JournalClub1
... The importance of CD4 T-cells • Differences of CD4 T-cell count reflect not only the quantity of mutations, but differences in the mutations that may be best suited to the host environment • Higher levels of genetic diversity is most frequently associated with more rapid CD4 T-cell decline ...
... The importance of CD4 T-cells • Differences of CD4 T-cell count reflect not only the quantity of mutations, but differences in the mutations that may be best suited to the host environment • Higher levels of genetic diversity is most frequently associated with more rapid CD4 T-cell decline ...
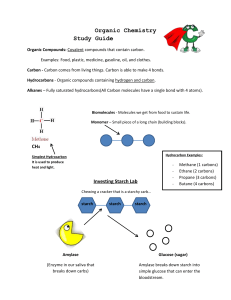
Organic Chemistry Study Guide Organic Compounds: Covalent
... Examples: Food, plastic, medicine, gasoline, oil, and clothes. Carbon - Carbon comes from living things. Carbon is able to make 4 bonds. Hydrocarbons - Organic compounds containing hydrogen and carbon. Alkanes – Fully saturated hydrocarbons(All Carbon molecules have a single bond with 4 atoms). ...
... Examples: Food, plastic, medicine, gasoline, oil, and clothes. Carbon - Carbon comes from living things. Carbon is able to make 4 bonds. Hydrocarbons - Organic compounds containing hydrogen and carbon. Alkanes – Fully saturated hydrocarbons(All Carbon molecules have a single bond with 4 atoms). ...
Evolution: An Introduction
... • Occurs in the cells that give rise to gametes (sperm and egg cells) • Are heritable (which means that they can be passed on to the offspring) ...
... • Occurs in the cells that give rise to gametes (sperm and egg cells) • Are heritable (which means that they can be passed on to the offspring) ...
Gel electrophoresis
... A gene is a discrete unit of hereditary information that usually specifies a protein. A single gene provides the genetic code for only one polypeptide. Thus, a protein consisting of four polypeptides requires the interaction of four genes to synthesize that specific protein. ...
... A gene is a discrete unit of hereditary information that usually specifies a protein. A single gene provides the genetic code for only one polypeptide. Thus, a protein consisting of four polypeptides requires the interaction of four genes to synthesize that specific protein. ...
2054, Chap. 12, page 1 I. Genes: Expression and Regulation A
... Amino acid + tRNA + ATP ÷ aminoacyl-tRNA + AMP + PPi b. at least 20 aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (1) no proofreading function in protein synthesis (2) aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases can proofread and will hydrolyze amino acid from tRNA is incorrect c. anticodon triplet complementary to mRNA codon 3. Ribos ...
... Amino acid + tRNA + ATP ÷ aminoacyl-tRNA + AMP + PPi b. at least 20 aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (1) no proofreading function in protein synthesis (2) aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases can proofread and will hydrolyze amino acid from tRNA is incorrect c. anticodon triplet complementary to mRNA codon 3. Ribos ...
Exemplar exam questions – Chapter 7
... and the candidate has said why they are important and so has ‘discussed’ them. Marks awarded for any four of the following: Solubility depends on the R groups present on the amino acids. Proteins with many polar R groups are more soluble. Proteins with hydrophilic (polar) side groups on the outside ...
... and the candidate has said why they are important and so has ‘discussed’ them. Marks awarded for any four of the following: Solubility depends on the R groups present on the amino acids. Proteins with many polar R groups are more soluble. Proteins with hydrophilic (polar) side groups on the outside ...
Exemplar exam questions – Chapter 7, Nucleic acids and proteins
... and the candidate has said why they are important and so has ‘discussed’ them. Marks awarded for any four of the following: Solubility depends on the R groups present on the amino acids. Proteins with many polar R groups are more soluble. Proteins with hydrophilic (polar) side groups on the outside ...
... and the candidate has said why they are important and so has ‘discussed’ them. Marks awarded for any four of the following: Solubility depends on the R groups present on the amino acids. Proteins with many polar R groups are more soluble. Proteins with hydrophilic (polar) side groups on the outside ...
insilico.mutagenesis.help.me.please
... The program asks you to provide your target nucleotide sequence (1), which includes flanking vector sequences up-and downstream of the gene (or target region: e.g. untranslated intergenic regions like promotors) of interest. Please provide a plain nucleotide sequence. All non-DNA characters (e.g. as ...
... The program asks you to provide your target nucleotide sequence (1), which includes flanking vector sequences up-and downstream of the gene (or target region: e.g. untranslated intergenic regions like promotors) of interest. Please provide a plain nucleotide sequence. All non-DNA characters (e.g. as ...
Biological Chemistry
... of another (-OC-NH-) 1. ___peptide - __ bonded amino acids 2. ______peptide – 10-15 bonded amino acids 3. ______peptide – more than 15 bonded amino acids 4. ____________ – polypeptide of 50 or more amino acids E. Levels of Protein Organization 1. _________ Structure - linear sequence of amino acids ...
... of another (-OC-NH-) 1. ___peptide - __ bonded amino acids 2. ______peptide – 10-15 bonded amino acids 3. ______peptide – more than 15 bonded amino acids 4. ____________ – polypeptide of 50 or more amino acids E. Levels of Protein Organization 1. _________ Structure - linear sequence of amino acids ...
Chalkboard Challenge
... 9 of 21) Which organelle (pictured below) carries ribosomes and proteins around within the cell? ...
... 9 of 21) Which organelle (pictured below) carries ribosomes and proteins around within the cell? ...
