Slide 1
... Cells and Organelles Cells are the basic “living” unit in an organism that has • structure • function • organization Organelles are the parts within a cell that work together for the cell to function. • Made up of molecules ...
... Cells and Organelles Cells are the basic “living” unit in an organism that has • structure • function • organization Organelles are the parts within a cell that work together for the cell to function. • Made up of molecules ...
PowerPoint
... Plasma (Cell) Membrane • Holds cell together • regulates the movement of materials into and out of the cell • Cell membrane is made up of proteins and a double layer of lipid (fat) molecules. • Border/City Wall ...
... Plasma (Cell) Membrane • Holds cell together • regulates the movement of materials into and out of the cell • Cell membrane is made up of proteins and a double layer of lipid (fat) molecules. • Border/City Wall ...
Cell Transport - Elmwood Park Memorial High School
... • In some cases- cells must move materials from an area of lower concentration to an area of high concentration. • up the concentration gradient • This type of transport requires the cell to expend energy • The energy needed is supplied directly or indirectly by ATP ...
... • In some cases- cells must move materials from an area of lower concentration to an area of high concentration. • up the concentration gradient • This type of transport requires the cell to expend energy • The energy needed is supplied directly or indirectly by ATP ...
ppt - Faculty
... • Larger more complex cells that make up most familiar life forms: plants, animals, fungi, algae • Surrounded by a cell membrane made of lipids • Text pg 60-61 ...
... • Larger more complex cells that make up most familiar life forms: plants, animals, fungi, algae • Surrounded by a cell membrane made of lipids • Text pg 60-61 ...
L2_Tour of the Cell_Fa08
... Complex of proteins & rRNA Function: Protein synthesis • Ribosome parts are made in nucleus by nucleolus • Parts travel out of nucleus, into cytoplasm Two types: • Bound ribosome – Bound to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) – Make proteins for membranes or exportation from cell ...
... Complex of proteins & rRNA Function: Protein synthesis • Ribosome parts are made in nucleus by nucleolus • Parts travel out of nucleus, into cytoplasm Two types: • Bound ribosome – Bound to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) – Make proteins for membranes or exportation from cell ...
1. Which statement is not true of cells and cell size? a) Large cells
... They are less complex than eukaryotic cells. b) They lack a true nucleus. c) In addition to the chromosome they often have additional loops of DNA called plasmids. d) Photosynthetic bacteria may have sheets of internal plasma membranes. e) They tend to be as large as eukaryotic cells, 100um is a typ ...
... They are less complex than eukaryotic cells. b) They lack a true nucleus. c) In addition to the chromosome they often have additional loops of DNA called plasmids. d) Photosynthetic bacteria may have sheets of internal plasma membranes. e) They tend to be as large as eukaryotic cells, 100um is a typ ...
Cell Wall (Plants Only) Chloroplasts (Plants Only)
... share many of the same structures. Some of the structures may look slightly different (for example, the size of the vacuole may differ), or they may not be as obvious (for example, the cell membrane in plant cells is often hidden by the cell wall). ...
... share many of the same structures. Some of the structures may look slightly different (for example, the size of the vacuole may differ), or they may not be as obvious (for example, the cell membrane in plant cells is often hidden by the cell wall). ...
Chapter 7 Cells - Beachwood City Schools
... cytoplasm. Site for protein synthesis (where proteins are made). b. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER): internal membrane system; site for lipid and protein synthesis. i. Rough ER: has ribosomes on its surface; the part of the ER involved in protein synthesis. ii. Smooth ER: does not have ribosomes on its s ...
... cytoplasm. Site for protein synthesis (where proteins are made). b. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER): internal membrane system; site for lipid and protein synthesis. i. Rough ER: has ribosomes on its surface; the part of the ER involved in protein synthesis. ii. Smooth ER: does not have ribosomes on its s ...
Cells and their organelles powerpoint
... Vacuole – Very large in plants – filled with aqueous solution of ions. Storage, waste disposal, growth. ...
... Vacuole – Very large in plants – filled with aqueous solution of ions. Storage, waste disposal, growth. ...
Cells - Cobb Learning
... 11. How does a plant or animal cell differ from a bacterial cell? 12. What organelles that are found in plant and animal cells are also found in bacteria cells?? 13. The cells in many-celled organisms look the same, have the same structure, or are quite different from one another?…..pick one! 14. Wh ...
