botany practice test i - answer key-doc
... Which of the following cells are a conspicuous component of the hard shells of nuts and hard coverings of certain types of seeds? These also create the gritty texture associated with certain fruit (i.e., pears). ...
... Which of the following cells are a conspicuous component of the hard shells of nuts and hard coverings of certain types of seeds? These also create the gritty texture associated with certain fruit (i.e., pears). ...
Cell Parts
... • Cell membranes contain specific proteins • Integral proteins are embedded within the bilayer • Peripheral proteins are on the only one side of the bilayer and are not embedded into it ...
... • Cell membranes contain specific proteins • Integral proteins are embedded within the bilayer • Peripheral proteins are on the only one side of the bilayer and are not embedded into it ...
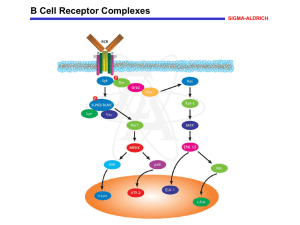
B Cell Receptor Complexes - Sigma
... family are activated initially and phosphorylate CD79 and CD79ß, thereby creating phosphotyrosine motifs that recruit downstream signaling molecules. In particular, phosphorylation of the BCR complex leads to the recruitment and activation of the protein tyrosine kinase Syk, which, in turn, promote ...
... family are activated initially and phosphorylate CD79 and CD79ß, thereby creating phosphotyrosine motifs that recruit downstream signaling molecules. In particular, phosphorylation of the BCR complex leads to the recruitment and activation of the protein tyrosine kinase Syk, which, in turn, promote ...
Cell Theory and Structure
... – are unicellular or multicellular. – have a cytoplasm with various membrane-bound organelles. – contain DNA in a nucleus. – some have flagella or cilia ...
... – are unicellular or multicellular. – have a cytoplasm with various membrane-bound organelles. – contain DNA in a nucleus. – some have flagella or cilia ...
Review Cell Organelle - Catawba County Schools
... These organelles are the cell's power producers. They convert energy into forms that are usable by the cell. They are the sites of cellular respiration which ultimately generates fuel (ATP) for the cell's activities. ATP is mostly sugar and phosphates. The number of these organelles in a cell can r ...
... These organelles are the cell's power producers. They convert energy into forms that are usable by the cell. They are the sites of cellular respiration which ultimately generates fuel (ATP) for the cell's activities. ATP is mostly sugar and phosphates. The number of these organelles in a cell can r ...
ws flip cell parts - Renton School District
... On a separate piece of paper, draw and label a large cell membrane that is approximately the size of the whole sheet. You will be filling it with sketches of organelles so make it big. In the corner of your paper, draw a close-up of section of the membrane showing the ...
... On a separate piece of paper, draw and label a large cell membrane that is approximately the size of the whole sheet. You will be filling it with sketches of organelles so make it big. In the corner of your paper, draw a close-up of section of the membrane showing the ...
cell structure and function
... Which CELL PART provides the energy for active transport? MITOCHONDRIA Which MOLECULE is produced by mitochondria and provides energy for transport? ATP Movement of molecules FROM a region of HIGH concentration TO a region of LOW concentration = DIFFUSION Which MOLECULE is produced by mitochondria a ...
... Which CELL PART provides the energy for active transport? MITOCHONDRIA Which MOLECULE is produced by mitochondria and provides energy for transport? ATP Movement of molecules FROM a region of HIGH concentration TO a region of LOW concentration = DIFFUSION Which MOLECULE is produced by mitochondria a ...
investigation 2
... Cells contain a variety of internal structures called organisms. Organelle is a cell component that performs specific functions for the cells. An entire cell is surrounded by a thin membrane, called cell membrane. Inside the cell are a variety of organelles, which are surrounded by their own membran ...
... Cells contain a variety of internal structures called organisms. Organelle is a cell component that performs specific functions for the cells. An entire cell is surrounded by a thin membrane, called cell membrane. Inside the cell are a variety of organelles, which are surrounded by their own membran ...
Chapter 5 Lecture Notes: Microbial Nutrition
... 3. Passage of compounds through outer membrane occurs via specific and "nonspecific" porins via simple diffusion (therefore, the concentration in the periplasm must be less than that of the external environment – see simple diffusion below) 4. Passage of compounds through sieve-like periplasm withou ...
... 3. Passage of compounds through outer membrane occurs via specific and "nonspecific" porins via simple diffusion (therefore, the concentration in the periplasm must be less than that of the external environment – see simple diffusion below) 4. Passage of compounds through sieve-like periplasm withou ...
Parts of The Eukaryotic Cell 1) Cell Membrane a) Selectively
... Sacs of digestive enzymes that work to clean up old cell parts and cellular wastes g) Cytoskeleton *Skeleton of the Cell* A mesh-like network that shapes the cell and anchors organelles in place h) Nucleus *Brain of the Cell* Directs all cell activities i) Nuclear envelope – *Bouncer of the Nucleus* ...
