Replication vs. Transcription vs. Translation
... 3. tRNA molecules bring the amino acids to the ribosome and connect them in a chain. 4. The sequence of nucleotides on the mRNA strand determines which amino acid will be added to the amino acid chain. ...
... 3. tRNA molecules bring the amino acids to the ribosome and connect them in a chain. 4. The sequence of nucleotides on the mRNA strand determines which amino acid will be added to the amino acid chain. ...
Ch4Carbonand5Macromolecules
... • Amino acids are linked together by condensation to form polypeptides. • There are 20 different amino acids in polypeptides synthesized on ribosomes. • Amino acids can be linked together in any sequence giving a huge range of possible polypeptides. • The amino acid sequence of polypeptides is coded ...
... • Amino acids are linked together by condensation to form polypeptides. • There are 20 different amino acids in polypeptides synthesized on ribosomes. • Amino acids can be linked together in any sequence giving a huge range of possible polypeptides. • The amino acid sequence of polypeptides is coded ...
tRNA
... Trp)—ie the genetic code is degenerate! - Of the 64 codons, only 61 encode amino acids—the other three serve as “nonsense” or “stop” codons in that they do not specify an amino acid but rather signal the end of the polypeptide chain when encountered by the ribosomal translational machinery - On the ...
... Trp)—ie the genetic code is degenerate! - Of the 64 codons, only 61 encode amino acids—the other three serve as “nonsense” or “stop” codons in that they do not specify an amino acid but rather signal the end of the polypeptide chain when encountered by the ribosomal translational machinery - On the ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... – Recognition helices of each repressor monomer nestle into the DNA major grooves in the 2 half-sites – Helices approach each other to hold the two monomers together in the repressor dimer – DNA is similar in shape to B-form DNA – Bending of DNA at the two ends of the DNA fragment as it curves aroun ...
... – Recognition helices of each repressor monomer nestle into the DNA major grooves in the 2 half-sites – Helices approach each other to hold the two monomers together in the repressor dimer – DNA is similar in shape to B-form DNA – Bending of DNA at the two ends of the DNA fragment as it curves aroun ...
DNA and genetic information
... • "words" (codons or triplets) are 3 letters long in genetic code • each group of 3 nucleotides corresponds to one amino acid. • A nucleotide sequence (sequence of codons) can be “translated” into an amino acid sequence, i.e., a peptide or protein ...
... • "words" (codons or triplets) are 3 letters long in genetic code • each group of 3 nucleotides corresponds to one amino acid. • A nucleotide sequence (sequence of codons) can be “translated” into an amino acid sequence, i.e., a peptide or protein ...
Gel electrophoresis - University of California, Santa Barbara
... translated into amino acid sequences • The “words” of the DNA “language” are triplets of bases called codons – 3 bases or nucleotides make one codon – Each codon specifies an amino acid – The codons in a gene specify the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide ...
... translated into amino acid sequences • The “words” of the DNA “language” are triplets of bases called codons – 3 bases or nucleotides make one codon – Each codon specifies an amino acid – The codons in a gene specify the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide ...
Supplementary Figure Legends - Word file
... residues are predominantly located between position 224 and 294, accounting for 32.4% of all amino acid residues within that region. ...
... residues are predominantly located between position 224 and 294, accounting for 32.4% of all amino acid residues within that region. ...
Reading Guide: The Origins of Life
... and extended this research. They have tested a variety of assumptions about available atmospheric gases and energy sources. Under many different conditions, these experiments have produced all 20 amino acids, several sugars, lipids, and even ATP. Leslie Orgle proved that the nitrogenous bases found ...
... and extended this research. They have tested a variety of assumptions about available atmospheric gases and energy sources. Under many different conditions, these experiments have produced all 20 amino acids, several sugars, lipids, and even ATP. Leslie Orgle proved that the nitrogenous bases found ...
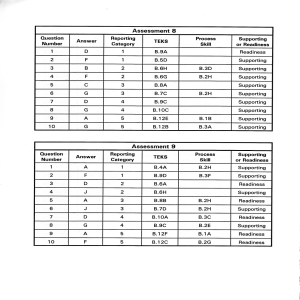
Assessment 8 Assessment I
... formed in cells into water and oxygen gas. Andi conducts an investigation to test her hypothesis that catalase is most active around 37"C, the average body temperature of many mammals. To test her hypothesis, Andi saturates a filter-paper disk with catalase obtained from liver. Wearing safety gloves ...
... formed in cells into water and oxygen gas. Andi conducts an investigation to test her hypothesis that catalase is most active around 37"C, the average body temperature of many mammals. To test her hypothesis, Andi saturates a filter-paper disk with catalase obtained from liver. Wearing safety gloves ...
171392_ProteinSyn
... and how the Nucleus uses it to control the cell. Why should you know about it? Because I say so!!! Just kidding. Really this process is one of the secrets of life so pay close attention. Today, ideas that are written in RED you should write down in your notes. Of course you can write down more if yo ...
... and how the Nucleus uses it to control the cell. Why should you know about it? Because I say so!!! Just kidding. Really this process is one of the secrets of life so pay close attention. Today, ideas that are written in RED you should write down in your notes. Of course you can write down more if yo ...
File
... For transcription, include both DNA strands and mRNA. Correctly base pair the nucleotides in your drawing. Label RNA polymerase, free nucleotides, the DNA template strand, the direction of transcription, and the orientation of the DNA and RNA strands (5’ or 3’). For translation, include an mRNA stra ...
