DNA notes
... are several ways to do this. Most of the molecular work has been done using plasmids (they are partition into daughter cells too) and we will look at that closely when we discuss plasmids later. •For now look at the system that partitions the plasmids called P1 and F. This are single copy plasmids a ...
... are several ways to do this. Most of the molecular work has been done using plasmids (they are partition into daughter cells too) and we will look at that closely when we discuss plasmids later. •For now look at the system that partitions the plasmids called P1 and F. This are single copy plasmids a ...
Biotechnology - BeautyinScience.com
... enough quantity that can be used for analysis. PCR uses DNA polymerase from a bacteria scooped up in a Yellowstone National Park hotspring.(More details are not required). 13-3 Cell Transformation Cell transformation occurs when a cell’s DNA is changed by inserting a gene from another species using ...
... enough quantity that can be used for analysis. PCR uses DNA polymerase from a bacteria scooped up in a Yellowstone National Park hotspring.(More details are not required). 13-3 Cell Transformation Cell transformation occurs when a cell’s DNA is changed by inserting a gene from another species using ...
Biology Final Exam Review
... These mice died of the same disease caused by the original pathogens. Based on this information, which statement would be a valid ...
... These mice died of the same disease caused by the original pathogens. Based on this information, which statement would be a valid ...
Lecture 27
... • Some proteins have extensive sequence similarity in the same organism resulting from a gene duplication. • Gene duplication is an efficient mode of evolution because the new gene can evolve a new functionality while the original directs synthesis of the ancestral protein. • Globins-an example-see ...
... • Some proteins have extensive sequence similarity in the same organism resulting from a gene duplication. • Gene duplication is an efficient mode of evolution because the new gene can evolve a new functionality while the original directs synthesis of the ancestral protein. • Globins-an example-see ...
SI Practice exam 2
... Part 1: Fill in the blank with the best term for the following definitions 1. _______________ are the types of bonds that maintain the secondary structure of a protein. 2. The process of assembling the proper amino acids into a protein, using the information in a molecule of mRNA is called _________ ...
... Part 1: Fill in the blank with the best term for the following definitions 1. _______________ are the types of bonds that maintain the secondary structure of a protein. 2. The process of assembling the proper amino acids into a protein, using the information in a molecule of mRNA is called _________ ...
Removed DNA - Cloudfront.net
... that potentially lasts for enough generations to serve as a unit of natural selection”.(39) As such a gene is an inherited unit which is somewhere between a nucleotide and a chromosome. Systemic Concept: The gene is a combination of (one or more) nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) sequences, defined by the s ...
... that potentially lasts for enough generations to serve as a unit of natural selection”.(39) As such a gene is an inherited unit which is somewhere between a nucleotide and a chromosome. Systemic Concept: The gene is a combination of (one or more) nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) sequences, defined by the s ...
Testing for Natural Selection on Conserved Non-genic Sequences in Mammals
... The observation of high DNA sequence conservation across long periods of evolutionary time is thought to be a good signal of important regions. Otherwise, the similarity between sequences of species would have eroded by neutral mutation processes. This is also why, in general, higher conservation is ...
... The observation of high DNA sequence conservation across long periods of evolutionary time is thought to be a good signal of important regions. Otherwise, the similarity between sequences of species would have eroded by neutral mutation processes. This is also why, in general, higher conservation is ...
Chapter 13, 14 Rev
... Of the following types of mutations, which is considered the least drastic? a. Insertion of one base b. Deletion of two bases c. A neutral base substitution d. A stop codon e. A substitution of a hydrophilic amino acid for a hydrophobic one A mutation that results in a change in the codon reading pa ...
... Of the following types of mutations, which is considered the least drastic? a. Insertion of one base b. Deletion of two bases c. A neutral base substitution d. A stop codon e. A substitution of a hydrophilic amino acid for a hydrophobic one A mutation that results in a change in the codon reading pa ...
Gene pool and evolution PPT
... – How many genes control this trait? 1, it is a single gene trait ...
... – How many genes control this trait? 1, it is a single gene trait ...
Biology—Midterm Study Guide
... 58. The pairing of _____ in DNA is the key feature that allows DNA to be copied. Nitrogenous Bases 59. What nucleotide pair bonds would be found in a RNA molecule? Guanine&Cytosine, Adenine&Uracil 60. Cytosine will form a base pair only with _______. Guanine 61. How Many amino acids will the result ...
... 58. The pairing of _____ in DNA is the key feature that allows DNA to be copied. Nitrogenous Bases 59. What nucleotide pair bonds would be found in a RNA molecule? Guanine&Cytosine, Adenine&Uracil 60. Cytosine will form a base pair only with _______. Guanine 61. How Many amino acids will the result ...
Questions - Humble ISD
... 1. What is the shape of DNA? Who determined this shape? 2. What biomolecule does DNA belong to? 3. What is the monomer of DNA. 4. What are the 3 parts of the monomer? 5. A single-ringed N-base is called _____ & includes ________ & _______ 6. A double-ringed N-base is called ______ & includes _______ ...
