Chapter 2
... Also regulates the endocrine system and aids in digestion y The Endocrine System Hormones y The Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenalcortical Axis (HYPAC axis) Integration of endocrine and nervous system function Neuroscience: Functions of Main Types of Neurotransmitters y Functions of Psychoactive D ...
... Also regulates the endocrine system and aids in digestion y The Endocrine System Hormones y The Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenalcortical Axis (HYPAC axis) Integration of endocrine and nervous system function Neuroscience: Functions of Main Types of Neurotransmitters y Functions of Psychoactive D ...
How your brain and nervous system work
... • Recall that the nerve impulse passes along the axon of a neurone. Higher tier only: high demand • Recall that the gap between neurones is called a synapse. • Describe how an impulse triggers the release of a transmitter substance in a synapse and how it diffuses across to bind with receptor molecu ...
... • Recall that the nerve impulse passes along the axon of a neurone. Higher tier only: high demand • Recall that the gap between neurones is called a synapse. • Describe how an impulse triggers the release of a transmitter substance in a synapse and how it diffuses across to bind with receptor molecu ...
MYELINATED AXON - Union County College Faculty Web Site
... neurons. They are more numerous in motor neurons. Nissle bodies are formed by clumps of ribosomes attached to portions of endoplasmic reticulum. They signify a high level of protein synthesis ...
... neurons. They are more numerous in motor neurons. Nissle bodies are formed by clumps of ribosomes attached to portions of endoplasmic reticulum. They signify a high level of protein synthesis ...
Nervous System
... • For example … you put your hand on a tac – Sensory neurons in your hand react to the pain by sending nerve impulses (signal) to the spinal cord – Interneurons relay the message to the motor neurons – Impulse travels to your arm which you lift quickly! ...
... • For example … you put your hand on a tac – Sensory neurons in your hand react to the pain by sending nerve impulses (signal) to the spinal cord – Interneurons relay the message to the motor neurons – Impulse travels to your arm which you lift quickly! ...
Barbiturate
... which falling asleep (increased sleep latency) is the primary complaint. The potential for abuse of ramelteon is believed to be minimal, and no evidence of dependence or withdrawal effects has been observed. Therefore, ramelteon can be administered long term. Common adverse effects of ramelteon incl ...
... which falling asleep (increased sleep latency) is the primary complaint. The potential for abuse of ramelteon is believed to be minimal, and no evidence of dependence or withdrawal effects has been observed. Therefore, ramelteon can be administered long term. Common adverse effects of ramelteon incl ...
Introduction to neural computation
... Modularity and the brain • Different bits of the cortex do different things. – Local damage to the brain has specific effects – Specific tasks increase the blood flow to specific regions. • But cortex looks pretty much the same all over. – Early brain damage makes functions relocate • Cortex is mad ...
... Modularity and the brain • Different bits of the cortex do different things. – Local damage to the brain has specific effects – Specific tasks increase the blood flow to specific regions. • But cortex looks pretty much the same all over. – Early brain damage makes functions relocate • Cortex is mad ...
Chapter 3
... Neurons and Glial Cells A layer of ectodermal cells form on the inner surface of neural tube and divide to form: Ventricular layer which then divides into daughter cells Daughter cells migrate: • between the intermediate and marginal layers to form the cortical plate which develops into the cort ...
... Neurons and Glial Cells A layer of ectodermal cells form on the inner surface of neural tube and divide to form: Ventricular layer which then divides into daughter cells Daughter cells migrate: • between the intermediate and marginal layers to form the cortical plate which develops into the cort ...
Slide ()
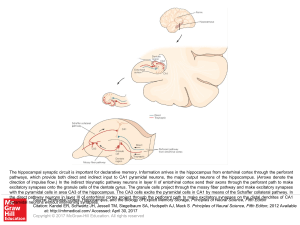
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Slide ()
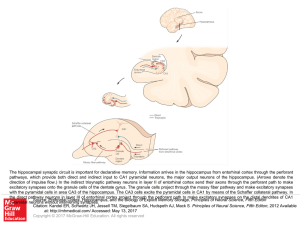
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Tackling Parkinson Disease with Bioinformatics and Genomics
... on a neurotransmitter/neurohormone within the brain called somatostatin, whose function, among others, might involve protection of spared neurons. One such lab in McGill University’s Royal Victoria Hospital in the Endocrinology Department directed by Dr. Yogesh Patel tests neuronal cultures grown f ...
... on a neurotransmitter/neurohormone within the brain called somatostatin, whose function, among others, might involve protection of spared neurons. One such lab in McGill University’s Royal Victoria Hospital in the Endocrinology Department directed by Dr. Yogesh Patel tests neuronal cultures grown f ...
013368718X_CH31_483-498.indd
... When a neuron is stimulated, the inside of its membrane temporarily becomes more positive than the outside. This reversal of charges is called an action potential, or nerve impulse. The nerve impulse moves along the axon. Not all stimuli are capable of starting an impulse. The minimum level of a sti ...
... When a neuron is stimulated, the inside of its membrane temporarily becomes more positive than the outside. This reversal of charges is called an action potential, or nerve impulse. The nerve impulse moves along the axon. Not all stimuli are capable of starting an impulse. The minimum level of a sti ...
How do we manage to remember smells despite the fact
... Olfactory sensory neurons, which sit in the mucus in the back of the nose and relay data into the brain via axons (fingerlike projections that transmit information out from the cell body), do not live forever. In fact, they are one of the increasingly large number of neuron types that are known to d ...
