Topic 9
... 1. An ion-channel receptor (the Amiloridesensitive sodium channel) allows EITHER sodium or hydrogen ions to pass into the taste bud. 2. This ion movement will lead to a depolarization which leads to the influx of calcium ions, stimulating the release of neurotrasmitter agents. 3. The hydrogen ions w ...
... 1. An ion-channel receptor (the Amiloridesensitive sodium channel) allows EITHER sodium or hydrogen ions to pass into the taste bud. 2. This ion movement will lead to a depolarization which leads to the influx of calcium ions, stimulating the release of neurotrasmitter agents. 3. The hydrogen ions w ...
Slide ()
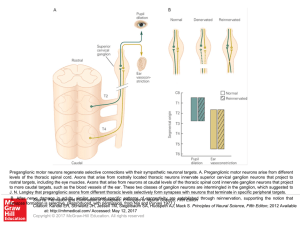
... levels of the thoracic spinal cord. Axons that arise from rostrally located thoracic neurons innervate superior cervical ganglion neurons that project to rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons ...
... levels of the thoracic spinal cord. Axons that arise from rostrally located thoracic neurons innervate superior cervical ganglion neurons that project to rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons ...
Singularity
... • The basic wiring method of the cerebellum is repeated billions of times. It is clear that the genome does not provide specific information about each repetition of this cerebellar structure, but rather specifies certain constraints as to how this structure is repeated (just as the genome does not ...
... • The basic wiring method of the cerebellum is repeated billions of times. It is clear that the genome does not provide specific information about each repetition of this cerebellar structure, but rather specifies certain constraints as to how this structure is repeated (just as the genome does not ...
Differential Permeability of the Membrane
... called the presynaptic membrane. The presynaptic membrane is separated from the other neuron by what is called the synaptic cleft. ...
... called the presynaptic membrane. The presynaptic membrane is separated from the other neuron by what is called the synaptic cleft. ...
Nervous Systems - manorlakesscience
... Nerve impulses that pass from sensory detectors to the brain and impulses that pass from the brain to other parts of the body travel along the spinal cord. Contains grey matter – made up of nerve cell bodies. Axons of these cells form the white matter of the spinal cord. ...
... Nerve impulses that pass from sensory detectors to the brain and impulses that pass from the brain to other parts of the body travel along the spinal cord. Contains grey matter – made up of nerve cell bodies. Axons of these cells form the white matter of the spinal cord. ...
Central Nervous system - UPM EduTrain Interactive Learning
... To learn how information is sent from the dendrites and soma of a neuron to its terminals, researchers study a neuron’s membrane potential (the difference in electrical charge between the inside and the outside of the neuron). Neuron There are two main types of neurotransmitters: small-molecule tr ...
... To learn how information is sent from the dendrites and soma of a neuron to its terminals, researchers study a neuron’s membrane potential (the difference in electrical charge between the inside and the outside of the neuron). Neuron There are two main types of neurotransmitters: small-molecule tr ...
Chapter 3
... 1. Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. 2. Know the main types of glia and their functions. 3. Be able to describe the advantages and disadvantages of the blood-brain barrier. Module 2.2 The Nerve Impulse 4. Understand why the neuron uses considerable ene ...
... 1. Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. 2. Know the main types of glia and their functions. 3. Be able to describe the advantages and disadvantages of the blood-brain barrier. Module 2.2 The Nerve Impulse 4. Understand why the neuron uses considerable ene ...
Class 10: Other Senses
... receptor opening ion channels ¢ Pacinian Corpuscle: pressure onset / offset detector • The structure of the Pacinian corpuscle makes the receptor selective to onset & offset stimuli and not to constant stimulus ...
... receptor opening ion channels ¢ Pacinian Corpuscle: pressure onset / offset detector • The structure of the Pacinian corpuscle makes the receptor selective to onset & offset stimuli and not to constant stimulus ...
Alzheimer`s Disease and its Effects on the Central Nervous System
... calcium ions. This causes the exocytosis of vacuoles containing a neurotransmitter. The neurotransmitter diffuses across the gap between the two membranes (called the synaptic cleft) and binds to receptors located on the opposing membrane. This transmits either an excitatory or an inhibitory signal ...
... calcium ions. This causes the exocytosis of vacuoles containing a neurotransmitter. The neurotransmitter diffuses across the gap between the two membranes (called the synaptic cleft) and binds to receptors located on the opposing membrane. This transmits either an excitatory or an inhibitory signal ...
The Nervous System
... ions are restored to resting potential This means Na+ are again pumped out, setting up a more positive charge outside the neuron ...
... ions are restored to resting potential This means Na+ are again pumped out, setting up a more positive charge outside the neuron ...
Chapter 10 Somatic and Special Senses
... The iris has two types of fibers, what are they? Inner layer: The inner tunic consists of the _________________, which contains photoreceptors; The inner tunic covers the back side of the eye to the ciliary body. In the center is the yellow area, the _______________ _______________ with the ________ ...
... The iris has two types of fibers, what are they? Inner layer: The inner tunic consists of the _________________, which contains photoreceptors; The inner tunic covers the back side of the eye to the ciliary body. In the center is the yellow area, the _______________ _______________ with the ________ ...
Nervous Regulation
... __________________________________________. Mechanism of Nervous Regulation Nerve cells carry ______________ through an organism. There are 2 types of structures that work with nerve cells. ______________________________________________ __________– a specialized structure that responds to the ...
... __________________________________________. Mechanism of Nervous Regulation Nerve cells carry ______________ through an organism. There are 2 types of structures that work with nerve cells. ______________________________________________ __________– a specialized structure that responds to the ...
