Unit M - Notes #1 Neurons - Mr. Lesiuk
... -Conduct a nerve impulse away from the cell body. 4. Myelin Sheath -Protective lipid coating of Schwann cells (type of neuroglial cell) forms insulating layer around longer axons and dendrites. OMIT "Larger __________" 5. Nodes of Ranvier -Interrupted areas of the Myelin Sheath due to gaps between o ...
... -Conduct a nerve impulse away from the cell body. 4. Myelin Sheath -Protective lipid coating of Schwann cells (type of neuroglial cell) forms insulating layer around longer axons and dendrites. OMIT "Larger __________" 5. Nodes of Ranvier -Interrupted areas of the Myelin Sheath due to gaps between o ...
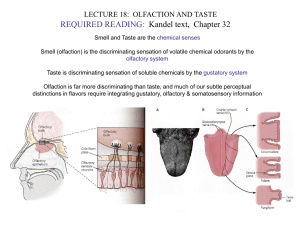
LECTURE18.Olfaction&Taste
... Each sensory neuron responds to a single odorant or a specific repertoire of chemically related odorants An odor is ENCODED by the specific combination of neurons which respond to it Sensory neurons respond to odorant by inward current flow, which depolarizes neuron. There is a relationship between ...
... Each sensory neuron responds to a single odorant or a specific repertoire of chemically related odorants An odor is ENCODED by the specific combination of neurons which respond to it Sensory neurons respond to odorant by inward current flow, which depolarizes neuron. There is a relationship between ...
2014 nervous system ppt
... binding of ligand, ion, hormone *Voltage gated = open in response to change in electrical charge across plasma membrane ...
... binding of ligand, ion, hormone *Voltage gated = open in response to change in electrical charge across plasma membrane ...
Nervous System Powerpoint
... * The Cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. 1. The cerebrum controls your thinking. 2. The cerebrum controls your memory. 3. The cerebrum controls your speaking. 4. The cerebrum controls your movement and identifies the information gathered by your sense organs. ...
... * The Cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. 1. The cerebrum controls your thinking. 2. The cerebrum controls your memory. 3. The cerebrum controls your speaking. 4. The cerebrum controls your movement and identifies the information gathered by your sense organs. ...
PETER SOMOGYI University of Oxford, United Kingdom Peter
... rhythmicity and high frequency ripple oscillations (SWR). Some of them exclusively innervate local cortical GABAergic interneurons. Individual MSDB neurons show a wide range of activity patterns, which may be related to their termination in different cortical areas and/or forming synapses with diffe ...
... rhythmicity and high frequency ripple oscillations (SWR). Some of them exclusively innervate local cortical GABAergic interneurons. Individual MSDB neurons show a wide range of activity patterns, which may be related to their termination in different cortical areas and/or forming synapses with diffe ...
The Nervous System Ch. 12 & 13
... Their affect is determined by the receptor, not the actual NT. ...
... Their affect is determined by the receptor, not the actual NT. ...
Overview
... the human is the most highly organized system of the body. The overall function of the nervous system is control and coordination of the human body. ...
... the human is the most highly organized system of the body. The overall function of the nervous system is control and coordination of the human body. ...
Study guide for Unit I - People Server at UNCW
... 1. What is a neuron? Be able to identify its parts. 2. What is the synapse? What happens there? 3. In what sense is neural transmission an electrochemical event? Where is it electrical? Where chemical? 4. What is a neurotransmitter? A receptor site? Be able to trace the processes involved in neural ...
... 1. What is a neuron? Be able to identify its parts. 2. What is the synapse? What happens there? 3. In what sense is neural transmission an electrochemical event? Where is it electrical? Where chemical? 4. What is a neurotransmitter? A receptor site? Be able to trace the processes involved in neural ...
Damage to the frontal lobes can lead to
... How do we know what we know about the brain? start at 5 min. video clip brain surgery ...
... How do we know what we know about the brain? start at 5 min. video clip brain surgery ...
