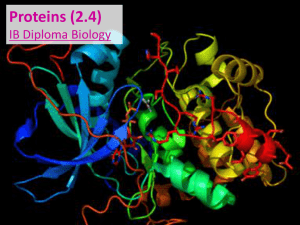
Mutations, Karyotyping, Pedigrees
... Occurs during crossing over and one chromosome ends up with more genes than it received. ...
... Occurs during crossing over and one chromosome ends up with more genes than it received. ...
10.6AC The Pattern - Texarkana Independent School District
... What is the major difference between a DNA nucleotide and an RNA nucleotide? Deoxyribose sugar is in DNA and ribose sugar is in RNA. May also include uracil substitutes for thymine in RNA. Why is mRNA single-stranded? So it can leave the nucleus. Double-stranded DNA cannot fit through the nuclear me ...
... What is the major difference between a DNA nucleotide and an RNA nucleotide? Deoxyribose sugar is in DNA and ribose sugar is in RNA. May also include uracil substitutes for thymine in RNA. Why is mRNA single-stranded? So it can leave the nucleus. Double-stranded DNA cannot fit through the nuclear me ...
Product Information Sheet
... Provides 100mg of l-theanine per tablet, an amino acid commonly found in tea. Supplies a highly concentrated dose in just one tablet. ...
... Provides 100mg of l-theanine per tablet, an amino acid commonly found in tea. Supplies a highly concentrated dose in just one tablet. ...
Biology - cloudfront.net
... karyotype to identify mutations or genetic disorders) What is a mutation? What are some sources of mutagens? At which two levels can mutation occur in the cells? What is the difference between point mutation and frameshift mutation? Give an example of the following mutation: inversion, deletion, and ...
... karyotype to identify mutations or genetic disorders) What is a mutation? What are some sources of mutagens? At which two levels can mutation occur in the cells? What is the difference between point mutation and frameshift mutation? Give an example of the following mutation: inversion, deletion, and ...
2_4 Slides
... But before they are functional, they must fold into specific structures based on the order / structure of their amino acid sequence. Remember, different amino acids have different chemical properties (i.e. polar / hydrophilic, non-polar / hydrophobic, +/charged, sulfur-containing, carbon rings, etc. ...
... But before they are functional, they must fold into specific structures based on the order / structure of their amino acid sequence. Remember, different amino acids have different chemical properties (i.e. polar / hydrophilic, non-polar / hydrophobic, +/charged, sulfur-containing, carbon rings, etc. ...
Genetics Review
... CGG CCC AAT to CGG CGC CAA T • Frame shift mutations have greater effects than a point mutation because they involve more triplets (recall how important triplets are to protein synthesis) ...
... CGG CCC AAT to CGG CGC CAA T • Frame shift mutations have greater effects than a point mutation because they involve more triplets (recall how important triplets are to protein synthesis) ...
Lecture 3
... Folds in polypeptide that form a more stable structure, often involving hydrogen bonding between R groups There are two types of secondary structure: Helical structure called an alpha helix (α-helix) (region of polypeptide chain coils around itself Pleated sheet (β sheet(: two parts of polypeptide c ...
... Folds in polypeptide that form a more stable structure, often involving hydrogen bonding between R groups There are two types of secondary structure: Helical structure called an alpha helix (α-helix) (region of polypeptide chain coils around itself Pleated sheet (β sheet(: two parts of polypeptide c ...
Document
... What ended up happening to Walter Gilbert’s team and their discovery of the insulin gene? ...
... What ended up happening to Walter Gilbert’s team and their discovery of the insulin gene? ...
Macromolecules For Identification
... • The different amino acids are similar in structure. • The different amino acids have different side chain, but are otherwise identical. • Proteins have many important roles in organisms. Structural proteins such as collagen or elastin, provide support. Regulatory proteins such as enzymes control c ...
... • The different amino acids are similar in structure. • The different amino acids have different side chain, but are otherwise identical. • Proteins have many important roles in organisms. Structural proteins such as collagen or elastin, provide support. Regulatory proteins such as enzymes control c ...
HW Questions on Lipids and Proteins
... Trans fats are linked to high LDL (bad) cholesterol, higher risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. 28. Which atoms are found in proteins? __CHON (S)_____ 29. Protein molecules are polymers. What is the basic component (or monomer) of a protein molecule? Amino Acid 30. What two functiona ...
... Trans fats are linked to high LDL (bad) cholesterol, higher risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. 28. Which atoms are found in proteins? __CHON (S)_____ 29. Protein molecules are polymers. What is the basic component (or monomer) of a protein molecule? Amino Acid 30. What two functiona ...
Exam 3
... involves a transfer of amino acids to an elongating chain. requires DNA ligase to seal DNA fragments. is a DNA-dependent RNA synthesis process. involves releasing factors. begins with a start codon. requires a promoter sequence. produces Okazaki fragments is a DNA-dependent DNA synthesis process. ...
... involves a transfer of amino acids to an elongating chain. requires DNA ligase to seal DNA fragments. is a DNA-dependent RNA synthesis process. involves releasing factors. begins with a start codon. requires a promoter sequence. produces Okazaki fragments is a DNA-dependent DNA synthesis process. ...
