Document
... microbe are not confined to that microbe but can be imported into others. A non-Darwinian mechanism, it adds a new twist to evolution by mutation and natural selection. Lynn Margulis proposed endosymbiosis in the 1960s, initially rejected by most, but now accepted as the origin of complexity in euka ...
... microbe are not confined to that microbe but can be imported into others. A non-Darwinian mechanism, it adds a new twist to evolution by mutation and natural selection. Lynn Margulis proposed endosymbiosis in the 1960s, initially rejected by most, but now accepted as the origin of complexity in euka ...
structure and effectively suppress the mutation in B· 4. Transfer
... of what is observed in proteins. Also, given any triplet coding for an amino acid, the next triplet could only be one of four. For example, if the first is GGG, ...
... of what is observed in proteins. Also, given any triplet coding for an amino acid, the next triplet could only be one of four. For example, if the first is GGG, ...
Biological Molecules Test Review Test covers carbohydrates, lipids
... Biological Molecules Test Review Test covers carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids A. What is dehydration synthesis? Draw an example. You will have to recognize the type of reaction. ...
... Biological Molecules Test Review Test covers carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids A. What is dehydration synthesis? Draw an example. You will have to recognize the type of reaction. ...
CSC 2417 Algorithms in Molecular Biology PS3: Due December 8
... approaches) assume independence of adjacent positions. This is not always a valid assumption; for example the bias against CpG di-nucleotides makes adjacent nucleotides non-independent. Develop an HMM representation of a profile that incorporates nonindependence of adjacent nucleotides. What is the ...
... approaches) assume independence of adjacent positions. This is not always a valid assumption; for example the bias against CpG di-nucleotides makes adjacent nucleotides non-independent. Develop an HMM representation of a profile that incorporates nonindependence of adjacent nucleotides. What is the ...
Molecular Genetics Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice
... c. linkage to histone molecules. All of the following are directly involved in translation except a. mRNA. b. tRNA. c. ribosomes. d. DNA. The genetic code is essentially the same for all organisms. From this, one can logically assume all of the following EXCEPT a. a gene from an organism could theor ...
... c. linkage to histone molecules. All of the following are directly involved in translation except a. mRNA. b. tRNA. c. ribosomes. d. DNA. The genetic code is essentially the same for all organisms. From this, one can logically assume all of the following EXCEPT a. a gene from an organism could theor ...
Chlorella CGF
... spherical or elliptical, containing a single elongated chloroplast that fills most cell. Fine powder, hygroscopic dark green color, characteristic flavor and odor. ...
... spherical or elliptical, containing a single elongated chloroplast that fills most cell. Fine powder, hygroscopic dark green color, characteristic flavor and odor. ...
RAFT: Genetics - Catawba County Schools
... Overview: These tiered RAFT assignments give students an opportunity to apply their knowledge of the key terms, concepts, and processes typically highlighted in a middle school-level genetics unit. They are listed in order of difficulty, with the first being the most difficult. Students may complete ...
... Overview: These tiered RAFT assignments give students an opportunity to apply their knowledge of the key terms, concepts, and processes typically highlighted in a middle school-level genetics unit. They are listed in order of difficulty, with the first being the most difficult. Students may complete ...
Review Problems #2 (Enzyme Review, Phosphatases
... 7) What are the carbon-containing precursors used for the synthesis of valine and isoleucine? What cofactor is common to both these biosynthetic pathways? Explain its role and draw a mechanism for the transformation. 8) The biosynthesis of valine and isoleucine have a rearrangement step that is very ...
... 7) What are the carbon-containing precursors used for the synthesis of valine and isoleucine? What cofactor is common to both these biosynthetic pathways? Explain its role and draw a mechanism for the transformation. 8) The biosynthesis of valine and isoleucine have a rearrangement step that is very ...
Neutralism - Winona State University
... Kimura, M. 1983. Neutral Theory of Molecular Evolution. Cambridge University Press. NY. Kreitman, M. and H. Akashi. 1995. Molecular evidence for natural selection. Ann. Rev. Ecol. ...
... Kimura, M. 1983. Neutral Theory of Molecular Evolution. Cambridge University Press. NY. Kreitman, M. and H. Akashi. 1995. Molecular evidence for natural selection. Ann. Rev. Ecol. ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... It may play a role in evolution, making it possible for small changes in DNA to have dramatic effects ...
... It may play a role in evolution, making it possible for small changes in DNA to have dramatic effects ...
Document
... • The idea of genetic inheritance gained support from the behavior of chromosomes in meiosis and fertilization. • Linkage analysis can give information about the relative location of genes on chromosomes. • The success of Mendelian genetics increased the importance of characterizing the genetic mate ...