THIS WEEK IN CHEMISTRY 19 OCTOBER - 25 OCTOBER 2014
... A chemical tracer based on the sweetener sorbitol allows realtime imaging of dangerous bacterial infections. It allows quick and reliable detection, monitoring of response to antibiotics, and allows distinction between bacterial and sterile inflammation in the body. ...
... A chemical tracer based on the sweetener sorbitol allows realtime imaging of dangerous bacterial infections. It allows quick and reliable detection, monitoring of response to antibiotics, and allows distinction between bacterial and sterile inflammation in the body. ...
Bionomics to present anti-anxiety drug treatment trial results and
... (alpha7 nAChR) in development for the treatment of anxiety and stress-related disorders. Bionomics’ research has demonstrated that single ascending doses of BNC210 are safe, well tolerated and avoid the side effects seen with standard of care drugs for anxiety such as benzodiazepines, Selective Sero ...
... (alpha7 nAChR) in development for the treatment of anxiety and stress-related disorders. Bionomics’ research has demonstrated that single ascending doses of BNC210 are safe, well tolerated and avoid the side effects seen with standard of care drugs for anxiety such as benzodiazepines, Selective Sero ...
chapter 2 - Forensic Consultation
... The Motor Cortex and The Sensory Cortex • The motor cortex, an arch-shaped region at the rear of the frontal lobes, controls voluntary muscle movements on the opposite side of the body. Body parts requiring the most precise control occupy the greatest amount of cortical space. In an effort to find ...
... The Motor Cortex and The Sensory Cortex • The motor cortex, an arch-shaped region at the rear of the frontal lobes, controls voluntary muscle movements on the opposite side of the body. Body parts requiring the most precise control occupy the greatest amount of cortical space. In an effort to find ...
peripheral nervous system
... The Motor Cortex and The Sensory Cortex • The motor cortex, an arch-shaped region at the rear of the frontal lobes, controls voluntary muscle movements on the opposite side of the body. Body parts requiring the most precise control occupy the greatest amount of cortical space. In an effort to find ...
... The Motor Cortex and The Sensory Cortex • The motor cortex, an arch-shaped region at the rear of the frontal lobes, controls voluntary muscle movements on the opposite side of the body. Body parts requiring the most precise control occupy the greatest amount of cortical space. In an effort to find ...
Draft Proposal to the Keck Foundation KECK CENTER FOR
... multiphoton microscopy, and lifetime resolved microscopy, are combined with genetic or exogenous optical markers to provide new ways to study processes such as cellular trafficking, vesicle membrane fusion, locally regulated dendritic ionic flows and protein synthesis, and rhythmic activities of ind ...
... multiphoton microscopy, and lifetime resolved microscopy, are combined with genetic or exogenous optical markers to provide new ways to study processes such as cellular trafficking, vesicle membrane fusion, locally regulated dendritic ionic flows and protein synthesis, and rhythmic activities of ind ...
Central nervous system
... – raise or lower number of receptors – alter neurotransmitter release, synthesis or breakdown – Some postsynaptic neurons release nitric oxide (NO) – ------“give me more!” ...
... – raise or lower number of receptors – alter neurotransmitter release, synthesis or breakdown – Some postsynaptic neurons release nitric oxide (NO) – ------“give me more!” ...
ANHB1102 Basic Principles of the Nervous System • The nervous
... - Terminal part is a little swelling that forms a synapse (junction) with the next cell. It contains synaptic vesicles full of neurotransmitter. Nervous impulse fundamentals - Action potential – momentary reversal of membrane potential. This change causes electrical signalling within neurons Resting ...
... - Terminal part is a little swelling that forms a synapse (junction) with the next cell. It contains synaptic vesicles full of neurotransmitter. Nervous impulse fundamentals - Action potential – momentary reversal of membrane potential. This change causes electrical signalling within neurons Resting ...
Lecture 1 Brain Structure
... Arvid Carlsson discovered dopamine is a neurotransmitter. Carlsson also found lack of dopamine in the brain of Parkinson patients. Paul Greengard studied in detail how neurotransmitters carry out their work in the neurons. Dopamine activated a certain protein (DARPP-32), which could change the funct ...