PCR - Polymerase Chain Reaction
... for proteins constructed at ribosomes • So – in an environmental/geological context, what is that info used for?? ...
... for proteins constructed at ribosomes • So – in an environmental/geological context, what is that info used for?? ...
The Central Dogma - Assets - Cambridge University Press
... Each of us has observed physical and other similarities among members of human families. While some of these similarities are due to the common environment these families share, others are inherited, that is, passed on from parent to child as part of the reproductive process. Traits such as eye colo ...
... Each of us has observed physical and other similarities among members of human families. While some of these similarities are due to the common environment these families share, others are inherited, that is, passed on from parent to child as part of the reproductive process. Traits such as eye colo ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... vitamins. All other food and drink were to be avoided. People on this diet typically lost 10 to 14 lb in the first week. (a) Opponents argued that the weight loss was almost entirely due to water loss and would be regained very soonafter a normal diet was resumed. What is the biochemical basis for t ...
... vitamins. All other food and drink were to be avoided. People on this diet typically lost 10 to 14 lb in the first week. (a) Opponents argued that the weight loss was almost entirely due to water loss and would be regained very soonafter a normal diet was resumed. What is the biochemical basis for t ...
chapter 11, 12, 13 practice questions
... change? What kind of mutation is this (point mutation or frameshift mutation)? F) Delete the 7th base in the original strand of DNA. How many amino acids are affected in the change? What kind of mutation is this (point mutation or frameshift mutation)? 2. Refer to Figure 11.12 on pg. 300 and describ ...
... change? What kind of mutation is this (point mutation or frameshift mutation)? F) Delete the 7th base in the original strand of DNA. How many amino acids are affected in the change? What kind of mutation is this (point mutation or frameshift mutation)? 2. Refer to Figure 11.12 on pg. 300 and describ ...
Slayt 1
... M-RNA is not polyadenylated No IRES in eukaryotes No introns in prokayotes (except some bacteriophages) ...
... M-RNA is not polyadenylated No IRES in eukaryotes No introns in prokayotes (except some bacteriophages) ...
Teaching DNA, Proteins, and Protein Synthesis
... Learn about amino acid side chains and construct primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary protein structures with the LEGO amino acids. ...
... Learn about amino acid side chains and construct primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary protein structures with the LEGO amino acids. ...
DNA Biology
... prior to cell division. Enzymes are responsible for each step of replication, including proofreading. The helix unwinds, separates, and each half acts as a template for the formation of a new complementary strand. ...
... prior to cell division. Enzymes are responsible for each step of replication, including proofreading. The helix unwinds, separates, and each half acts as a template for the formation of a new complementary strand. ...
the essence of life
... RNA • Is a single stranded nucleic acid that is the intermediate agent in production of proteins • Components of RNA are similar to that of DNA, except uracil (U) is substituted for thymine (T) • There are several kinds of RNA, including – Messenger mRNA ...
... RNA • Is a single stranded nucleic acid that is the intermediate agent in production of proteins • Components of RNA are similar to that of DNA, except uracil (U) is substituted for thymine (T) • There are several kinds of RNA, including – Messenger mRNA ...
word - marric
... pairs are incorrectly matched (e.g., A bonded to C rather than A bonded to T) and can, but usually do not, improve the product coded by the gene. Inserting or deleting base pairs in an existing gene can cause a mutation by changing the codon reading frame used by a ribosome. Mutations that occur in ...
... pairs are incorrectly matched (e.g., A bonded to C rather than A bonded to T) and can, but usually do not, improve the product coded by the gene. Inserting or deleting base pairs in an existing gene can cause a mutation by changing the codon reading frame used by a ribosome. Mutations that occur in ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... specific ligand as part of a membrane or another molecule. Thus, in the study of proteins, you will hear of catalytic domains, DNA-binding domains, and so on. The result is that a protein must be looked at as being composed of a series of structural and functional modules. Obviously, the presence of ...
... specific ligand as part of a membrane or another molecule. Thus, in the study of proteins, you will hear of catalytic domains, DNA-binding domains, and so on. The result is that a protein must be looked at as being composed of a series of structural and functional modules. Obviously, the presence of ...
Highlight Review – Common Assessment #4 Multiple Choice
... ____ 21. During transcription, the genetic information for making a protein is “rewritten” as a molecule of a. messenger RNA. c. transfer RNA. b. ribosomal RNA. d. translation RNA. ____ 22. Which type(s) of RNA is(are) involved in protein synthesis? a. transfer RNA only b.messenger RNA only c. ribos ...
... ____ 21. During transcription, the genetic information for making a protein is “rewritten” as a molecule of a. messenger RNA. c. transfer RNA. b. ribosomal RNA. d. translation RNA. ____ 22. Which type(s) of RNA is(are) involved in protein synthesis? a. transfer RNA only b.messenger RNA only c. ribos ...
Document
... A protein superfamily comprises set of protein sequences that are evolutionary and therefore functionally and structurally related Protein sequences in a family share some common motifs Two protein sequences are assigned to the same class if they have high homology in the sequence level (e.g., c ...
... A protein superfamily comprises set of protein sequences that are evolutionary and therefore functionally and structurally related Protein sequences in a family share some common motifs Two protein sequences are assigned to the same class if they have high homology in the sequence level (e.g., c ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.