This exam is worth 50 points Evolutionary Biology You may take this
... adenine in the DNA strand there will be guanine; addition, for example, when a base like thymine is simply spliced into the DNA strand lengthening it by one base; or a deletion (subtraction), say when a base such as cytosine is lost from the DNA molecule shortening it by one base. Why are additions ...
... adenine in the DNA strand there will be guanine; addition, for example, when a base like thymine is simply spliced into the DNA strand lengthening it by one base; or a deletion (subtraction), say when a base such as cytosine is lost from the DNA molecule shortening it by one base. Why are additions ...
Objectives • Explain the "one gene–one polypeptide" hypothesis
... a signal to "start" translating an RNA transcript. There are also three "stop" codons that do not code for amino acids, but signal the end of each genetic message. This same genetic coding system is shared by almost all organisms. In experiments, genes can be transcribed and translated after being t ...
... a signal to "start" translating an RNA transcript. There are also three "stop" codons that do not code for amino acids, but signal the end of each genetic message. This same genetic coding system is shared by almost all organisms. In experiments, genes can be transcribed and translated after being t ...
ch 20 study guide: dna technology
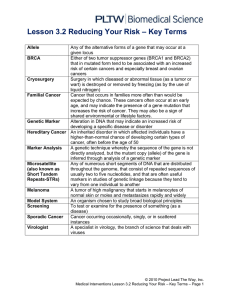
... Poly - = many; morph - = form (Single nucleotide polymorphisms: one-base-pair variations in the genome sequence) ...
... Poly - = many; morph - = form (Single nucleotide polymorphisms: one-base-pair variations in the genome sequence) ...
DNA Notes How was the DNA Model Formed? 1) In the 1950`s a
... One of the unique characteristics of DNA is that it can copy itself using one of the strands as a template. DNA can replicate and match base pairs to make complementary strands EX: Strand 1: A T C C G T A G C Strand 2 ...
... One of the unique characteristics of DNA is that it can copy itself using one of the strands as a template. DNA can replicate and match base pairs to make complementary strands EX: Strand 1: A T C C G T A G C Strand 2 ...
Threading-based Protein Structure Prediction
... • Two types of organisms – Prokaryotes (single-celled organisms with no nuclei. e.g., bacteria) – Eukaryotes (organisms with single or multiple cells. their cells have nuclei. e.g., plant & animal) ...
... • Two types of organisms – Prokaryotes (single-celled organisms with no nuclei. e.g., bacteria) – Eukaryotes (organisms with single or multiple cells. their cells have nuclei. e.g., plant & animal) ...
Document
... Q2. (8pts) Sanger sequencing is a rather simple technique. 1. It takes advantage of inhibiting replication with _____________________________. 2. And the coupling of what to the above answer? ________________________. 3. Finally, fragments are run on a size fractionation matrix. Are those fragments ...
... Q2. (8pts) Sanger sequencing is a rather simple technique. 1. It takes advantage of inhibiting replication with _____________________________. 2. And the coupling of what to the above answer? ________________________. 3. Finally, fragments are run on a size fractionation matrix. Are those fragments ...
... The final isolates were plated on spermidine-containing medium as a test for the persistence of parental nuclei among the conidial population. Fourteen of the 26 cultures retained spe-1 nuclei. This outcome was not wholly surprising, because selection on minimal medium is for prototrophic conidial c ...
the element makes na RNA copy of itself which is reversed
... • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on complementary base pairing. ...
... • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on complementary base pairing. ...
Gene Section FAM123B (family with sequence similarity 123B) in Oncology and Haematology
... residues 280-368; APCBD2, 380-531; and APCBD3, 717-834) that mediate its interaction with the armadillo (ARM) repeats of the tumor suppressor APC, as well as a beta-catenin binding site (located between residue 367 and the C-terminus), an acidic domain (residues 370-411), two coiled-coil domains (re ...
... residues 280-368; APCBD2, 380-531; and APCBD3, 717-834) that mediate its interaction with the armadillo (ARM) repeats of the tumor suppressor APC, as well as a beta-catenin binding site (located between residue 367 and the C-terminus), an acidic domain (residues 370-411), two coiled-coil domains (re ...
Lecture #7 Date ______ - Phillips Scientific Methods
... 2) How does the DNA and amino acid sequences differ from a person with sickle cell anemia and a person with normal hemoglobin in their RBC’s? 3) When mRNA is “processed” what is taken out (spliced)? 4) How many sites are present in the ribosome? Name the enzyme that is used to attach an amino acid t ...
... 2) How does the DNA and amino acid sequences differ from a person with sickle cell anemia and a person with normal hemoglobin in their RBC’s? 3) When mRNA is “processed” what is taken out (spliced)? 4) How many sites are present in the ribosome? Name the enzyme that is used to attach an amino acid t ...