... • The idea of genetic inheritance gained support from the behavior of chromosomes in meiosis and fertilization. • Linkage analysis can give information about the relative location of genes on chromosomes. • The success of Mendelian genetics increased the importance of characterizing the genetic mate ...
Components needed for Translation tRNAs Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases
... – fmet is the initiating amino acids in bacteria, but methionine is used in eukaryotes – In both cases, a special initiating tRNA is used. • met-tRNAm met is used at internal codons. ...
... – fmet is the initiating amino acids in bacteria, but methionine is used in eukaryotes – In both cases, a special initiating tRNA is used. • met-tRNAm met is used at internal codons. ...
File - Schuette Science
... Two Types of Gene Mutations 1. Point mutations: one nucleotide that affects one amino acid. Example: Substitution C changes to G ...
... Two Types of Gene Mutations 1. Point mutations: one nucleotide that affects one amino acid. Example: Substitution C changes to G ...
Translation - Olympic High School
... Genetic diseases • Most changes are harmless, but some can cause specific diseases. • One way to determine whether a disease is inheritable is to trace the family history of a disease by creating a type of family tree called a pedigree. • One inheritable disease caused by a specific substitution (o ...
... Genetic diseases • Most changes are harmless, but some can cause specific diseases. • One way to determine whether a disease is inheritable is to trace the family history of a disease by creating a type of family tree called a pedigree. • One inheritable disease caused by a specific substitution (o ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR CHAPTER 12 – DNA Two Main Processes for
... DNA is a double helix, a small portion of one side of DNA is shown below, use the base pair rules to complete the complementary strand. G ...
... DNA is a double helix, a small portion of one side of DNA is shown below, use the base pair rules to complete the complementary strand. G ...
Mutation Reading--How the Gene for Sickle Cell Hemoglobin
... the blood flow in the tiny capillaries, causing pain and damage to body organs. In addition, sickleshaped red blood cells do not last nearly as long as normal red blood cells, so the person does not have enough red blood cells, causing anemia. ...
... the blood flow in the tiny capillaries, causing pain and damage to body organs. In addition, sickleshaped red blood cells do not last nearly as long as normal red blood cells, so the person does not have enough red blood cells, causing anemia. ...
Slide 1
... Alanine-Glucose cycle is important for transporting nitrogen to the liver from muscles and in gluconeogenesis, DNA synthesis ... Its major function is to remove “excess” pyruvate from the muscles in the form of alanine and convert the alanine into glucose in the liver for transport back to the musc ...
... Alanine-Glucose cycle is important for transporting nitrogen to the liver from muscles and in gluconeogenesis, DNA synthesis ... Its major function is to remove “excess” pyruvate from the muscles in the form of alanine and convert the alanine into glucose in the liver for transport back to the musc ...
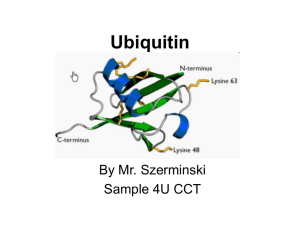
Ubiquitin
... Topics to be discussed • General info: - it is a regulatory protein that has been found in almost all tissues of eukaryotes - one of its functions: it directs protein recycling - can attach to proteins and label them for destruction. - discovery won the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 2004 ...
... Topics to be discussed • General info: - it is a regulatory protein that has been found in almost all tissues of eukaryotes - one of its functions: it directs protein recycling - can attach to proteins and label them for destruction. - discovery won the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 2004 ...
Special Topics gene expression
... I. Definition of gene expression II. Proteins- the end product of gene expression A. Polymers of monomers B. Joined by peptide bond C. Denaturing of proteins leads to loss of function i. Ways to denature protiens D. Genes code for proteins i. Genome vs. gene ii. Polymer of monomers (nucleic acid vs. ...
... I. Definition of gene expression II. Proteins- the end product of gene expression A. Polymers of monomers B. Joined by peptide bond C. Denaturing of proteins leads to loss of function i. Ways to denature protiens D. Genes code for proteins i. Genome vs. gene ii. Polymer of monomers (nucleic acid vs. ...
biochem study guide
... 2. Identify the functional groups. Given an unknown organic molecule, recognize and name the functional groups. 3. Describe the structure of a typical monosaccharide such as glucose. Write out a condensation reaction between two glucose molecules, and explain hydrolysis. 4. Explain the difference be ...
... 2. Identify the functional groups. Given an unknown organic molecule, recognize and name the functional groups. 3. Describe the structure of a typical monosaccharide such as glucose. Write out a condensation reaction between two glucose molecules, and explain hydrolysis. 4. Explain the difference be ...
Evidence for Evolution Student Answer Sheet
... 6. Read and summarize the article “Modern Cancer Type Found In Neanderthal Remains.” ...
... 6. Read and summarize the article “Modern Cancer Type Found In Neanderthal Remains.” ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.