Ch. 9-11 Review ppt.
... 3) Write the reaction for forming a triglyceride and the saponification of a triglyceride. 4) What’s the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated fat? How does that relate to their m.p. and what phase they are at room temperature? 5)Fat soluble vs. water soluble vitamins? ...
... 3) Write the reaction for forming a triglyceride and the saponification of a triglyceride. 4) What’s the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated fat? How does that relate to their m.p. and what phase they are at room temperature? 5)Fat soluble vs. water soluble vitamins? ...
Chapter 25 Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... proteins - small subunits contains 1 rRNA molecule and 21 proteins - large subunits contains 2 rRNA molecules and 34 proteins - includes enzymes that form peptide bonds between amino acids - attach and move along mRNA to decide the amino acid sequence for a protein - several ribosomes (a polyribosom ...
... proteins - small subunits contains 1 rRNA molecule and 21 proteins - large subunits contains 2 rRNA molecules and 34 proteins - includes enzymes that form peptide bonds between amino acids - attach and move along mRNA to decide the amino acid sequence for a protein - several ribosomes (a polyribosom ...
Chapter 16 and 17 Review
... 32. What subunit does m-RNA bind two? What amino acid does the initiator t-RNA bring? What is the name of the complex that is formed. 33. When the large ribosomal subunit joins the complex, the initiator t-RNA is in which site? 34. What is a codon? 35. What are the two important places on a t-RNA mo ...
... 32. What subunit does m-RNA bind two? What amino acid does the initiator t-RNA bring? What is the name of the complex that is formed. 33. When the large ribosomal subunit joins the complex, the initiator t-RNA is in which site? 34. What is a codon? 35. What are the two important places on a t-RNA mo ...
lecture 47 slides no animations
... Some combinations of torsion angles are much more likely than others Ramachandran plot: shows frequency of (f,y) observed for residues in folded proteins ...
... Some combinations of torsion angles are much more likely than others Ramachandran plot: shows frequency of (f,y) observed for residues in folded proteins ...
GHW#10-Questions
... c. Which amino acid gives an acidic solution? d. Which amino acid gives a basic solution? ...
... c. Which amino acid gives an acidic solution? d. Which amino acid gives a basic solution? ...
Organic and Inorganic Molecules - Cal State LA
... - Very specific for the reaction helped - Enzyme is not consumed during the reaction - Name usually ends in “-ase” - oxidase: adds oxygen - hydrolase: adds water - dehydrogenase: removes hydrogen - aminase: removes amino group - decarboxylase: removes carbon - isomerase: moves position of group on a ...
... - Very specific for the reaction helped - Enzyme is not consumed during the reaction - Name usually ends in “-ase” - oxidase: adds oxygen - hydrolase: adds water - dehydrogenase: removes hydrogen - aminase: removes amino group - decarboxylase: removes carbon - isomerase: moves position of group on a ...
Primary Structure - LaurensAPBiology
... Many biological molecules are macromolecules – huge assemblies of atoms. Biological macromolecules are formed by linking together a set of building blocks (monomers) into long chains (a polymer). ...
... Many biological molecules are macromolecules – huge assemblies of atoms. Biological macromolecules are formed by linking together a set of building blocks (monomers) into long chains (a polymer). ...
Secretory Protein mRNA Finds Another Way Out
... One example of this tendency was the bias for leucines over isoleucines noted above—fewer leucine-encoding codons contain an adenine than do isoleucine-encoding codons. Lastly, within each hydrophobic amino acid there was a bias toward codons lacking adenine (this last bias was seen only in vertebra ...
... One example of this tendency was the bias for leucines over isoleucines noted above—fewer leucine-encoding codons contain an adenine than do isoleucine-encoding codons. Lastly, within each hydrophobic amino acid there was a bias toward codons lacking adenine (this last bias was seen only in vertebra ...
Learning Objectives
... amino acid reacts with the amino group of another amino acid to form an amide bond (also called a peptide bond). This is a condensation reaction! ...
... amino acid reacts with the amino group of another amino acid to form an amide bond (also called a peptide bond). This is a condensation reaction! ...
reduced size
... Basic chemistry and biochemistry - building blocks of biology Remember Star Trek? We are “carbon-based” creatures, as compared to other extraterrestrial races (if any exist)!!! The chemical elements (periodic table) in nature combine in various ways to form molecules (compounds). - most common elem ...
... Basic chemistry and biochemistry - building blocks of biology Remember Star Trek? We are “carbon-based” creatures, as compared to other extraterrestrial races (if any exist)!!! The chemical elements (periodic table) in nature combine in various ways to form molecules (compounds). - most common elem ...
Biology Ch. 12 Vocab
... 5. decoding of a mRNA message into a polypeptide chain 6. copying process by which a cell duplicates its DNA ...
... 5. decoding of a mRNA message into a polypeptide chain 6. copying process by which a cell duplicates its DNA ...
Macromolecules College Notes
... ______________________- formed by hydrogen bonding between the amino acid R groups. (β-pleated sheets and α helix). ______________________ - formed when the polypeptide chain folds and the R groups of different amino acids form covalent and ionic bonds with each other ______________________ - only i ...
... ______________________- formed by hydrogen bonding between the amino acid R groups. (β-pleated sheets and α helix). ______________________ - formed when the polypeptide chain folds and the R groups of different amino acids form covalent and ionic bonds with each other ______________________ - only i ...
Lecture Powerpoint Here
... Causes of Mutations • Exposure to harmful radiation and chemicals in the environment can cause DNA mutations • Genetic defects to genes that repair mutations leave mutations behind in ...
... Causes of Mutations • Exposure to harmful radiation and chemicals in the environment can cause DNA mutations • Genetic defects to genes that repair mutations leave mutations behind in ...
