5 Problem set
... factor in moving substances across cell membranes and through fluid portions of cytoplasm. When the concentration gradient is steep, diffusion is (choose one) ( ) slower ( ) faster. As the gradient decreases and the number of molecules moving down the gradient decreases, diffusion is (choose one) ( ...
... factor in moving substances across cell membranes and through fluid portions of cytoplasm. When the concentration gradient is steep, diffusion is (choose one) ( ) slower ( ) faster. As the gradient decreases and the number of molecules moving down the gradient decreases, diffusion is (choose one) ( ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.