Nervous Systems
... Bring signals from other neurons. 2 Dendrites: Receive signals from other neurons. ...
... Bring signals from other neurons. 2 Dendrites: Receive signals from other neurons. ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... in order to form tumors. Neurons don’t divide, so it would be less likely that they would lose the ability to regulate cell division. 14. How does the peripheral nervous system interact with the central nervous system to produce perceptions of stimuli? The peripheral nervous system is responsible fo ...
... in order to form tumors. Neurons don’t divide, so it would be less likely that they would lose the ability to regulate cell division. 14. How does the peripheral nervous system interact with the central nervous system to produce perceptions of stimuli? The peripheral nervous system is responsible fo ...
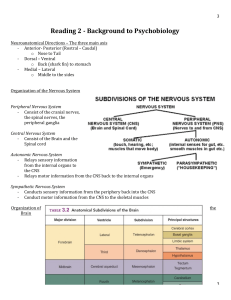
Reading 2 - Background to Psychobiology
... - Gyrus (plural) – The bumps created by two sulci - Sulcus (plural) – The space between the folds of the cerebral cortex - Fissure – A space that is not created by a fold of the brain - The white matter mostly consist of axons o You can think of the brain as many servers that are interconnec ...
... - Gyrus (plural) – The bumps created by two sulci - Sulcus (plural) – The space between the folds of the cerebral cortex - Fissure – A space that is not created by a fold of the brain - The white matter mostly consist of axons o You can think of the brain as many servers that are interconnec ...
The History and Scope of Psychology Module 1
... cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. ...
... cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. ...
Document
... cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. ...
... cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. ...
Chapter2 - cfhssocialstudies
... cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. ...
... cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. ...
Brain 1
... (a) A particular experience causes a neuron to fire and transmitter to be released. The record indicates the rate of nerve firing measured in the postsynaptic neuron due to this initial experience. (b) After continued firing occurs due to repetitions of the experience, structural changes at the syna ...
... (a) A particular experience causes a neuron to fire and transmitter to be released. The record indicates the rate of nerve firing measured in the postsynaptic neuron due to this initial experience. (b) After continued firing occurs due to repetitions of the experience, structural changes at the syna ...
Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses Quiz Answers
... a) one dendrite and many axons covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier b) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier c) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by the synapse d) one dendrite and many axon ...
... a) one dendrite and many axons covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier b) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier c) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by the synapse d) one dendrite and many axon ...
Psychopharmacology Dr. Sujit Kumar kar
... – Drug distribution depends on how soluble the drug molecule is in fat (to pass through membranes) and on the extent to which the drug binds to blood proteins (albumin) – Drug elimination is accomplished by excretion into urine and/or by inactivation by enzymes in the liver ...
... – Drug distribution depends on how soluble the drug molecule is in fat (to pass through membranes) and on the extent to which the drug binds to blood proteins (albumin) – Drug elimination is accomplished by excretion into urine and/or by inactivation by enzymes in the liver ...
SVHS ADV BIOLOGY NAME: 9th ed. Tortora PERIOD: 1 2 3 4 5 6
... The two main subdivisions of the nervous system are _________________________________ and __________________________________ ...
... The two main subdivisions of the nervous system are _________________________________ and __________________________________ ...
Biology
... Sensory- carry messages from sense organs to spinal cord or brain Motor- carry messages from spinal cord or brain to muscles or glands Interneurons- carry messages from one neuron to another and do most of the work of the nervous system ...
... Sensory- carry messages from sense organs to spinal cord or brain Motor- carry messages from spinal cord or brain to muscles or glands Interneurons- carry messages from one neuron to another and do most of the work of the nervous system ...
Biology The Nervous System
... information from other neurons and pass the message through the cell body Axon- carries messages away from the neuron, single fiber Myelin- covering of the axon, insulates and protects the axon, helps to speed up the transmission of the message Axon terminal- small fibers branching out from an axon ...
... information from other neurons and pass the message through the cell body Axon- carries messages away from the neuron, single fiber Myelin- covering of the axon, insulates and protects the axon, helps to speed up the transmission of the message Axon terminal- small fibers branching out from an axon ...
CNS Neuroglial Cells
... • Contains normal cellular structures (golgi apparatus, mitochondria, cytoplasm, cell membrane, etc.) • Neurofibrils – fine threads that extend into the axon • Nissl bodies (chromatophilic substances) – Membranous sacs in the cytoplasm – Similar to rough ER – Ribosomes on Nissl bodies synthesize ...
... • Contains normal cellular structures (golgi apparatus, mitochondria, cytoplasm, cell membrane, etc.) • Neurofibrils – fine threads that extend into the axon • Nissl bodies (chromatophilic substances) – Membranous sacs in the cytoplasm – Similar to rough ER – Ribosomes on Nissl bodies synthesize ...
Student Answer Sheet
... 1c. List five technologies used to scan the brain. Include their acronyms. (Sentences are not required for this answer.) ...
