DNA - PROTEIN SYNTHESIS: Quick Check In this activity, you have
... DNA - PROTEIN SYNTHESIS: Quick Check In this activity, you have done DNA translation as a code-deciphering process, but you were asked to follow intermediate steps much the way molecular intermediaries in our cells do it. In order to check your understanding of the cellular players in the real proce ...
... DNA - PROTEIN SYNTHESIS: Quick Check In this activity, you have done DNA translation as a code-deciphering process, but you were asked to follow intermediate steps much the way molecular intermediaries in our cells do it. In order to check your understanding of the cellular players in the real proce ...
Notes
... Translation (in cytoplasm): mRNA amino acids (protein) mRNA serves as instructions to create an amino acid sequence, or protein. If the “instructions” are changed, the protein created may also change. Ribosome (rRNA): Codon: Anticodon: Steps: ...
... Translation (in cytoplasm): mRNA amino acids (protein) mRNA serves as instructions to create an amino acid sequence, or protein. If the “instructions” are changed, the protein created may also change. Ribosome (rRNA): Codon: Anticodon: Steps: ...
DNA and Genes student
... The effects of point mutations • A point mutation is a change in a single base pair in DNA. • A change in a single nitrogenous base can change the entire structure of a protein because a change in a single amino acid can affect the shape of the protein. ...
... The effects of point mutations • A point mutation is a change in a single base pair in DNA. • A change in a single nitrogenous base can change the entire structure of a protein because a change in a single amino acid can affect the shape of the protein. ...
NCEA Level 2 Biology (91159) 2015
... affected by the environmental conditions that exist internally or externally for an organism without the genotype itself being altered in any way. The genotype provides the instruction set for a particular protein or function, but this may not be able to be fully expressed / reach its maximum geneti ...
... affected by the environmental conditions that exist internally or externally for an organism without the genotype itself being altered in any way. The genotype provides the instruction set for a particular protein or function, but this may not be able to be fully expressed / reach its maximum geneti ...
ppt - Language Log
... determine human biology and provides the basic background for human variation ...
... determine human biology and provides the basic background for human variation ...
2.1 Molecules to metabolim
... 2.1.A1 Urea as an example of a compound that is produced by living organisms but can also be artificially synthesized. Nature of Science: Falsification of theories—the artificial synthesis of urea helped to falsify vitalism. (1.9) Wöhler accidentally synthesised urea in 1828, whilst attempting to p ...
... 2.1.A1 Urea as an example of a compound that is produced by living organisms but can also be artificially synthesized. Nature of Science: Falsification of theories—the artificial synthesis of urea helped to falsify vitalism. (1.9) Wöhler accidentally synthesised urea in 1828, whilst attempting to p ...
Digestive System
... leaves through the same opening. • These organisms must finish digesting before eating again. ...
... leaves through the same opening. • These organisms must finish digesting before eating again. ...
Chapter 3
... regular, repeated patterns in different regions in the polypeptide chain. • This shape is influenced primarily by hydrogen bonds arising from the amino acid sequence (the primary structure). • The two common secondary structures are the a helix and the b pleated sheet. ...
... regular, repeated patterns in different regions in the polypeptide chain. • This shape is influenced primarily by hydrogen bonds arising from the amino acid sequence (the primary structure). • The two common secondary structures are the a helix and the b pleated sheet. ...
Gene Structure: Searching Genbank and Interpreting
... 62206 is mutated from a normal ‘a’ nucleotide to ‘t’ in the sickle cell anemia from. Normally the amino acid glutanic acid is in the beta chain of hemoglobin, in the mutant form it is substituted by valine. (10) What is the difference between the normal beta-globin protein and the beta-globin thalas ...
... 62206 is mutated from a normal ‘a’ nucleotide to ‘t’ in the sickle cell anemia from. Normally the amino acid glutanic acid is in the beta chain of hemoglobin, in the mutant form it is substituted by valine. (10) What is the difference between the normal beta-globin protein and the beta-globin thalas ...
Biology I What is pH?
... Bases react more easily with protein than with metal; they are often used for cleaning Examples: ...
... Bases react more easily with protein than with metal; they are often used for cleaning Examples: ...
Genetics exam 4
... E. Polypeptides are synthesized by addition of amino acids to the amino terminus _____ Which of the following features is common to both DNA replication and transcription? A. Nucleotides are added to the 5' end of the newly synthesized strand B. A sugar-phosphate bond is formed between the 3' hydrox ...
... E. Polypeptides are synthesized by addition of amino acids to the amino terminus _____ Which of the following features is common to both DNA replication and transcription? A. Nucleotides are added to the 5' end of the newly synthesized strand B. A sugar-phosphate bond is formed between the 3' hydrox ...
Mutations in the code
... • If a mutation in sperm or egg DNA is not corrected, the new sequence of DNA is passed on to offspring. • Over generations, more mutations ...
... • If a mutation in sperm or egg DNA is not corrected, the new sequence of DNA is passed on to offspring. • Over generations, more mutations ...
Pattern Matching: Organic Molecules
... major group of molecules, are not a major food group. Nucleic acids include two kinds of molecules, RNA (ribonucleic acid) and DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), and their subunits. In most organisms, DNA contains the genetic blueprint for the organism and is reproduced in its entirety in every cell of it ...