Symptoms: visual disturbances, ______, loss of
... 2. Differential permeability of the plasma membrane iii. Differences in ionic makeup 1. ICF has _______ concentration of Na+ and Cl- than ECF 2. ICF has _______ concentration of K+ and negatively charged proteins (A-) than ECF iv. Sodium-potassium pump stabilizes the resting membrane potential by ma ...
... 2. Differential permeability of the plasma membrane iii. Differences in ionic makeup 1. ICF has _______ concentration of Na+ and Cl- than ECF 2. ICF has _______ concentration of K+ and negatively charged proteins (A-) than ECF iv. Sodium-potassium pump stabilizes the resting membrane potential by ma ...
Clinical Therapeutics Lecture #6 Drugs for Sexual Dysfunction Drug
... Testosterone replacement therapy is used to treat ED due to Hypogonadism, where Testosterone is low or where Prolactin is Increased. Testosterone enanthate or cypionate IM injection every 2 to 3 weeks Testosterone Scrotal Patches (Testoderm) QD in the am, the Scrotal Patch has the best absorption Te ...
... Testosterone replacement therapy is used to treat ED due to Hypogonadism, where Testosterone is low or where Prolactin is Increased. Testosterone enanthate or cypionate IM injection every 2 to 3 weeks Testosterone Scrotal Patches (Testoderm) QD in the am, the Scrotal Patch has the best absorption Te ...
EASTERN MICHIGAN UNIVERSITY Chemistry Department Seminar Wednesday December 3, 2014 2:00 p.m.
... Neurotransmitter sodium symporters (NSS) including human dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine transporters harness sodium and chloride gradients to facilitate reuptake of neurotransmitters from the synapse into presynaptic neurons. This function is vital for terminating neurochemical signals, mai ...
... Neurotransmitter sodium symporters (NSS) including human dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine transporters harness sodium and chloride gradients to facilitate reuptake of neurotransmitters from the synapse into presynaptic neurons. This function is vital for terminating neurochemical signals, mai ...
Drugs and Alcohol
... PCP prevents the actions normally caused when a neurotransmitter, called glutamate, attaches to its receptor in the brain. It also disrupts the actions of other neurotransmitters. This drug’s effects are very unpredictable. For example, it may make some people hallucinate and become aggressive, whil ...
... PCP prevents the actions normally caused when a neurotransmitter, called glutamate, attaches to its receptor in the brain. It also disrupts the actions of other neurotransmitters. This drug’s effects are very unpredictable. For example, it may make some people hallucinate and become aggressive, whil ...
Slide 1
... Twin, adoption, and family studies can provide important estimates for the role of genes in development and behavior However, these estimates do not tell us about how genes turn into the structures that will become a brain What are genes, how do they work, and how can they affect behavior? ...
... Twin, adoption, and family studies can provide important estimates for the role of genes in development and behavior However, these estimates do not tell us about how genes turn into the structures that will become a brain What are genes, how do they work, and how can they affect behavior? ...
Neuroplasticity - University of Michigan–Flint
... • Short-term learning occurs by altering existing synapses – ↑or ↓release of neurotransmitter affecting the excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) ...
... • Short-term learning occurs by altering existing synapses – ↑or ↓release of neurotransmitter affecting the excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) ...
Human nervous system_Final
... The nervous system The nervous system is an organ system containing a network of specialized cells called neurons that coordinate the actions of human and transmit signals between different parts of its body. The human nervous system has two main divisions as seen in the concept map, they are the ce ...
... The nervous system The nervous system is an organ system containing a network of specialized cells called neurons that coordinate the actions of human and transmit signals between different parts of its body. The human nervous system has two main divisions as seen in the concept map, they are the ce ...
Love at First Smell — The 2004 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
... These genes thus constitute the largest gene repertoires known to date. Meanwhile, the tally of the total number of genes in mice and humans has dropped to roughly 25,000. This means that 4 percent of all genes in mice and 1.4 percent in humans encode odorant receptors. The story of Buck and Axel is ...
... These genes thus constitute the largest gene repertoires known to date. Meanwhile, the tally of the total number of genes in mice and humans has dropped to roughly 25,000. This means that 4 percent of all genes in mice and 1.4 percent in humans encode odorant receptors. The story of Buck and Axel is ...
CNS_Part2
... distributed throughout the brain in three important dopamine systems (pathways): the nigrostriatal, mesocorticolimbic, and the tuberohypophyseal pathways. A decreased brain dopamine concentration is a contributing factor in Parkinsonユs disease, while an increase in dopamine concentration has a role ...
... distributed throughout the brain in three important dopamine systems (pathways): the nigrostriatal, mesocorticolimbic, and the tuberohypophyseal pathways. A decreased brain dopamine concentration is a contributing factor in Parkinsonユs disease, while an increase in dopamine concentration has a role ...
Unit 3A Nervous System - Teacher Version
... Antidepressants such as Prozac target which neurotransmitter? ...
... Antidepressants such as Prozac target which neurotransmitter? ...
Glutamatergic Modulation of the Pedunculopontine Nucleus and its
... many areas of the brain, including glutamatergic input from other mesopontine nuclei and the thalamus. Studies involving microinjections into the PPN in the freely moving rat have demonstrated that glutamate increases waking and REM sleep. These studies showed that glutamate induced wakefulness may ...
... many areas of the brain, including glutamatergic input from other mesopontine nuclei and the thalamus. Studies involving microinjections into the PPN in the freely moving rat have demonstrated that glutamate increases waking and REM sleep. These studies showed that glutamate induced wakefulness may ...