... For transcription, include both DNA strands and mRNA. Correctly base pair the nucleotides in your drawing. Label RNA polymerase, free nucleotides, the DNA template strand, the direction of transcription, and the orientation of the DNA and RNA strands (5’ or 3’). For translation, include an mRNA stra ...
Name Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological
... 8. In terms of glycosidic linkages, what makes cellulose much more difficult to digest than starch? 9. Name the additional functional groups found in chitin. 10. What are the consequences of lipids having small polar regions and large domains of carbons and hydrogen? 11. Fats are often referred to a ...
... 8. In terms of glycosidic linkages, what makes cellulose much more difficult to digest than starch? 9. Name the additional functional groups found in chitin. 10. What are the consequences of lipids having small polar regions and large domains of carbons and hydrogen? 11. Fats are often referred to a ...
SB2a Build DNA using the Nucleotides Then Print
... molecule in half by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the bases so that transcription can occur. Copy and paste the nucleotides from a previous slide to show how transcription occurs. RNA nucleotides are provided below to build your mRNA strand between the DNA strands using the top DNA strand as a ...
... molecule in half by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the bases so that transcription can occur. Copy and paste the nucleotides from a previous slide to show how transcription occurs. RNA nucleotides are provided below to build your mRNA strand between the DNA strands using the top DNA strand as a ...
Give an account of gene mutation under the following
... 6. Gene mutation is a change in the bases/base type/base sequence/base order (nucleotide can be taken to be equivalent to base) 7. Substitution: base/bases are replaced with another/others 8. Inversion: order of bases reversed/bases turned around 9. Substitution/inversion may change base order of co ...
... 6. Gene mutation is a change in the bases/base type/base sequence/base order (nucleotide can be taken to be equivalent to base) 7. Substitution: base/bases are replaced with another/others 8. Inversion: order of bases reversed/bases turned around 9. Substitution/inversion may change base order of co ...
Protein Synthesis Project
... b. Explain the structural effect that this point mutation has on the hemoglobin protein. ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... b. Explain the structural effect that this point mutation has on the hemoglobin protein. ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Molecules to Eye Color - Springfield School District
... 2 identical strands of DNA An enzyme called DNA polymerase “unzips” the two strands by breaking the H-bonds. Nucleotides with complimentary bases are attached to the exposed strands ...
... 2 identical strands of DNA An enzyme called DNA polymerase “unzips” the two strands by breaking the H-bonds. Nucleotides with complimentary bases are attached to the exposed strands ...
Nutrients & Assessments
... Iron combines with protein to form hemoglobin Iodine is needed by thyroid gland to produce thyroxine Copper is necessary in the formation of hemoglobin Fluorine helps reduce incidence of tooth decay Zinc plays an important role in the formation of protein, thus, assists in wound healing, blood forma ...
... Iron combines with protein to form hemoglobin Iodine is needed by thyroid gland to produce thyroxine Copper is necessary in the formation of hemoglobin Fluorine helps reduce incidence of tooth decay Zinc plays an important role in the formation of protein, thus, assists in wound healing, blood forma ...
Topic 2.4 Proteins Notes 2.4 Proteins 14-15
... • sites on the two arms bind to the antigen on pathogens (bacteria), the other parts act as a marker for phagocytes to engulf the pathogen • Body produces a range with different types of binding ...
... • sites on the two arms bind to the antigen on pathogens (bacteria), the other parts act as a marker for phagocytes to engulf the pathogen • Body produces a range with different types of binding ...
macromolecule notes
... 1.) ________________________ compounds- Contain ______________ and __________________ atoms 2.) ________________________ compounds- Can have one or the other, but do not contain both carbon and hydrogen atoms A. Most of your body’s molecules are _______________________ compounds. a. ________________ ...
... 1.) ________________________ compounds- Contain ______________ and __________________ atoms 2.) ________________________ compounds- Can have one or the other, but do not contain both carbon and hydrogen atoms A. Most of your body’s molecules are _______________________ compounds. a. ________________ ...
Gene Expression
... into a sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide • NOTE: the mRNA is not “turned into” protein! ...
... into a sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide • NOTE: the mRNA is not “turned into” protein! ...
A1984SY56700001
... ensued. The Zurich group synthesised a series of active ester derivatives which we tested as routes for incorporating 125J into pro. (ems. The N-hydroxysuccinimide 2 ester of p-hydroxyphenyl propionic acid, which re- ...
... ensued. The Zurich group synthesised a series of active ester derivatives which we tested as routes for incorporating 125J into pro. (ems. The N-hydroxysuccinimide 2 ester of p-hydroxyphenyl propionic acid, which re- ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... 2. is a problem in species that have more autosomes than sex chromosomes. 3. cannot be directed by enhancing X-chromosome activity. 4. works in the same way in all animals. ...
... 2. is a problem in species that have more autosomes than sex chromosomes. 3. cannot be directed by enhancing X-chromosome activity. 4. works in the same way in all animals. ...
RNA and Protein
... What are the 3 types of RNA? What is the function of each? mRNA – messenger RNA carries genetic information from DNA in the nucleus to direct protein synthesis in the cytoplasm. ...
... What are the 3 types of RNA? What is the function of each? mRNA – messenger RNA carries genetic information from DNA in the nucleus to direct protein synthesis in the cytoplasm. ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.