Chapter 17 Practice Multple Choice
... d. a DNA—RNA sequence combination that results in an enzymatic product e. a discrete unit of hereditary information that consists of a sequence of amino acids ____ 23. The anticodon of a particular tRNA molecule is a. complementary to the corresponding mRNA codon. b. complementary to the correspond ...
... d. a DNA—RNA sequence combination that results in an enzymatic product e. a discrete unit of hereditary information that consists of a sequence of amino acids ____ 23. The anticodon of a particular tRNA molecule is a. complementary to the corresponding mRNA codon. b. complementary to the correspond ...
AP Biology – Molecular Genetics (Chapters 14-17)
... c. three base code (43) = a three base code will produce 64 possibilities, more than enough 2. codon = 3 bases found on mRNA a. 3 “stop” codons b. 1 “start” codon c. third base in the codon is often less specific than the first two d. several codons can code for the same amino acid (degenerate) 3. g ...
... c. three base code (43) = a three base code will produce 64 possibilities, more than enough 2. codon = 3 bases found on mRNA a. 3 “stop” codons b. 1 “start” codon c. third base in the codon is often less specific than the first two d. several codons can code for the same amino acid (degenerate) 3. g ...
Transcription & Translation
... – Making Proteins from RNA – amino acids are assembled from information encoded in mRNA 1. mRNA codons move through the ribosome 2. tRNAs add specific amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain 3. Process continues until a stop codon is reached 4. Newly made protein is released ...
... – Making Proteins from RNA – amino acids are assembled from information encoded in mRNA 1. mRNA codons move through the ribosome 2. tRNAs add specific amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain 3. Process continues until a stop codon is reached 4. Newly made protein is released ...
Acid - Perkins Science
... If blood pH goes up, e.g. excessive vomiting and loss of gastric HCl, then: Carbonic acid (H2CO3) ...
... If blood pH goes up, e.g. excessive vomiting and loss of gastric HCl, then: Carbonic acid (H2CO3) ...
A Zero-Knowledge Based Introduction to Biology
... ($300,000 DARPA project – 2002) “ Once the entire sequence was replicated, it was reconverted into RNA by enzymatic means. Viral propagation and replication were accomplished by throwing the virus into a predesigned protein soup that contained all the polymerases and other enzymatic ingredients nece ...
... ($300,000 DARPA project – 2002) “ Once the entire sequence was replicated, it was reconverted into RNA by enzymatic means. Viral propagation and replication were accomplished by throwing the virus into a predesigned protein soup that contained all the polymerases and other enzymatic ingredients nece ...
File
... I. Chemistry of Carbon • Characteristics of Carbon: 1. Carbon atoms have 4 valence electrons 2. Each electron can join with an electron from another atom to form a strong covalent bond 3. Carbon can bond with many elements such as ...
... I. Chemistry of Carbon • Characteristics of Carbon: 1. Carbon atoms have 4 valence electrons 2. Each electron can join with an electron from another atom to form a strong covalent bond 3. Carbon can bond with many elements such as ...
CH 5 - shsbiology
... • Carbon & water are most important biomolecules to life • Carbon has 4 e- in highest energy level – Can therefore make 4 bonds with other atoms – Carbon bonds with other carbons in various ...
... • Carbon & water are most important biomolecules to life • Carbon has 4 e- in highest energy level – Can therefore make 4 bonds with other atoms – Carbon bonds with other carbons in various ...
Review 3
... (deoxy)ribonucleotides • Carbamoyl phosphate and urea • Pyruvate, oxaloacetate, a-ketoglutarate • PRPP ...
... (deoxy)ribonucleotides • Carbamoyl phosphate and urea • Pyruvate, oxaloacetate, a-ketoglutarate • PRPP ...
Mutations - Miss Garry`s Biology Class Website!
... b. Beneficial effect phenotype is affected. The organism is better adapted to its environment c. Harmful effect phenotype is different. The organism is less adapted to it environment ...
... b. Beneficial effect phenotype is affected. The organism is better adapted to its environment c. Harmful effect phenotype is different. The organism is less adapted to it environment ...
What`s a Designer baby? What is PGD? The term `designer baby
... In vitro fertilization (IVF) technique involves the fertilization of the egg by the sperm in test tubes, outside the mother's body. This allows doctors to screen the embryos. Genetic screening has made it possible to eliminate genes associated with several genetic defects and terminal illnesses. A r ...
... In vitro fertilization (IVF) technique involves the fertilization of the egg by the sperm in test tubes, outside the mother's body. This allows doctors to screen the embryos. Genetic screening has made it possible to eliminate genes associated with several genetic defects and terminal illnesses. A r ...
nucleic acid - 4J Blog Server
... • The major function of fats is energy storage • Fat is a compact way for animals to carry their energy stores with them ...
... • The major function of fats is energy storage • Fat is a compact way for animals to carry their energy stores with them ...
Biochemistry - El Camino College
... A. Structural proteins - give strength and shape to different tissues (e.g.: keratin in hair & nails, collagen in connective tissues, _________ proteins, etc.) ...
... A. Structural proteins - give strength and shape to different tissues (e.g.: keratin in hair & nails, collagen in connective tissues, _________ proteins, etc.) ...
Syllabus Checklist
... Mitochondrial DNA is believed to control the production of proteins which are involved in respiration. Which sex contributes this DNA to the offspring? ...
... Mitochondrial DNA is believed to control the production of proteins which are involved in respiration. Which sex contributes this DNA to the offspring? ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.