Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false
... 1. A trait is a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another. _________________________ ...
... 1. A trait is a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another. _________________________ ...
SOLVING REAL WORLD PROBLEMS-
... INVERSION- chromosome piece attaches to original chromosome in reverse orientation ...
... INVERSION- chromosome piece attaches to original chromosome in reverse orientation ...
Unit 5 Vocabulary List 2 Sexual reproduction
... Sexual reproduction- reproduction by an egg cell and a sperm cell uniting to form a single cell; an entirely new organism which is genetically different from the parent organism. Fertilization- the uniting of the sperm cell and egg cell. Genes- pieces of DNA that carry all the information passed fro ...
... Sexual reproduction- reproduction by an egg cell and a sperm cell uniting to form a single cell; an entirely new organism which is genetically different from the parent organism. Fertilization- the uniting of the sperm cell and egg cell. Genes- pieces of DNA that carry all the information passed fro ...
File
... • Bacterial genomes are larger than viral genomes, but much smaller than a typical eukaryotic genome • Most DNA in a bacterium is found in a single circular chromosome that is composed of double-stranded DNA found in the nucleiod region. ...
... • Bacterial genomes are larger than viral genomes, but much smaller than a typical eukaryotic genome • Most DNA in a bacterium is found in a single circular chromosome that is composed of double-stranded DNA found in the nucleiod region. ...
Gene Section GSDMA (gasdermin A) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... apoptosis induction in pit cells of the gastric epithelium. Signaling from TGF-beta receptor up-regulates LMO1, a transcription factor. LMO1 binds to the promoter of GSDMA gene and enhances its expression, that results in the apoptosis induction in the pit cells. ...
... apoptosis induction in pit cells of the gastric epithelium. Signaling from TGF-beta receptor up-regulates LMO1, a transcription factor. LMO1 binds to the promoter of GSDMA gene and enhances its expression, that results in the apoptosis induction in the pit cells. ...
Basic Bioinformatics Laboratory
... acid sequence of each organism (in a one letter code – for interpretation of the code go to http://wwwchem.csustan.edu/chem4400/code.htm 5. Choose one of the comparisons (with at least five organisms) and using the human as a base, count the number of amino acid differences for the other organisms. ...
... acid sequence of each organism (in a one letter code – for interpretation of the code go to http://wwwchem.csustan.edu/chem4400/code.htm 5. Choose one of the comparisons (with at least five organisms) and using the human as a base, count the number of amino acid differences for the other organisms. ...
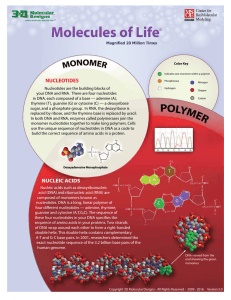
Nucleic Acids Placemat
... Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA specifies the ...
... Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA specifies the ...
Epigenetics
... DNA wrapped around histones with methyl (green) and acetyl (red) groups controlling how tightly they are wrapped ...
... DNA wrapped around histones with methyl (green) and acetyl (red) groups controlling how tightly they are wrapped ...
Learning Targets
... different base sequences and is “read” in groups of three (codons). What is a codon, and what does it code for? 10. Using a model (create one), explain the steps of DNA replication in cells and hereditary coding. 11. What are the roles of the DNA, mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, and ribosomes in protein synthesis ...
... different base sequences and is “read” in groups of three (codons). What is a codon, and what does it code for? 10. Using a model (create one), explain the steps of DNA replication in cells and hereditary coding. 11. What are the roles of the DNA, mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, and ribosomes in protein synthesis ...
Bonding is more than attraction
... - It is a long chain of smaller molecules called nucleotides. • What is a nucleotide? - A nucleotide has three parts: a sugar, a base, and a phosphate group, which contains phosphorus and oxygen atoms. ...
... - It is a long chain of smaller molecules called nucleotides. • What is a nucleotide? - A nucleotide has three parts: a sugar, a base, and a phosphate group, which contains phosphorus and oxygen atoms. ...
Biobowl 3
... 23. Meselson and Stahl’s use of the isotope ______ showed that DNA __________ 24. Chargaff showed that ______ equals ______ in the DNA of many organisms. 25. The experiments of Hershey and Chase used the isotope ______ to demonstrate that ________ (a molecule) entered E. coli and was therefore the g ...
... 23. Meselson and Stahl’s use of the isotope ______ showed that DNA __________ 24. Chargaff showed that ______ equals ______ in the DNA of many organisms. 25. The experiments of Hershey and Chase used the isotope ______ to demonstrate that ________ (a molecule) entered E. coli and was therefore the g ...
rss_genetics_lesson
... • 3 types: • messenger RNA: mRNA carries the DNA nucleotide sequence for a protein from the nucleus to the ribosome • transfer RNA: tRNA transports amino acids (building blocks of proteins) to the ribosome • ribosomal RNA: rRNA makes up the structure of the ribosome ...