... 11. How does a plant or animal cell differ from a bacterial cell? 12. What organelles that are found in plant and animal cells are also found in bacteria cells?? 13. The cells in many-celled organisms look the same, have the same structure, or are quite different from one another?…..pick one! 14. Wh ...
C8-Cellular Transport
... of water across a selectively permeable membrane Passive Transport Active Transport ...
... of water across a selectively permeable membrane Passive Transport Active Transport ...
CLASSIFYING LIVING THINGS
... Cell membrane - protects the cell , controls what comes in and out of the cell Nucleus - directs cell activities(BRAIN) ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum)- sends messages(HIGHWAY)/where some ribosomes are found Golgi Body – packages proteins to be delivered around the cell(mailmen) Ribosome - makes ...
... Cell membrane - protects the cell , controls what comes in and out of the cell Nucleus - directs cell activities(BRAIN) ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum)- sends messages(HIGHWAY)/where some ribosomes are found Golgi Body – packages proteins to be delivered around the cell(mailmen) Ribosome - makes ...
Chapter 4: Tour of the Cell
... Ribosomes move through the pores of the nucleus then are responsible for protein synthesis. Some are associated with “rough” ER others remain suspended in the cytosol. ...
... Ribosomes move through the pores of the nucleus then are responsible for protein synthesis. Some are associated with “rough” ER others remain suspended in the cytosol. ...
cell powerpoint
... Long protein strands found in the cell Provide support for the cell Help to maintain the shape of a cell Help in the movement of chromosomes when the cell divides Vital to the survival of the cell, if these proteins die the cell will loose it’s shape and die as well ...
... Long protein strands found in the cell Provide support for the cell Help to maintain the shape of a cell Help in the movement of chromosomes when the cell divides Vital to the survival of the cell, if these proteins die the cell will loose it’s shape and die as well ...
CSM 101 Fall 2010 Timeline
... Dephosphorylation returns the molecule to its inactive form. 2. Describe at least three ways in which membrane proteins can help substances cross a cell membrane. Ion channels: they form pores, or openings, ions move through theses openings in a predictable direction, from high concentration to lo ...
... Dephosphorylation returns the molecule to its inactive form. 2. Describe at least three ways in which membrane proteins can help substances cross a cell membrane. Ion channels: they form pores, or openings, ions move through theses openings in a predictable direction, from high concentration to lo ...
cell transport
... •PROBLEM: Some needed substances are needed in HIGHER concentration inside the cell. •This means that after equilibrium is reached, these substances must move AGAINST their CONCENTRATION GRADIENT and move from an area of LOW concentration to HIGH concentration SOLUTION: Pumps Active Transport ...
... •PROBLEM: Some needed substances are needed in HIGHER concentration inside the cell. •This means that after equilibrium is reached, these substances must move AGAINST their CONCENTRATION GRADIENT and move from an area of LOW concentration to HIGH concentration SOLUTION: Pumps Active Transport ...
lecture notes endomembrane system 4
... trans compartment and the TGN. 13. Because the oligosaccharide chains are added/modified on the luminal side of the ER and the GA, the distribution of carbohydrate on membrane proteins and lipids is asymmetric. That is within the cell the carbohydrates are on the lumen side, and those on the plasma ...
... trans compartment and the TGN. 13. Because the oligosaccharide chains are added/modified on the luminal side of the ER and the GA, the distribution of carbohydrate on membrane proteins and lipids is asymmetric. That is within the cell the carbohydrates are on the lumen side, and those on the plasma ...
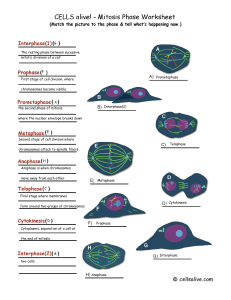
1.2 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis
... 6. A cell dies as a normal part of the functioning of healthy multicellular organisms. This regulated, or controlled, cell death is known as _____. 7. During _____, sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes and move to opposite poles. 9. In animal cells, a pair of organelles called ____ ...
... 6. A cell dies as a normal part of the functioning of healthy multicellular organisms. This regulated, or controlled, cell death is known as _____. 7. During _____, sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes and move to opposite poles. 9. In animal cells, a pair of organelles called ____ ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.