
02 Cell Notes
... Organelles – like organs in your body, these small parts of the cell do all the jobs for the cell ...
... Organelles – like organs in your body, these small parts of the cell do all the jobs for the cell ...
cells internet activity answers
... 1. What is the function of lysosomes? Lysosomes contain chemicals (enzymes) that digest wastes and worn-out cell parts. These chemicals also break down food. CELL WALL: 1. What does the cell wall do for the cell? The cell wall supports and protects the cell. 2. Where is the cell wall found? The cell ...
... 1. What is the function of lysosomes? Lysosomes contain chemicals (enzymes) that digest wastes and worn-out cell parts. These chemicals also break down food. CELL WALL: 1. What does the cell wall do for the cell? The cell wall supports and protects the cell. 2. Where is the cell wall found? The cell ...
Cell City Analogy – Let`s Practice Writing Analogies!
... hall has the instructions for widget making, widgets come in all shapes and sizes and any citizen of Grant can get the instructions and begin making their own widgets. Widgets are generally produced in small shops around the city, these small shops can be built by the carpenters union (whose headqua ...
... hall has the instructions for widget making, widgets come in all shapes and sizes and any citizen of Grant can get the instructions and begin making their own widgets. Widgets are generally produced in small shops around the city, these small shops can be built by the carpenters union (whose headqua ...
Archaea
... •Eukaryotes are more structurally and func7onally complex •Eukaryotes have a membrane –bound nucleus •Eukaryotes have a diverse collec7on of organelles •Replica7on is more complex –mitosis and meoisis •Eukaryotes carry out complex processes such as enodcytosis, amoeboid movement etc. ...
... •Eukaryotes are more structurally and func7onally complex •Eukaryotes have a membrane –bound nucleus •Eukaryotes have a diverse collec7on of organelles •Replica7on is more complex –mitosis and meoisis •Eukaryotes carry out complex processes such as enodcytosis, amoeboid movement etc. ...
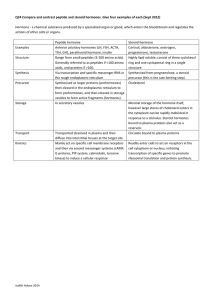
Q24 Compare and contrast peptide and steroid hormones. Give four
... then cleaved in the endoplasmic reticulum to form prohormones, and then cleaved in storage vesicles to form active fragments (hormones) Storage In secretory vesicles Minimal storage of the hormone itself, ...
... then cleaved in the endoplasmic reticulum to form prohormones, and then cleaved in storage vesicles to form active fragments (hormones) Storage In secretory vesicles Minimal storage of the hormone itself, ...
Absorption and Secretion
... • One end of a phospholipid molecule is hydrophilic (water loving), this is called the tail. The other end is hydrophobic (water hating), this is called the head. • The hydrophillic heads are water soluble and make up the 2 outer surfaces, where they form bonds with hydrogen molecules. • The hydroph ...
... • One end of a phospholipid molecule is hydrophilic (water loving), this is called the tail. The other end is hydrophobic (water hating), this is called the head. • The hydrophillic heads are water soluble and make up the 2 outer surfaces, where they form bonds with hydrogen molecules. • The hydroph ...
Standard B-2
... The cell membrane regulates the passage of materials into and out of the cell. A cell membrane is semipermeable (selectively permeable), meaning that some substances can pass directly through the cell membrane while other substances can not. Materials can enter or exit through the cell membrane by p ...
... The cell membrane regulates the passage of materials into and out of the cell. A cell membrane is semipermeable (selectively permeable), meaning that some substances can pass directly through the cell membrane while other substances can not. Materials can enter or exit through the cell membrane by p ...
SBI 3CI
... It is rough or smooth& transports material through tubes thast are connected together in the cytoplasm It has tubes that are NOT connected together in the cytoplasm and it packages material like protein to be excreted from the cell. They’re vacuoles with digestive enzymes & found only in animal cell ...
... It is rough or smooth& transports material through tubes thast are connected together in the cytoplasm It has tubes that are NOT connected together in the cytoplasm and it packages material like protein to be excreted from the cell. They’re vacuoles with digestive enzymes & found only in animal cell ...
AntimicrobialCopper[1]
... After punching holes, how do copper ions further damage the cell? Now that the cells main defense (its outer envelope) has been breached, there is an unopposed stream of copper ions entering the cell. This puts several vital processes inside the cell in danger. Copper literally overwhelms the insid ...
... After punching holes, how do copper ions further damage the cell? Now that the cells main defense (its outer envelope) has been breached, there is an unopposed stream of copper ions entering the cell. This puts several vital processes inside the cell in danger. Copper literally overwhelms the insid ...
Sample presentation slides (Green and gold texture design)
... from its surroundings and also determine what comes in and what goes out. How can a cell separate itself from its environment and still allow material to enter and leave? ...
... from its surroundings and also determine what comes in and what goes out. How can a cell separate itself from its environment and still allow material to enter and leave? ...