... major group of molecules, are not a major food group. Nucleic acids include two kinds of molecules, RNA (ribonucleic acid) and DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), and their subunits. In most organisms, DNA contains the genetic blueprint for the organism and is reproduced in its entirety in every cell of it ...
Your assignment is to label each scenario, as either Lamarck`s
... Codons are made up of three “letters” or ______________________ (A, T, C, G) and they form amino acids. Each amino acid is made up of three letters. There are ____________different amino acids which combine in various sequences and quantities to formulate the hundreds of thousands of _______________ ...
... Codons are made up of three “letters” or ______________________ (A, T, C, G) and they form amino acids. Each amino acid is made up of three letters. There are ____________different amino acids which combine in various sequences and quantities to formulate the hundreds of thousands of _______________ ...
Slide 1
... Ribosomes build polypeptides Translation occurs on the surface of the ribosome. – Ribosomes coordinate the functioning of mRNA , tRNA & therefore synthesis of polypeptides. – Ribosomes have two subunits: small and large. – Each subunit is composed of ribosomal RNAs and proteins. – Ribosomal subun ...
... Ribosomes build polypeptides Translation occurs on the surface of the ribosome. – Ribosomes coordinate the functioning of mRNA , tRNA & therefore synthesis of polypeptides. – Ribosomes have two subunits: small and large. – Each subunit is composed of ribosomal RNAs and proteins. – Ribosomal subun ...
Class Notes
... o Nirenberg created an artificial mRNA molecule entirely of uracil and added it to a testtube mixture of amino acids, ribosomes, and other components for protein synthesis. o This “poly-U” translated into a polypeptide containing a single amino acid, phenylalanine, in a long chain. ...
... o Nirenberg created an artificial mRNA molecule entirely of uracil and added it to a testtube mixture of amino acids, ribosomes, and other components for protein synthesis. o This “poly-U” translated into a polypeptide containing a single amino acid, phenylalanine, in a long chain. ...
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN
... o Nirenberg created an artificial mRNA molecule entirely of uracil and added it to a testtube mixture of amino acids, ribosomes, and other components for protein synthesis. o This “poly-U” translated into a polypeptide containing a single amino acid, phenylalanine, in a long chain. ...
... o Nirenberg created an artificial mRNA molecule entirely of uracil and added it to a testtube mixture of amino acids, ribosomes, and other components for protein synthesis. o This “poly-U” translated into a polypeptide containing a single amino acid, phenylalanine, in a long chain. ...
DNA Biology
... DNA codes for the sequence of amino acids in a protein. A codon is three basepairs long and is a segment of mRNA that codes for an amino acid. ...
... DNA codes for the sequence of amino acids in a protein. A codon is three basepairs long and is a segment of mRNA that codes for an amino acid. ...
Why there is more to protein evolution than protein function: splicing
... sequence preferences, governed by the differential bending and twisting attributes of the underlying nucleotide string [37]. Relative affinities vary by several orders of magnitude [38]. Although nucleosomes can be coerced on to rigid DNA by remodelling factors, this incurs an energy cost. Where nuc ...
... sequence preferences, governed by the differential bending and twisting attributes of the underlying nucleotide string [37]. Relative affinities vary by several orders of magnitude [38]. Although nucleosomes can be coerced on to rigid DNA by remodelling factors, this incurs an energy cost. Where nuc ...
DNA - Renton School District
... In eukaryotes, the completed pre-mRNA strand is “edited”, removing introns. The remaining exons are spliced together, forming the mRNA. ...
... In eukaryotes, the completed pre-mRNA strand is “edited”, removing introns. The remaining exons are spliced together, forming the mRNA. ...
Exam 3 Review -Key - Iowa State University
... - In the cytoplasm, an enzyme is going to cut the hairpin loop, forming a doublestranded RNA molecule. - The double-stranded RNA is going to bind to a group of proteins called the RISC protein complex (RNA induced silencing complex) and one strand of the RNA is going to be degraded. o This is called ...
... - In the cytoplasm, an enzyme is going to cut the hairpin loop, forming a doublestranded RNA molecule. - The double-stranded RNA is going to bind to a group of proteins called the RISC protein complex (RNA induced silencing complex) and one strand of the RNA is going to be degraded. o This is called ...
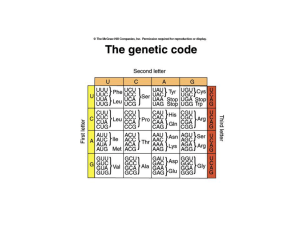
Features of the genetic code
... • Open reading frame starting at the initiation codon (AUG) • Each codon has 5’ base and a 3’ base e.g. 5’CGU3’ • Mutations that modify the genetic code are of 3 types: frameshift (include deletions and insertions), missense (lead to an amino acid replacement) and nonsense (mutation that generates a ...
... • Open reading frame starting at the initiation codon (AUG) • Each codon has 5’ base and a 3’ base e.g. 5’CGU3’ • Mutations that modify the genetic code are of 3 types: frameshift (include deletions and insertions), missense (lead to an amino acid replacement) and nonsense (mutation that generates a ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.