Proteins
... - determined by bonds between side chains (R groups) often between linearly distant amino acids -ionic bonds, disulfide bonds, van der Waals forces, H-bonds - contributes to 3-D conformation ...
... - determined by bonds between side chains (R groups) often between linearly distant amino acids -ionic bonds, disulfide bonds, van der Waals forces, H-bonds - contributes to 3-D conformation ...
bch425 tutorial kit - Covenant University
... (DNA, ATP); Comparative genomes (genetics); Antibiotic resistance; Polymerization of amino acids to proteins; Formation of protobionts and liposomes in laboratory; Slime mold existence as single cells and colonies; Mitochondria seen in eukaroyotes; Universal genetic code; Urey – Miller experiment; C ...
... (DNA, ATP); Comparative genomes (genetics); Antibiotic resistance; Polymerization of amino acids to proteins; Formation of protobionts and liposomes in laboratory; Slime mold existence as single cells and colonies; Mitochondria seen in eukaroyotes; Universal genetic code; Urey – Miller experiment; C ...
File
... b. Cut out all components. c. Arrange the cut-outs so that each monomer creates the correct polymer. (Include equal sign.) d. Tape or glue down your cut-outs. e. Tape or glue down the words “monomers” and “polymer” under correct structure and draw a line from the words to label them more specificall ...
... b. Cut out all components. c. Arrange the cut-outs so that each monomer creates the correct polymer. (Include equal sign.) d. Tape or glue down your cut-outs. e. Tape or glue down the words “monomers” and “polymer” under correct structure and draw a line from the words to label them more specificall ...
9 . What is a gene mutation and how do mutations occur
... What is a gene mutation and how do mutations occur? A gene mutation is a permanent change in the DNA sequence that makes up a gene. Mutations range in size from a single DNA building block (DNA base) to a large segment of a chromosome. Gene mutations occur in two ways: they can be inherited from a p ...
... What is a gene mutation and how do mutations occur? A gene mutation is a permanent change in the DNA sequence that makes up a gene. Mutations range in size from a single DNA building block (DNA base) to a large segment of a chromosome. Gene mutations occur in two ways: they can be inherited from a p ...
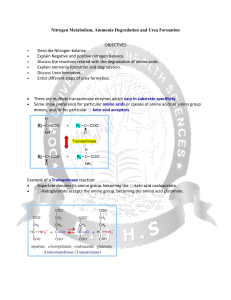
Nitrogen Metabolism, Ammonia Degradation and Urea Formation
... A complete Krebs Cycle functions only within mitochondria. But cytosolic isozymes of some Krebs Cycle enzymes are involved in regenerating aspartate from fumarate. ...
... A complete Krebs Cycle functions only within mitochondria. But cytosolic isozymes of some Krebs Cycle enzymes are involved in regenerating aspartate from fumarate. ...
Continuity of life-forms
... to the genetic processes that all organisms share. All life on Earth, share at least the same 2 structures Nucleic acids (RNA or DNA) carry code for protein synthesis Proteins (all life composed of same 20 amino acids) ...
... to the genetic processes that all organisms share. All life on Earth, share at least the same 2 structures Nucleic acids (RNA or DNA) carry code for protein synthesis Proteins (all life composed of same 20 amino acids) ...
What is a gene mutation and how do mutations occur Article
... What is a gene mutation and how do mutations occur? A gene mutation is a permanent change in the DNA sequence that makes up a gene. Mutations range in size from a single DNA building block (DNA base) to a large segment of a chromosome. Gene mutations occur in two ways: they can be inherited from a p ...
... What is a gene mutation and how do mutations occur? A gene mutation is a permanent change in the DNA sequence that makes up a gene. Mutations range in size from a single DNA building block (DNA base) to a large segment of a chromosome. Gene mutations occur in two ways: they can be inherited from a p ...
Chapter 21 Biosynthesis of amino acids, nucleotides and related
... • Only certain bacteria are able to fix N2 into ammonia (NH3 or NH4+). ...
... • Only certain bacteria are able to fix N2 into ammonia (NH3 or NH4+). ...
Point Mutation
... from GCATCG to GAT CG – mRNA: from CGU AGC to CUA GC – Amino Acid: from Arg Ser to Leu ...
... from GCATCG to GAT CG – mRNA: from CGU AGC to CUA GC – Amino Acid: from Arg Ser to Leu ...
Biochemistry of life
... heart disease The male hormone testosterone and the female hormone estrogen are also steroids ...
... heart disease The male hormone testosterone and the female hormone estrogen are also steroids ...
Organic Macromolecules
... Most plant oils tend to be low in saturated fatty acids & exist as liquids at room temperature (oils) ...
... Most plant oils tend to be low in saturated fatty acids & exist as liquids at room temperature (oils) ...
Replication, Transcription, Translation
... The sequence in an mRNA is a coded sentence that spells out the order in which amino acid residues should be joined to form a protein. Codon A sequence of three ribonucleotides that codes for a specific amino acid or stops translation. Genetic code The sequence of nucleotides, coded in triplets (cod ...
... The sequence in an mRNA is a coded sentence that spells out the order in which amino acid residues should be joined to form a protein. Codon A sequence of three ribonucleotides that codes for a specific amino acid or stops translation. Genetic code The sequence of nucleotides, coded in triplets (cod ...
IS91 transposase is related to the rolling-circle
... from Pseudomonas syringae (3). In particular, their transposases are 35% identical proteins of 426 and 410 amino acids respectively (2,3). Apart from this, IS91 is unrelated to other presently known IS elements. Figure 1 shows the four conserved motifs between the IS91/IS8O1 transposases and a famil ...