Cell similes
... of the cell. It is crucial that they know this in order for your team of microbiologists to do their job. In order to teach your team you decide the quickest and easiest way for them to understand all the organelles/parts is to create “cell similes.” A simile is a good way to compare things using th ...
... of the cell. It is crucial that they know this in order for your team of microbiologists to do their job. In order to teach your team you decide the quickest and easiest way for them to understand all the organelles/parts is to create “cell similes.” A simile is a good way to compare things using th ...
Transport through the cell membrane
... excess sodium outside the cell cause sodium to diffuse to the inside the cell. this diffusion of sodium can pull other substances with the sodium through the cell membrane. This is called co-transport. The carrier in this instance has as an attachment site for both the sodium ion and the substance. ...
... excess sodium outside the cell cause sodium to diffuse to the inside the cell. this diffusion of sodium can pull other substances with the sodium through the cell membrane. This is called co-transport. The carrier in this instance has as an attachment site for both the sodium ion and the substance. ...
Week 3 Agenda and Notes
... Animal cell v Plant cell Plant cell: cell wall (gives support and shape); Green plants contain chloroplasts (are the organelles responsible for photosynthesis) Central Vacuole Animal Cell ...
... Animal cell v Plant cell Plant cell: cell wall (gives support and shape); Green plants contain chloroplasts (are the organelles responsible for photosynthesis) Central Vacuole Animal Cell ...
Organization and Structure of Cells
... communication, also provides a protective layer cell (plasma) membrane – roughly 50:50% lipid:protein ratio; selectively permeable membrane; contains various systems for influx of extracellular molecules (pumps, channels, transporters); important proteins are located here nucleus – separated from th ...
... communication, also provides a protective layer cell (plasma) membrane – roughly 50:50% lipid:protein ratio; selectively permeable membrane; contains various systems for influx of extracellular molecules (pumps, channels, transporters); important proteins are located here nucleus – separated from th ...
87881e9f4bc5cca
... The gap junction channel is much less selective than the potassium channel. It forms a tube, 1.5 nm in diameter, through which any solute of Mr ≤ 1000 can pass. The gap junction channel is not always open. It opens only when it connects with a second gap junction channel on another cell, forming a t ...
... The gap junction channel is much less selective than the potassium channel. It forms a tube, 1.5 nm in diameter, through which any solute of Mr ≤ 1000 can pass. The gap junction channel is not always open. It opens only when it connects with a second gap junction channel on another cell, forming a t ...
Cells - Krum ISD
... Match the cell part to the job is does: A. Controls the cell B. Outer protective layer in plants and prokaryotes ...
... Match the cell part to the job is does: A. Controls the cell B. Outer protective layer in plants and prokaryotes ...
7-2 and 7-3 worksheet key
... What is the function of active transport in moving small molecules and ions across cell membranes? Give an example. ...
... What is the function of active transport in moving small molecules and ions across cell membranes? Give an example. ...
Curriculum - Rivers2Lake
... the other complete a plant cell (green rope) with the matching red and green cards for animal cell parts and plant cell parts, respectively. Please note to students not to destroy other living things to make their cell (no ripping tree branches off, etc.). Also, encourage them to be creative and rea ...
... the other complete a plant cell (green rope) with the matching red and green cards for animal cell parts and plant cell parts, respectively. Please note to students not to destroy other living things to make their cell (no ripping tree branches off, etc.). Also, encourage them to be creative and rea ...
cells
... cytoplasm, & dozens of other specialized structures that perform special functions (organelles) • Some are single celled organisms, but most make up multicellular organisms • All plants, animals, fungi, and many microorganisms are eukaryotes ...
... cytoplasm, & dozens of other specialized structures that perform special functions (organelles) • Some are single celled organisms, but most make up multicellular organisms • All plants, animals, fungi, and many microorganisms are eukaryotes ...
NOT animal cells.
... Chloroplasts are where PHOTOSYNTHESIS occurs. • Contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that traps the energy from light. • Found in plant cells and some protists, NOT found in animal cells. ...
... Chloroplasts are where PHOTOSYNTHESIS occurs. • Contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that traps the energy from light. • Found in plant cells and some protists, NOT found in animal cells. ...
Cellular Structures Test Study Guide
... 17. The above diagram shows the process of osmosis. Only the water molecules could enter the cell because water molecules are ________________ than the protein molecules. 18. A plant’s green color is due to the presence of which organelle?_____________________ 19. One advantage of electron microscop ...
... 17. The above diagram shows the process of osmosis. Only the water molecules could enter the cell because water molecules are ________________ than the protein molecules. 18. A plant’s green color is due to the presence of which organelle?_____________________ 19. One advantage of electron microscop ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.









![AntimicrobialCopper[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006183415_1-46f42e14087e0060861546e4331c0742-300x300.png)