... 1c. List five technologies used to scan the brain. Include their acronyms. (Sentences are not required for this answer.) ...
Overview Functions of the Nervous System
... • travel across the synapse to the postsynaptic cells, where they are converted back into electrical signals • Axon terminal: contains many tiny, membrane-bounded sacs (synaptic vesicles) containing thousands of neurotransmitter molecules • Neurotransmitter receptor region on the membrane of a dendr ...
... • travel across the synapse to the postsynaptic cells, where they are converted back into electrical signals • Axon terminal: contains many tiny, membrane-bounded sacs (synaptic vesicles) containing thousands of neurotransmitter molecules • Neurotransmitter receptor region on the membrane of a dendr ...
KS4_MRI_Teachers_Notes_0
... Key Stage 4 – MRI Watching the brain at work Notes for teachers At a glance This activity introduces students to an exciting technique at the forefront of brain research, functional magnetic resonance imaging, or fMRI. Researchers use this powerful imaging technique to pinpoint precisely which areas ...
... Key Stage 4 – MRI Watching the brain at work Notes for teachers At a glance This activity introduces students to an exciting technique at the forefront of brain research, functional magnetic resonance imaging, or fMRI. Researchers use this powerful imaging technique to pinpoint precisely which areas ...
Module 4 - the Brain
... processes visual information including seeing colour and perceiving and recognizing animals, people and objects Primary Visual Cortex is at the very back, receives electrcal signals from receptors in the eye and changes them to basic visual sensation (ie light, shadow, texture) Visual Associat ...
... processes visual information including seeing colour and perceiving and recognizing animals, people and objects Primary Visual Cortex is at the very back, receives electrcal signals from receptors in the eye and changes them to basic visual sensation (ie light, shadow, texture) Visual Associat ...
The Brain ppt module 4
... processes visual information including seeing colour and perceiving and recognizing animals, people and objects Primary Visual Cortex is at the very back, receives electrcal signals from receptors in the eye and changes them to basic visual sensation (ie light, shadow, texture) Visual Associat ...
... processes visual information including seeing colour and perceiving and recognizing animals, people and objects Primary Visual Cortex is at the very back, receives electrcal signals from receptors in the eye and changes them to basic visual sensation (ie light, shadow, texture) Visual Associat ...
Unit 1 Practice
... 1. What are the short, branchlike structures of a neuron that receive signals from other neurons? a. axons b. dendrites c. soma d. axon terminals 2. The electric charge of an inactive neuron is called its a. ion potential. b. after potential. c. action potential. d. resting potential. 3. Communicati ...
... 1. What are the short, branchlike structures of a neuron that receive signals from other neurons? a. axons b. dendrites c. soma d. axon terminals 2. The electric charge of an inactive neuron is called its a. ion potential. b. after potential. c. action potential. d. resting potential. 3. Communicati ...
Biological Bases of Behavior : Quiz 1
... a. Exerting pressure on the eyeball induces flashes of light. b. Changes in brain chemistry cause altered consciousness in most people. c. The strength of the stimulus determines neural conduction speed. d. Different kinds of electrical activity are found in different sensory nerves. ...
... a. Exerting pressure on the eyeball induces flashes of light. b. Changes in brain chemistry cause altered consciousness in most people. c. The strength of the stimulus determines neural conduction speed. d. Different kinds of electrical activity are found in different sensory nerves. ...
Bio70 Psychobiology Fall 2006 First Midterm October 12 Version A
... You must put your name and student ID number on both the paper test and your Scantron. Make sure to put the test version number on your Scantron. You must turn in both the test and the Scantron. We will not grade any Scantron without an accompanying test. Show your ID when you turn in ...
... You must put your name and student ID number on both the paper test and your Scantron. Make sure to put the test version number on your Scantron. You must turn in both the test and the Scantron. We will not grade any Scantron without an accompanying test. Show your ID when you turn in ...
Medication Strategies for Behavior Patients Lynne Seibert DVM, MS
... GABA is an amino acid neurotransmitter that is synthesized from glutamate. GABA neurons are primarily inhibitory, are widely distributed in the CNS, and are the site of action of the benzodiazepines and barbiturates. Acetylcholine is the most widely distributed neurotransmitter. Cholinergic neurons ...
... GABA is an amino acid neurotransmitter that is synthesized from glutamate. GABA neurons are primarily inhibitory, are widely distributed in the CNS, and are the site of action of the benzodiazepines and barbiturates. Acetylcholine is the most widely distributed neurotransmitter. Cholinergic neurons ...
The fertile brain - Health Research Council
... A recent Fertility New Zealand study found nearly 25 per cent of New Zealand women report they have been infertile - defined as having been unable to conceive after having tried for over a year. Although the brain clearly controls fertility, surprisingly little is known about how. Understanding that ...
... A recent Fertility New Zealand study found nearly 25 per cent of New Zealand women report they have been infertile - defined as having been unable to conceive after having tried for over a year. Although the brain clearly controls fertility, surprisingly little is known about how. Understanding that ...