... Sacs of digestive enzymes that work to clean up old cell parts and cellular wastes g) Cytoskeleton *Skeleton of the Cell* A mesh-like network that shapes the cell and anchors organelles in place h) Nucleus *Brain of the Cell* Directs all cell activities i) Nuclear envelope – *Bouncer of the Nucleus* ...
Simple Bacterial Cell
... outer membrane of lipopolysaccharides outer membrane peptidoglycan plasma membrane ...
... outer membrane of lipopolysaccharides outer membrane peptidoglycan plasma membrane ...
C - Anderson High School
... 7. Circle the letter of the sentence that best explains what osmosis is. A. Osmosis is the movement of water across a membrane from where it is in high amounts to low amounts. B. Osmosis is the movement of water across a membrane from where it is in low amounts to high amounts. C. Osmosis is the mov ...
... 7. Circle the letter of the sentence that best explains what osmosis is. A. Osmosis is the movement of water across a membrane from where it is in high amounts to low amounts. B. Osmosis is the movement of water across a membrane from where it is in low amounts to high amounts. C. Osmosis is the mov ...
Cancer cells have characteristic shapes that are easily distinguished
... such as clathrin coated pit, caveolae, filopodia, lamellipodia, and podosomes. These mesoscale membrane structures are described as the assembly of tens to hundreds of proteins and thousands of lipids but have not been described enough. 2. Research objectives ...
... such as clathrin coated pit, caveolae, filopodia, lamellipodia, and podosomes. These mesoscale membrane structures are described as the assembly of tens to hundreds of proteins and thousands of lipids but have not been described enough. 2. Research objectives ...
Cells
... Small bodies that receive instructions from the nucleus to make proteins. They are found throughout the cytoplasm or attached to rough E.R. Proteins are widely used in cells to serve diverse functions. Some proteins provide the structural support for cells while others act as enzymes to catalyze bio ...
... Small bodies that receive instructions from the nucleus to make proteins. They are found throughout the cytoplasm or attached to rough E.R. Proteins are widely used in cells to serve diverse functions. Some proteins provide the structural support for cells while others act as enzymes to catalyze bio ...
Thursday, February 18, 2010
... compare and contrast the structure and function of different types of prokaryotes, eukaryotes, and viruses (e.g., compare and contrast genetic material, metabolism, organelles, and other cell parts) A Background to Cell Structure ...
... compare and contrast the structure and function of different types of prokaryotes, eukaryotes, and viruses (e.g., compare and contrast genetic material, metabolism, organelles, and other cell parts) A Background to Cell Structure ...
Cell Wall - Qld Science Teachers
... Mitochondria have a double membrane – the outer membrane around the entire mitochondrion, and the inner membrane folded back and forth for large surface area for chemical reactions It is thought that mitochondria in eukaryotic cells may have evolved from ancient symbiotic prokaryotic bacteria th ...
... Mitochondria have a double membrane – the outer membrane around the entire mitochondrion, and the inner membrane folded back and forth for large surface area for chemical reactions It is thought that mitochondria in eukaryotic cells may have evolved from ancient symbiotic prokaryotic bacteria th ...
Questions to answer
... 1. How does the second law of thermodynamics allow for diffusion of substances? 2. Explain the major difference between simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion. 3. How is active transport possible, since it contradicts the tendencies of the second law of thermodynamics? 4. Where does the energy t ...
... 1. How does the second law of thermodynamics allow for diffusion of substances? 2. Explain the major difference between simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion. 3. How is active transport possible, since it contradicts the tendencies of the second law of thermodynamics? 4. Where does the energy t ...
Biology and you - properties of life and the scientific method
... 1.All organisms are composed of one or more cells 2.Cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells Cell Basics: 1. Structure must compliment the function. 2. Cells varies widely because they are capable of doing many things. 3. Size plays ...
... 1.All organisms are composed of one or more cells 2.Cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells Cell Basics: 1. Structure must compliment the function. 2. Cells varies widely because they are capable of doing many things. 3. Size plays ...
cells - tjwscience
... 1. Have a nucleus with a nuclear envelope 2. Bigger and more complex than prokaryotes 3. Have membrane bound organelles (Golgi, ER, lysosomes, etc.) 4. DNA – forms chromosomes (highly organized) 5. Can be uni- OR multicellular organisms 6. Ex: animals, plants, fungi ...
... 1. Have a nucleus with a nuclear envelope 2. Bigger and more complex than prokaryotes 3. Have membrane bound organelles (Golgi, ER, lysosomes, etc.) 4. DNA – forms chromosomes (highly organized) 5. Can be uni- OR multicellular organisms 6. Ex: animals, plants, fungi ...
AP BIOLOGY Chapter 4 Cell Structure and Function Early Scientist
... Cells must remain small in size due to the ratio of ____________________ and __________________. As the cell increases in size, its surface area becomes too small to ____________________its internal structures._____________________ and other important substances cannot diffuse fast enough. Cells tha ...
... Cells must remain small in size due to the ratio of ____________________ and __________________. As the cell increases in size, its surface area becomes too small to ____________________its internal structures._____________________ and other important substances cannot diffuse fast enough. Cells tha ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.