MEMBRANE PERMEABILITY ! membranes are highly impermeable
... ! when open, forms doughnut-like pore through which solutes flow rapidly by diffusion ! always move from high c to low c (down gradient) ! transport rate # substrate concentration, not saturable ! ΔG !ve, spontaneous, no energy required ! animal cells have many ion channels; highly selective, only l ...
... ! when open, forms doughnut-like pore through which solutes flow rapidly by diffusion ! always move from high c to low c (down gradient) ! transport rate # substrate concentration, not saturable ! ΔG !ve, spontaneous, no energy required ! animal cells have many ion channels; highly selective, only l ...
The fluid mosaic model describes the plasma membrane structure
... twofatty acid molecules attached to carbons 1 and 2, and a phosphate-containing group attached to the third carbon. This arrangement gives the overall molecule an area described as its head (the phosphate-containing group), which has a polar character or negative charge, and an area called the tail ...
... twofatty acid molecules attached to carbons 1 and 2, and a phosphate-containing group attached to the third carbon. This arrangement gives the overall molecule an area described as its head (the phosphate-containing group), which has a polar character or negative charge, and an area called the tail ...
Organelle Matching Worksheet
... Converts sugar to a usable form of energy Modifies (changes) and packages proteins Membranes that act as channels and a transport system in the cell Destroy waste material in the cell Support the cell’s structure and also act as a transport system in the cell Contains the genetic material and acts a ...
... Converts sugar to a usable form of energy Modifies (changes) and packages proteins Membranes that act as channels and a transport system in the cell Destroy waste material in the cell Support the cell’s structure and also act as a transport system in the cell Contains the genetic material and acts a ...
homeostasis and cell transport
... B. Active Transport- the movement of chemical substances, usually across the cell membrane, against a concentration gradient; requires cells to use energy 1. Cell membrane pumps ...
... B. Active Transport- the movement of chemical substances, usually across the cell membrane, against a concentration gradient; requires cells to use energy 1. Cell membrane pumps ...
GCSE activity labelling plant and animal cells
... 1. To label animal and plant cells 2. To compare and contrast animal, plant and fungal cells 3. To understand the concept of a common ancestor ...
... 1. To label animal and plant cells 2. To compare and contrast animal, plant and fungal cells 3. To understand the concept of a common ancestor ...
Cell Organelles and Functions
... Freely permeable to water and most solutes Only in Plant cells Maintains cell turgidity Provide mechanical support Protect from mechanical damage ...
... Freely permeable to water and most solutes Only in Plant cells Maintains cell turgidity Provide mechanical support Protect from mechanical damage ...
Topic - the science teacher
... 1. To label animal and plant cells 2. To compare and contrast animal, plant and fungal cells 3. To understand the concept of a common ancestor ...
... 1. To label animal and plant cells 2. To compare and contrast animal, plant and fungal cells 3. To understand the concept of a common ancestor ...
Unit I File
... (intracellular) and outer (extracellular) surfaces 2. Function a. Selectively permeable barrier: controls what enters and leaves the cell b. Phospholipids are liquid at body temperature, so proteins float around in the membrane -functions as a Fluid Mosaic ...
... (intracellular) and outer (extracellular) surfaces 2. Function a. Selectively permeable barrier: controls what enters and leaves the cell b. Phospholipids are liquid at body temperature, so proteins float around in the membrane -functions as a Fluid Mosaic ...
Chapter 4 and 5 Tests
... only perform properly within a narrow pH range) The Central Vacuole The Fluid Mosaic Model The phospholipid bi-layer Blood Types and Antigens What decides if molecules can pass through the membrane? What is an acid and how do cells control the pH of their internal environment? Which surface proteins ...
... only perform properly within a narrow pH range) The Central Vacuole The Fluid Mosaic Model The phospholipid bi-layer Blood Types and Antigens What decides if molecules can pass through the membrane? What is an acid and how do cells control the pH of their internal environment? Which surface proteins ...
cell functions for chart File
... - Proteins are made at these structures in all cells. - those floating freely in the cytoplasm produce proteins that will stay in the cell. E. - A large fluid-filled organelle - typically store water - Some store enzymes. Some store wastes. Some waste products are toxic and can benefit the plant. ...
... - Proteins are made at these structures in all cells. - those floating freely in the cytoplasm produce proteins that will stay in the cell. E. - A large fluid-filled organelle - typically store water - Some store enzymes. Some store wastes. Some waste products are toxic and can benefit the plant. ...
PowerPoint on the parts of a cell
... thread like material in the nucleus that contain the genetic material and direct the cells functions. ...
... thread like material in the nucleus that contain the genetic material and direct the cells functions. ...
cell
... These are the organelles in plant cells that are the site of photosynthesis. They are composed of on outer boundary membrane and an inner boundary membrane. Within these membranes is an inner compartment called the stroma, Within the stroma are flattened closed sacs called thylakoids. Stacks of thes ...