Walk the Dogma - Nutley Public Schools
... information is copied from DNA to RNA • DNA double-strand “unzips” • RNA polymerase (an enzyme) binds to a specific region on DNA called a promoter • RNA polymerase travels along the gene, creating a chain of mRNA that is complementary to the strand of DNA • RNA polymerase reaches the termination si ...
... information is copied from DNA to RNA • DNA double-strand “unzips” • RNA polymerase (an enzyme) binds to a specific region on DNA called a promoter • RNA polymerase travels along the gene, creating a chain of mRNA that is complementary to the strand of DNA • RNA polymerase reaches the termination si ...
Document
... 51. What is the cell cycle? 52. What are the two major phases of the cell cycle? What happens in each of these phases? 53. What is cytokinesis? 54. What is apoptosis? Why would a cell perform apoptosis? 55. What is a chromosome? 56. What is a histone? 57. Why do your cells make chromosomes from chro ...
... 51. What is the cell cycle? 52. What are the two major phases of the cell cycle? What happens in each of these phases? 53. What is cytokinesis? 54. What is apoptosis? Why would a cell perform apoptosis? 55. What is a chromosome? 56. What is a histone? 57. Why do your cells make chromosomes from chro ...
Part VI - OCCC.edu
... that A in triplet #143, and reorder the remaining bases downstream as triplets, three at a time, without that A. The new DNA would then read: ...
... that A in triplet #143, and reorder the remaining bases downstream as triplets, three at a time, without that A. The new DNA would then read: ...
... dna replication is necessary for the transmission of genetic information and thus such a process must achieve accurate copying of the genome. Since the last century the replicon model has been proposed in order to explain the general mechanism of genome duplication in bacteria. Later work in yeast l ...
Genetics and Protein Synthesis
... Gene - a unit of inheritance that usually is directly responsible for one trait or character. Allele - an alternate form of a gene. Usually there are two alleles for every gene, sometimes as many a three or four. Homozygous - when the two alleles are the same. Heterozygous - when the two alleles are ...
... Gene - a unit of inheritance that usually is directly responsible for one trait or character. Allele - an alternate form of a gene. Usually there are two alleles for every gene, sometimes as many a three or four. Homozygous - when the two alleles are the same. Heterozygous - when the two alleles are ...
Test 3
... Indicate where the CRP protein binds within this operon. When it is bound to this site, does the CRP protein have a positive or negative effect on gene expression in this system? Start with a figure like 28-7a with the addition of a CRP site just upstream from the promoter site. When the CRP protein ...
... Indicate where the CRP protein binds within this operon. When it is bound to this site, does the CRP protein have a positive or negative effect on gene expression in this system? Start with a figure like 28-7a with the addition of a CRP site just upstream from the promoter site. When the CRP protein ...
File
... f. If the first cytosine nucleotide was deleted from the sequence of DNA above, how would the amino acid sequence be affected? What would be the new sequence of amino acids? What is this type of mutation called? ...
... f. If the first cytosine nucleotide was deleted from the sequence of DNA above, how would the amino acid sequence be affected? What would be the new sequence of amino acids? What is this type of mutation called? ...
Genetics Webquest Worksheet
... 16. In humans, how many chromosomes does each parent pass on to their offspring? ...
... 16. In humans, how many chromosomes does each parent pass on to their offspring? ...
Make an Alien Lab
... Genes determine what characteristics an organism will have. Genes are segments of DNA molecules that are the instructions for building the proteins of the cell. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in the proteins. In a process called transcription, which takes p ...
... Genes determine what characteristics an organism will have. Genes are segments of DNA molecules that are the instructions for building the proteins of the cell. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in the proteins. In a process called transcription, which takes p ...
Nucleic Acid Notes
... • Since shape is determined by amino acid sequence; changing sequence changes 3D shape • EX: Sickle cell anemia mutation changes one amino acid in the sequence (glu → ala) Abnormal hemoglobin molecules crystallize; cause blood cells to become sickle shaped ...
... • Since shape is determined by amino acid sequence; changing sequence changes 3D shape • EX: Sickle cell anemia mutation changes one amino acid in the sequence (glu → ala) Abnormal hemoglobin molecules crystallize; cause blood cells to become sickle shaped ...
Unit 6: Mendelian Genetics
... 2 copies of allele = death at early age 1 copy of allele = brain cells produce only ½ the enzyme in it's proper form (other ½ is mutated form) ...
... 2 copies of allele = death at early age 1 copy of allele = brain cells produce only ½ the enzyme in it's proper form (other ½ is mutated form) ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.