... • 3 types: • messenger RNA: mRNA carries the DNA nucleotide sequence for a protein from the nucleus to the ribosome • transfer RNA: tRNA transports amino acids (building blocks of proteins) to the ribosome • ribosomal RNA: rRNA makes up the structure of the ribosome ...
Protein Synthesis: Part I: Transcription
... RNA polymerase uses one strand of the DNA as a template and complimentary RNA nucleotides are assembled into single stranded mRNA ...
... RNA polymerase uses one strand of the DNA as a template and complimentary RNA nucleotides are assembled into single stranded mRNA ...
How does genetic variation lead to evolution?
... Pg. 1: The Results of Genetic Variation 12. Identify the three types of variation (changes) within a species that can lead to evolution? ...
... Pg. 1: The Results of Genetic Variation 12. Identify the three types of variation (changes) within a species that can lead to evolution? ...
BIOLOGY Cells Unit GUIDE SHEET
... 12. Explain why doctors recommend that you use UVA/UVB sunblock when going outside. ...
... 12. Explain why doctors recommend that you use UVA/UVB sunblock when going outside. ...
The chemical basis of heredity Nucleic acid
... and contact with the mRNA ,there are number of tRNA more than amino acid number , there for there are more than one tRNA for one amino acid . 3.Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) : this type participate in building of ribosomes and play role in uniting the amino acid to creating peptide chain . ...
... and contact with the mRNA ,there are number of tRNA more than amino acid number , there for there are more than one tRNA for one amino acid . 3.Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) : this type participate in building of ribosomes and play role in uniting the amino acid to creating peptide chain . ...
Variation of Traits Name: #____ Genetics and Inheritance Date
... utagen. A mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA, of an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause c ancer, mutagens are therefore also likely to be carcinogens, al ...
... utagen. A mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA, of an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause c ancer, mutagens are therefore also likely to be carcinogens, al ...
Patterns of Heredity Can Be Complex
... order for a person to develop and function normally, the proteins encoded by his or her genes must function precisely. ► Sometimes genes are damaged or copied incorrectly, resulting in faulty proteins. ► Changes in genetic material are called mutations. ► Mutations are rare because most of the time ...
... order for a person to develop and function normally, the proteins encoded by his or her genes must function precisely. ► Sometimes genes are damaged or copied incorrectly, resulting in faulty proteins. ► Changes in genetic material are called mutations. ► Mutations are rare because most of the time ...
LE 3
... Special enzymes break these bonds (unzipping them apart) into 2 strands Both strands pair up with free-floating bases following A-T & C-G pairing rules. Two identical DNA sequence copies are formed. ...
... Special enzymes break these bonds (unzipping them apart) into 2 strands Both strands pair up with free-floating bases following A-T & C-G pairing rules. Two identical DNA sequence copies are formed. ...
phsi3001.phillips1
... Clone channel Make specific mutations to particular amino acids Express wild-type cf mutant in Xenopus oocytes Measure changes in gating, conductance etc with patch clamp recordings of membrane currents ...
... Clone channel Make specific mutations to particular amino acids Express wild-type cf mutant in Xenopus oocytes Measure changes in gating, conductance etc with patch clamp recordings of membrane currents ...
protein synthesis notes
... No operons…b/c genes w/similar functions are scattered among different chromosomes Multicellular organisms have different types of cells, all somatic cells contain the same DNA…but what makes them different is which genes are turned on/off Ex. Every cell has hemoglobin genes, but only turned “ ...
... No operons…b/c genes w/similar functions are scattered among different chromosomes Multicellular organisms have different types of cells, all somatic cells contain the same DNA…but what makes them different is which genes are turned on/off Ex. Every cell has hemoglobin genes, but only turned “ ...
DNA RNA
... 4. Two DNA molecules are produced each made of one new strand and one template ________→ ________→ ________→ ________ ...
... 4. Two DNA molecules are produced each made of one new strand and one template ________→ ________→ ________→ ________ ...
Chapter 12 Lecture Notes: The Nature of the Gene I. How genes
... 6. It is now known that the valine substitution creates a sticky patch on the surface of Hb-S. Hb-A, of course, does not have this patch. Under conditions of low oxygen tension, a hydrophobic patch in Hb-S is uncovered which can bind to the sticky patch in another molecule of Hb-S. This causes long ...
... 6. It is now known that the valine substitution creates a sticky patch on the surface of Hb-S. Hb-A, of course, does not have this patch. Under conditions of low oxygen tension, a hydrophobic patch in Hb-S is uncovered which can bind to the sticky patch in another molecule of Hb-S. This causes long ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.