... These are the organelles in plant cells that are the site of photosynthesis. They are composed of on outer boundary membrane and an inner boundary membrane. Within these membranes is an inner compartment called the stroma, Within the stroma are flattened closed sacs called thylakoids. Stacks of thes ...
Biology I Cells
... protein channels – Cell uses no energy, substances move from high to low concentration (still diffusion) – Used when molecules are polar, charged, or too big ...
... protein channels – Cell uses no energy, substances move from high to low concentration (still diffusion) – Used when molecules are polar, charged, or too big ...
III - Humble ISD
... b. Name refers to presence of ribosomes; Site of secretory protein production (proteins destined for outside the cell) and additional membrane production. Proteins packaged in transport bubbles called vesicles. “Cell postmaster”; Receives transport vesicles from ER; modifies, stores, and ships produ ...
... b. Name refers to presence of ribosomes; Site of secretory protein production (proteins destined for outside the cell) and additional membrane production. Proteins packaged in transport bubbles called vesicles. “Cell postmaster”; Receives transport vesicles from ER; modifies, stores, and ships produ ...
Cell Organelles
... like a pathway between the nuclear membrane and the cell membrane. In both plant and animal cells ...
... like a pathway between the nuclear membrane and the cell membrane. In both plant and animal cells ...
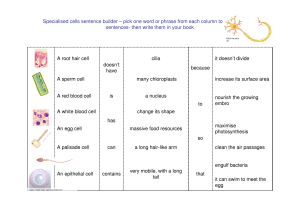
engulf bacteria to change its shape has A white blood cell nourish
... Specialised cells sentence builder – pick one word or phrase from each column to make 7 correct sentences- then write them in your book ...
... Specialised cells sentence builder – pick one word or phrase from each column to make 7 correct sentences- then write them in your book ...
Cell Powerpoint - stephanieccampbell.com
... The Cell Theory 1. Every living organism is made of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function. It is the smallest unit that can perform life functions. 3. All cells arise from preexisting cells. ...
... The Cell Theory 1. Every living organism is made of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function. It is the smallest unit that can perform life functions. 3. All cells arise from preexisting cells. ...
Basic Structure of a Cell
... a. ________________________________________________________________________ b. ________________________________________________________________________ c. ________________________________________________________________________ Discoveries Since the Cell Theory 4. a. In 1970, what did Lynn Margulis ...
... a. ________________________________________________________________________ b. ________________________________________________________________________ c. ________________________________________________________________________ Discoveries Since the Cell Theory 4. a. In 1970, what did Lynn Margulis ...
cell - CSB | SJU Employees Personal Web Sites
... passage of small chemical substances between cells (mostly ions); found in excitable tissues. D. Functions of plasma membrane: functions of proteins found within membrane. 1. Membrane transport. - membrane is selectively permeable. - substances can be transported across either passively or actively. ...
... passage of small chemical substances between cells (mostly ions); found in excitable tissues. D. Functions of plasma membrane: functions of proteins found within membrane. 1. Membrane transport. - membrane is selectively permeable. - substances can be transported across either passively or actively. ...
Chapter 16
... • To know evolution, you must know something about genetics & heritable traits …before that, you need to understand, cellular reproduction, proteins, & DNA …before that, how a cell works, how a protein comes about, what makes up DNA …membranes, organelles …even down to molecules, atoms, etc. ...
... • To know evolution, you must know something about genetics & heritable traits …before that, you need to understand, cellular reproduction, proteins, & DNA …before that, how a cell works, how a protein comes about, what makes up DNA …membranes, organelles …even down to molecules, atoms, etc. ...
Cell Transport Video Recap
... diffusion, (F) facilitated diffusion, or (A) active transport. 8. _____ For water to travel across the cell membrane at a substantial rate, the water molecules travel through protein channels known as aquaporins. 9. _____ While water molecules are polar, they are also very small. One fact not mentio ...
... diffusion, (F) facilitated diffusion, or (A) active transport. 8. _____ For water to travel across the cell membrane at a substantial rate, the water molecules travel through protein channels known as aquaporins. 9. _____ While water molecules are polar, they are also very small. One fact not mentio ...
Homework Questions – Unit 1 – Biochemistry
... The conditions inside every cell must remain nearly constant in order for it to continue to function normally. This steady state inside a cell is called homeostasis. It is important to cells in order for them to function properly and do their jobs. 6. Diffusion allows for the effective movemen ...
... The conditions inside every cell must remain nearly constant in order for it to continue to function normally. This steady state inside a cell is called homeostasis. It is important to cells in order for them to function properly and do their jobs. 6. Diffusion allows for the effective movemen ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.