... Olfactory sensory neurons, which sit in the mucus in the back of the nose and relay data into the brain via axons (fingerlike projections that transmit information out from the cell body), do not live forever. In fact, they are one of the increasingly large number of neuron types that are known to d ...
bio310 test 1 answers
... {1 mark} Therefore the only effect changed by the drug is the HR response during SNS stimulation. Therefore the drug is likely a beta blocker. ...
... {1 mark} Therefore the only effect changed by the drug is the HR response during SNS stimulation. Therefore the drug is likely a beta blocker. ...
Sensation
... eye to the brain Blind Spot Point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye. Fovea Central point in the retina, around which the eye’s cones cluster ...
... eye to the brain Blind Spot Point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye. Fovea Central point in the retina, around which the eye’s cones cluster ...
Blue Brain PPT
... • The Blue Brain Project is an attempt to reverse engineer the human brain and recreate it at the cellular level inside a computer simulation. • The project was founded in May 2005 by Henry Markram at the EPFL in Lausanne, Switzerland. ...
... • The Blue Brain Project is an attempt to reverse engineer the human brain and recreate it at the cellular level inside a computer simulation. • The project was founded in May 2005 by Henry Markram at the EPFL in Lausanne, Switzerland. ...
Optogenetics: Molecular and Optical Tools for Controlling Life with
... Over the last several years we and our colleagues have developed a toolbox of fully genetically encoded molecules that, when expressed in neurons, enable the electrical potentials of the neurons to be controlled in a temporally precise fashion by brief pulses of light. Some of the molecules enable t ...
... Over the last several years we and our colleagues have developed a toolbox of fully genetically encoded molecules that, when expressed in neurons, enable the electrical potentials of the neurons to be controlled in a temporally precise fashion by brief pulses of light. Some of the molecules enable t ...
投影片 1
... Indirectly increasing synaptic norepinephrine and serotonin through blockade of central presynaptic alpha2-adrenergic receptors. Blocking histamine (H1), 5-HT2 and 5-HT3 receptors. Causing less insomnia, sexual dysfunction, nausea/vomiting than SSRIs. Effective for pain, insomnia and anorexia/cachex ...
... Indirectly increasing synaptic norepinephrine and serotonin through blockade of central presynaptic alpha2-adrenergic receptors. Blocking histamine (H1), 5-HT2 and 5-HT3 receptors. Causing less insomnia, sexual dysfunction, nausea/vomiting than SSRIs. Effective for pain, insomnia and anorexia/cachex ...
Nerve
... smallesttree: diameter unmyelinated fibers e.g. Dendritic all neurites. Neural signals: ...
... smallesttree: diameter unmyelinated fibers e.g. Dendritic all neurites. Neural signals: ...
Chapter 7
... movement of Ca2+ ions into the cytoplasm from storage sites in the taste receptor, increasing the release of neurotransmitters. ...
... movement of Ca2+ ions into the cytoplasm from storage sites in the taste receptor, increasing the release of neurotransmitters. ...
Part 2 of Unit Test 4
... Part 2 of Unit Test 4 Written portion Directions: Answer the following short answer questions using complete sentences. (5 points each) ...
... Part 2 of Unit Test 4 Written portion Directions: Answer the following short answer questions using complete sentences. (5 points each) ...
Handout 1 - Porterville College Home
... 4. Neurotransmitter finds its _____________________ site on next neuron 5. Activation of receptor __________________________ in post-synaptic vessel 6. ______________________ of neurotransmitter(s): ________________ action! G. Synthesized in the ___________________________ H. Special Properties: _ ...
... 4. Neurotransmitter finds its _____________________ site on next neuron 5. Activation of receptor __________________________ in post-synaptic vessel 6. ______________________ of neurotransmitter(s): ________________ action! G. Synthesized in the ___________________________ H. Special Properties: _ ...
Grant Clay
... 1. Why is the cerebral cortex considered the part of the brain that makes people uniquely human? 2. How do we know what we know about the brain? 3. What are the major processes at work in the developing brain? 4. Is our behavior determined by nature, nurture, or both? 5. Why do studies of identical ...
... 1. Why is the cerebral cortex considered the part of the brain that makes people uniquely human? 2. How do we know what we know about the brain? 3. What are the major processes at work in the developing brain? 4. Is our behavior determined by nature, nurture, or both? 5. Why do studies of identical ...
States of Consciousness
... Drugs are either…. • Agonists • Antagonists • Reuptake inhibitors If a drug is used often, a tolerance is created for the drug. Thus you need more of the drug to feel the same effect. If you stop using a drug you can develop withdrawal symptoms. ...
... Drugs are either…. • Agonists • Antagonists • Reuptake inhibitors If a drug is used often, a tolerance is created for the drug. Thus you need more of the drug to feel the same effect. If you stop using a drug you can develop withdrawal symptoms. ...
Nervous System
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Nerves that connect all parts of the body to the brain. Nerve: A cable-like bundles of axons that make up the peripheral nervous system. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): Controls all involuntary activities not under conscious control like breathing. Somatic Nervous Sy ...
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Nerves that connect all parts of the body to the brain. Nerve: A cable-like bundles of axons that make up the peripheral nervous system. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): Controls all involuntary activities not under conscious control like breathing. Somatic Nervous Sy ...