Open Reading Frames and Codon Bias in Streptomyces coelicolor
... sense strand +1, and sense strand +2, respectively. The numbering 3, 4, 5 represent the antisense strand, antisense +1 and antisense +2, respectively. These represent the five additional reading frames. These scripts were also used to tabulate the use of the 64 codons in each of the six reading fram ...
... sense strand +1, and sense strand +2, respectively. The numbering 3, 4, 5 represent the antisense strand, antisense +1 and antisense +2, respectively. These represent the five additional reading frames. These scripts were also used to tabulate the use of the 64 codons in each of the six reading fram ...
Presented
... Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) has a 10-fold higher rate of mutations than that found in nuclear DNA. ...
... Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) has a 10-fold higher rate of mutations than that found in nuclear DNA. ...
Slide 1
... 1. RNA consists of a single strand of nucleotides instead of the two strands found in DNA 2. RNA nucleotides contain the fivecarbon sugar ribose rather than the sugar deoxyribose, which is found in DNA nucleotides 3. In addition to the A, G, and C nitrogen bases found in DNA, RNA nucleotides can hav ...
... 1. RNA consists of a single strand of nucleotides instead of the two strands found in DNA 2. RNA nucleotides contain the fivecarbon sugar ribose rather than the sugar deoxyribose, which is found in DNA nucleotides 3. In addition to the A, G, and C nitrogen bases found in DNA, RNA nucleotides can hav ...
Activity
... Then the mRNA carries this information in the form of a code to the ribosomes, where protein synthesis takes place. The code, in DNA or mRNA, specifies the order in which the amino acids are joined together to form a polypeptide. The code words in mRNA, however, are not directly recognized by the co ...
... Then the mRNA carries this information in the form of a code to the ribosomes, where protein synthesis takes place. The code, in DNA or mRNA, specifies the order in which the amino acids are joined together to form a polypeptide. The code words in mRNA, however, are not directly recognized by the co ...
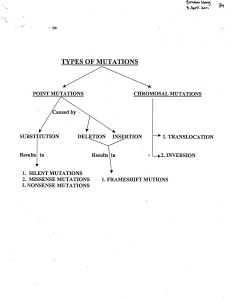
CHROMOSAL MUTATIONS SUBSTITUTION
... effects for an organism. • Some mutations in the genome lead to the developme nt of diseases that may be inherited. Example: Cystic Fibrosis disease is an example of Negative (deleteriou s) Side Effect. Mutations in the Cystic Fibrosis Transmem brane Regulator (CFTR) gene that res~lt in Cystic Fibro ...
... effects for an organism. • Some mutations in the genome lead to the developme nt of diseases that may be inherited. Example: Cystic Fibrosis disease is an example of Negative (deleteriou s) Side Effect. Mutations in the Cystic Fibrosis Transmem brane Regulator (CFTR) gene that res~lt in Cystic Fibro ...
Ch. 5 Biochemistry
... • Lipids with 4 fused carbon rings • Ex: cholesterol: cell membranes; precursor for other steroids (sex hormones); atherosclerosis ...
... • Lipids with 4 fused carbon rings • Ex: cholesterol: cell membranes; precursor for other steroids (sex hormones); atherosclerosis ...
DNA Fill in the blank notes.
... Protein Synthesis or Translation Once a strand of mRNA is made, and moves out of the nucleus, the process of making proteins can begin. This process is called ____________________. The process takes place ‘in ribosomes”. 1. A strand of mRNA is the template for protein synthesis. Each 3 base pairs ...
... Protein Synthesis or Translation Once a strand of mRNA is made, and moves out of the nucleus, the process of making proteins can begin. This process is called ____________________. The process takes place ‘in ribosomes”. 1. A strand of mRNA is the template for protein synthesis. Each 3 base pairs ...
Mutations Worksheet
... Complete the boxes below. Classify each as either Frameshift or Point mutations, then specify further with Deletion, Insertion, or Substitution. Use the chart on the following page in order to determine the amino acid sequence. Remember, RNA has Uracil instead of Thymine. ...
... Complete the boxes below. Classify each as either Frameshift or Point mutations, then specify further with Deletion, Insertion, or Substitution. Use the chart on the following page in order to determine the amino acid sequence. Remember, RNA has Uracil instead of Thymine. ...
Lectures 1-3: Review of forces and elementary statistical
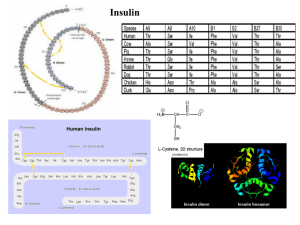
... As described above, human insulin consists of 51 amino acids, divided into two chains, commonly labeled A and B, with 21 and 30 amino acids respectively. The chains are linked by three disulfide bridges, two forming inter-chain cystine at A7-B7 and A20-B19, and one forming an intra-chain cystine at ...
... As described above, human insulin consists of 51 amino acids, divided into two chains, commonly labeled A and B, with 21 and 30 amino acids respectively. The chains are linked by three disulfide bridges, two forming inter-chain cystine at A7-B7 and A20-B19, and one forming an intra-chain cystine at ...
Molecole per la vita
... Triglycerides are lipids that are obtained by means of the esterification reaction between glycerol and fatty acids and form the fatty tissues of animals and plants. Triglycerides may be saturated or unsaturated depending on whether the hydrocarbon chains of the fatty acids contain double bonds or n ...
... Triglycerides are lipids that are obtained by means of the esterification reaction between glycerol and fatty acids and form the fatty tissues of animals and plants. Triglycerides may be saturated or unsaturated depending on whether the hydrocarbon chains of the fatty acids contain double bonds or n ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.