... 1. What is the shape of DNA? Who determined this shape? 2. What biomolecule does DNA belong to? 3. What is the monomer of DNA. 4. What are the 3 parts of the monomer? 5. A single-ringed N-base is called _____ & includes ________ & _______ 6. A double-ringed N-base is called ______ & includes _______ ...
Chp 7 DNA Structure and Gene Function 1
... • Remember that codons are sequences of three nucleotides • Each word in the sentences above represents one codon ...
... • Remember that codons are sequences of three nucleotides • Each word in the sentences above represents one codon ...
Fragile Sites and Cancer Powerpoint
... • 120 fragile sites have been identified to date. • Considered part of normal chromosome structure and present in nearly all individuals. ...
... • 120 fragile sites have been identified to date. • Considered part of normal chromosome structure and present in nearly all individuals. ...
Chapter 21 The Genetic Control of Animal Development
... The Homeotic Genes of Drosophila The Drosophila homeotic genes form two large clusters on one of the autosomes. All of the homeotic genes encode helix-turn-helix transcription factors with a conserved homeodomain region involved in DNA binding. These genes control a regulatory cascade of targe ...
... The Homeotic Genes of Drosophila The Drosophila homeotic genes form two large clusters on one of the autosomes. All of the homeotic genes encode helix-turn-helix transcription factors with a conserved homeodomain region involved in DNA binding. These genes control a regulatory cascade of targe ...
Slide 1
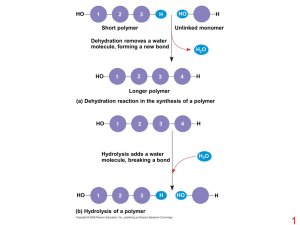
... • Nucleic acid is a long chain (polymer), or strand made up of nucleotides • DNA Nucleotides – made up of a nitrogen base, a deoxyribose sugar, and a triphosphate group – will have one of four different nitrogen bases: Adenine (A), Cytosine ©, guanine (G), and ...
... • Nucleic acid is a long chain (polymer), or strand made up of nucleotides • DNA Nucleotides – made up of a nitrogen base, a deoxyribose sugar, and a triphosphate group – will have one of four different nitrogen bases: Adenine (A), Cytosine ©, guanine (G), and ...
Final Review
... 6. Diagram a molecule of DNA and explain how its features allow for both heredity and protein synthesis. 7. Explain how RNA and DNA differ in structure and function. 8. Explain the role of mRNA, tRNA and rRNA in protein synthesis 9. Explain the relationship between DNA, RNA, Protein, Cells and the O ...
... 6. Diagram a molecule of DNA and explain how its features allow for both heredity and protein synthesis. 7. Explain how RNA and DNA differ in structure and function. 8. Explain the role of mRNA, tRNA and rRNA in protein synthesis 9. Explain the relationship between DNA, RNA, Protein, Cells and the O ...
Key for Practice Exam 4
... that have not been transformed. This allows for elimination of cells that are not carrying recombinant molecules. ...
... that have not been transformed. This allows for elimination of cells that are not carrying recombinant molecules. ...
Microsoft Word 97
... three nitrogen bases in a DNA molecule which code a specific amino acid a series of codons which direct the formation of one complete protein messenger RNA, which carries out the "orders" of DNA all the DNA bases in one "twist" of the DNA helix ...
... three nitrogen bases in a DNA molecule which code a specific amino acid a series of codons which direct the formation of one complete protein messenger RNA, which carries out the "orders" of DNA all the DNA bases in one "twist" of the DNA helix ...
Biotechnology
... In addition to the nucleoid, many bacteria often contain small nonchromosomal DNA molecules called plasmids. Plasmids usually contain between 5 and 100 genes. Plasmids are not essential for normal bacterial growth and bacteria may lose or gain them without harm Transposons (transposable elements or ...
... In addition to the nucleoid, many bacteria often contain small nonchromosomal DNA molecules called plasmids. Plasmids usually contain between 5 and 100 genes. Plasmids are not essential for normal bacterial growth and bacteria may lose or gain them without harm Transposons (transposable elements or ...
Biotechnology Notes HONORS
... 1. Choose an organism to change, and one to obtain the gene from (host) 2. Choose a bacterial vector that will transform the gene incorporate gene into its own DNA 3. Gene Splicing Cleave (cut) the pieces of DNA of interest from the host organism restriction enzyme“cleaves” 4. Isolate the gene lo ...
... 1. Choose an organism to change, and one to obtain the gene from (host) 2. Choose a bacterial vector that will transform the gene incorporate gene into its own DNA 3. Gene Splicing Cleave (cut) the pieces of DNA of interest from the host organism restriction enzyme“cleaves” 4. Isolate the gene lo ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.