... Arvid Carlsson discovered dopamine is a neurotransmitter. Carlsson also found lack of dopamine in the brain of Parkinson patients. Paul Greengard studied in detail how neurotransmitters carry out their work in the neurons. Dopamine activated a certain protein (DARPP-32), which could change the funct ...
Nervous System PowerPoint
... equilibrium and b_____; muscle tone; only 10% of brain but contains more _____ than the rest of the brain combined; _____ working part of the brain; capable of making _____ based on previous experiences; enables rest of brain to work more _____ because it can carry out tasks _____ without conscious ...
... equilibrium and b_____; muscle tone; only 10% of brain but contains more _____ than the rest of the brain combined; _____ working part of the brain; capable of making _____ based on previous experiences; enables rest of brain to work more _____ because it can carry out tasks _____ without conscious ...
The Brain and the Nervous System
... the Corpus Collosum Each hemisphere receives and sends information to the opposite side of the body Each hemisphere also specializes in certain functions LEFT and Right tightly coordinated -Both necessary for efficient and normal brain function Each hemisphere has some special abilities: The Left He ...
... the Corpus Collosum Each hemisphere receives and sends information to the opposite side of the body Each hemisphere also specializes in certain functions LEFT and Right tightly coordinated -Both necessary for efficient and normal brain function Each hemisphere has some special abilities: The Left He ...
1-Antipsychotic drug..
... divided into two groups: The typical = 1st generation and the atypical = 2nd generation antipsychotics Atypical drugs are preferred as a first line treatment because they: 1- have fewer side effects 2- have additional benefits for the ...
... divided into two groups: The typical = 1st generation and the atypical = 2nd generation antipsychotics Atypical drugs are preferred as a first line treatment because they: 1- have fewer side effects 2- have additional benefits for the ...
Ch 4 Drug Effects on the Brain
... and morphine activate specific receptors Caffeine, the mild stimulant found in coffee and soft drinks, prevents a neurotransmitter called adenosine from binding to its receptor In normal situations, adenosine causes sedation; it is a natural sleep-inducer Instead of causing sedation, caffeine blocks ...
... and morphine activate specific receptors Caffeine, the mild stimulant found in coffee and soft drinks, prevents a neurotransmitter called adenosine from binding to its receptor In normal situations, adenosine causes sedation; it is a natural sleep-inducer Instead of causing sedation, caffeine blocks ...
States of consciousness
... b) Phase 2: follows about 10 minutes later – deeper sleep and wave frequencies are mixed – seen in sleep spindles (sporadic increased=s in frequency) – can be Kcomplexes (occasional waves with sharp peaks) – mechanisms to prevent a person from waking by reducing sensory input ...
... b) Phase 2: follows about 10 minutes later – deeper sleep and wave frequencies are mixed – seen in sleep spindles (sporadic increased=s in frequency) – can be Kcomplexes (occasional waves with sharp peaks) – mechanisms to prevent a person from waking by reducing sensory input ...
Physiological Complications (550-106)
... Directions: Complete the matrix on drug classifications. Consider drug classifications and drugs not addressed in the learning plans of the course this semester, but that are included in the chapters not covered in the textbook. Consider what sub-categories may exist within a drug classification, ex ...
... Directions: Complete the matrix on drug classifications. Consider drug classifications and drugs not addressed in the learning plans of the course this semester, but that are included in the chapters not covered in the textbook. Consider what sub-categories may exist within a drug classification, ex ...
Biology 621 - Chapter 12 Midterm Exam Review
... 22. A(n) __ is an automatic response to a stimulus. 23 Subdivision of the PNS that regulates the activity of the heart and smooth muscle and of glands; also called the involuntary nervous system. ___ 24. ____ neurons carry impulses from receptors to the spinal cord. 25. What are the two major divisi ...
... 22. A(n) __ is an automatic response to a stimulus. 23 Subdivision of the PNS that regulates the activity of the heart and smooth muscle and of glands; also called the involuntary nervous system. ___ 24. ____ neurons carry impulses from receptors to the spinal cord. 25. What are the two major divisi ...