... from Pseudomonas syringae (3). In particular, their transposases are 35% identical proteins of 426 and 410 amino acids respectively (2,3). Apart from this, IS91 is unrelated to other presently known IS elements. Figure 1 shows the four conserved motifs between the IS91/IS8O1 transposases and a famil ...
Recently genetic tests for DNA markers for marbling and tenderness
... Microsatellites are stretches of DNA that consist of tandem repeats of a simple sequence of nucleotides (e.g. “AC” repeated 15 times in succession). The tandem repeats tend to vary in number such that it is unlikely two individuals will have the same number of repeats. To date, the molecular markers ...
... Microsatellites are stretches of DNA that consist of tandem repeats of a simple sequence of nucleotides (e.g. “AC” repeated 15 times in succession). The tandem repeats tend to vary in number such that it is unlikely two individuals will have the same number of repeats. To date, the molecular markers ...
Macromolecule/enzyme notes
... 1. DNA = 2 strands wrapped around each other forming a double helix • A pairs with T • C pairs with G Functions: compose genes, determine the structure of proteins 2. RNA = single strand Functions: copy & transfer DNA so proteins can be made ...
... 1. DNA = 2 strands wrapped around each other forming a double helix • A pairs with T • C pairs with G Functions: compose genes, determine the structure of proteins 2. RNA = single strand Functions: copy & transfer DNA so proteins can be made ...
Stephen J. Freeland and Melissa Ilardo – Language Evolution in
... codons (and the nucleotides of which they are composed) are, in the modern system, symbolic signifiers for the amino acids they encode. By the late 1950’s, this much was known (Hoagland, Stephenson, Scott, Hecht & Zamecnik, 1958), and the concept of a truly symbolic code is important to much of what ...
... codons (and the nucleotides of which they are composed) are, in the modern system, symbolic signifiers for the amino acids they encode. By the late 1950’s, this much was known (Hoagland, Stephenson, Scott, Hecht & Zamecnik, 1958), and the concept of a truly symbolic code is important to much of what ...
Picture This
... Nucleic acids are the fourth group of biological macromolecules. Nucleic acids are complex macromolecules that store and transmit genetic information. Repeating subunits, called nucleotides, make up nucleic acids. Nucleotides are composed of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and hydrogen. All nu ...
... Nucleic acids are the fourth group of biological macromolecules. Nucleic acids are complex macromolecules that store and transmit genetic information. Repeating subunits, called nucleotides, make up nucleic acids. Nucleotides are composed of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and hydrogen. All nu ...
Chapter 10 Structure and Function of DNA
... A mutation is any change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA. Mutations can change the amino acids in a protein. Mutations can involve: Large regions of a chromosome Just a single nucleotidepair, as occurs in sickle cell anemia Mutations within a gene can occur as a result of: Base substitutio ...
... A mutation is any change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA. Mutations can change the amino acids in a protein. Mutations can involve: Large regions of a chromosome Just a single nucleotidepair, as occurs in sickle cell anemia Mutations within a gene can occur as a result of: Base substitutio ...
Suggested Project for LEADHER program Name Fadel A. Sharif
... The project results will reveal the genetic causes of many childhood congenital malformations and that is of utmost importance for genetic counseling and future prenatal and preimplantation genetic testing. ...
... The project results will reveal the genetic causes of many childhood congenital malformations and that is of utmost importance for genetic counseling and future prenatal and preimplantation genetic testing. ...
Biology 105
... – Tastes and texture is similar to fats, but as with artificial sweeteners, will not break down along the digestive tract. ...
... – Tastes and texture is similar to fats, but as with artificial sweeteners, will not break down along the digestive tract. ...
Chapter 30: Protein Synthesis
... pairing? 4. What is the structure of ribosomes, and how are they assembled? 5. What are the mechanics of mRNA translation? 6. How are proteins synthesized in eukaryotic cells? ...
... pairing? 4. What is the structure of ribosomes, and how are they assembled? 5. What are the mechanics of mRNA translation? 6. How are proteins synthesized in eukaryotic cells? ...
A.P. Biology Summer Work: Worksheet
... organic compounds, so carbon is essential to life on Earth. Without carbon, life as we know it could not exist. Why is carbon so basic to life? The reason is carbon’s ability to form stable bonds with many elements, including itself. This property allows carbon to form a huge variety of very large a ...
... organic compounds, so carbon is essential to life on Earth. Without carbon, life as we know it could not exist. Why is carbon so basic to life? The reason is carbon’s ability to form stable bonds with many elements, including itself. This property allows carbon to form a huge variety of very large a ...
Problem Set 3 Solution
... 2nd amino acid into the nascent polypeptide. The 2nd codon is 5’UUA3’ so the corresponding anticodon on the tRNA should be 3’AAU3’ and the codon – anticodon should undergo complementary base pairing. d) Would a 3rd base substitution within the codon for the second amino acid in the above mRNA transc ...
... 2nd amino acid into the nascent polypeptide. The 2nd codon is 5’UUA3’ so the corresponding anticodon on the tRNA should be 3’AAU3’ and the codon – anticodon should undergo complementary base pairing. d) Would a 3rd base substitution within the codon for the second amino acid in the above mRNA transc ...
Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the
... conserved in all /3',A (respectively A') subunits of bacterial, eucaryal and archaeal RNA polymerases known so far (3, 4, 5). Frequently, an oligonucleotide primer derived from this sequence, specifically hybridized to three G. lamblia chromosomal DNA fragments, whether digested with Sad, Aval, BamH ...
... conserved in all /3',A (respectively A') subunits of bacterial, eucaryal and archaeal RNA polymerases known so far (3, 4, 5). Frequently, an oligonucleotide primer derived from this sequence, specifically hybridized to three G. lamblia chromosomal DNA fragments, whether digested with Sad, Aval, BamH ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.