SECTION 30.2 Measuring the Stars 1. Constellations are a. the
... a. the brightest stars. b. stars over Greece. c. groups of stars named after animals, mythological characters, or everyday objects. d. found only in the northern hemisphere. 2. Ursa Major, or the big dipper, is an example of a a. circumpolar constellation. b. constellation that can be seen only in w ...
... a. the brightest stars. b. stars over Greece. c. groups of stars named after animals, mythological characters, or everyday objects. d. found only in the northern hemisphere. 2. Ursa Major, or the big dipper, is an example of a a. circumpolar constellation. b. constellation that can be seen only in w ...
Astronomy - Surfin` Through the Solar System
... 3. Constellation- a group of stars that can be seen as a pattern from Earth 4. Comet- a bright body that orbits the sun in an oval shaped path 5. Meteor- chunks of rock or metal flying through space 6. Asteroid Belt- asteroids that orbit the sun between Mars and Jupiter Procedures/Activities 1. Read ...
... 3. Constellation- a group of stars that can be seen as a pattern from Earth 4. Comet- a bright body that orbits the sun in an oval shaped path 5. Meteor- chunks of rock or metal flying through space 6. Asteroid Belt- asteroids that orbit the sun between Mars and Jupiter Procedures/Activities 1. Read ...
THE REASON FOR THE SEASONS OVERVIEW Program
... Ask for a volunteer from one of the groups to come to the front of the classroom with their “sun” (flashlight). Have the rest of the students sit on the floor in a small area near the center of the classroom but facing the sun. Ask students to imagine that the floor is the Northern Hemisphere of the ...
... Ask for a volunteer from one of the groups to come to the front of the classroom with their “sun” (flashlight). Have the rest of the students sit on the floor in a small area near the center of the classroom but facing the sun. Ask students to imagine that the floor is the Northern Hemisphere of the ...
Textbook support Describing Earth
... not featureless. The bottom of the oceans are almost as variable as the land areas. The hydrosphere is Earth’s thinnest layer, averaging about 4 km in depth. Furthermore, scientists think the oceans are where life began on Earth The liquid hydrosphere can be divided into two parts. About 99 percent ...
... not featureless. The bottom of the oceans are almost as variable as the land areas. The hydrosphere is Earth’s thinnest layer, averaging about 4 km in depth. Furthermore, scientists think the oceans are where life began on Earth The liquid hydrosphere can be divided into two parts. About 99 percent ...
January 2016 - Newbury Astronomical Society
... As well as being one of the most spectacular and A star like our Sun will fuse Hydrogen into Helium and beautiful constellations, Orion is also very interesting towards the end of its life will begin to fuse some of the because we can see evidence of all the stages of the life Helium. A larger star ...
... As well as being one of the most spectacular and A star like our Sun will fuse Hydrogen into Helium and beautiful constellations, Orion is also very interesting towards the end of its life will begin to fuse some of the because we can see evidence of all the stages of the life Helium. A larger star ...
951 Gaspra
... 1. Small objects in the solar system are leftovers that never accreted into planets 2. Minor planets mostly orbit between Mars and Jupiter 3. Comets formed in the outer solar system and were flung outward by close encounters with other planets 4. Comets can be trapped in the inner solar system by pl ...
... 1. Small objects in the solar system are leftovers that never accreted into planets 2. Minor planets mostly orbit between Mars and Jupiter 3. Comets formed in the outer solar system and were flung outward by close encounters with other planets 4. Comets can be trapped in the inner solar system by pl ...
Export To Word
... habitable exoplanet that has been discovered. This planet formed outside our Milky Way and is about 11.5 billion years old. The planet looks like it could support water, has a rocky terrain, and is about five times bigger than Earth. Its proximity to its red dwarf star has led scientists to believe ...
... habitable exoplanet that has been discovered. This planet formed outside our Milky Way and is about 11.5 billion years old. The planet looks like it could support water, has a rocky terrain, and is about five times bigger than Earth. Its proximity to its red dwarf star has led scientists to believe ...
Deep Space Mystery Note Form 2
... Iron atoms are so squeezed so much. The forces of their nuclei create a recoil of the squeezed core. Then is the supernova. Type II Type II Binary stars are when there are two stars and they revolve around each other. In these systems supernovas occur also. Stars up to eight times the ...
... Iron atoms are so squeezed so much. The forces of their nuclei create a recoil of the squeezed core. Then is the supernova. Type II Type II Binary stars are when there are two stars and they revolve around each other. In these systems supernovas occur also. Stars up to eight times the ...
5th Grade Science Curriculum Overview
... • By breathing, people take in oxygen they need to live. • For the body to use food for energy and building materials, the food must first be digested into molecules that are absorbed and transported to cells. • To burn food for the release of energy stored in it, oxygen must be supplied to the cell ...
... • By breathing, people take in oxygen they need to live. • For the body to use food for energy and building materials, the food must first be digested into molecules that are absorbed and transported to cells. • To burn food for the release of energy stored in it, oxygen must be supplied to the cell ...
Transit surveys for Earths in the habitable zones of white dwarfs
... WDHZ and CHZ. First, the range of white dwarf temperatures in the portion of the CHZ within the WDHZ is that of cool white dwarfs, ≈3000–9000 K (right hand axis in Figure 1), similar to the Sun. At the hotter end higher ultraviolet flux might affect the retention of an atmosphere, these planets woul ...
... WDHZ and CHZ. First, the range of white dwarf temperatures in the portion of the CHZ within the WDHZ is that of cool white dwarfs, ≈3000–9000 K (right hand axis in Figure 1), similar to the Sun. At the hotter end higher ultraviolet flux might affect the retention of an atmosphere, these planets woul ...
ReadingsAst
... position) until you can't resolve them any more, and the headlights blur into one light. This happens when the angle between them becomes less than the angular resolution of your eye, or less than about 2 arcminutes. The Small - Angle Formula is very useful for calculating the apparent angular diame ...
... position) until you can't resolve them any more, and the headlights blur into one light. This happens when the angle between them becomes less than the angular resolution of your eye, or less than about 2 arcminutes. The Small - Angle Formula is very useful for calculating the apparent angular diame ...
Warm- up Question Tell me what you know about The Big Bang
... The magnetic fields cause large clouds of hot gas to arch high above the sun’s surface The arch follows the magnetic field lines; can last a few days to a year Solar flares a violent eruptions of gas; can last several hours Flares thrown into space; cause magnetic storms on earth that can ...
... The magnetic fields cause large clouds of hot gas to arch high above the sun’s surface The arch follows the magnetic field lines; can last a few days to a year Solar flares a violent eruptions of gas; can last several hours Flares thrown into space; cause magnetic storms on earth that can ...
Weighing a Galaxy15 Nov 11/15/2010
... M = R3 / T2 for R in AU, T in years, and M in solar masses. ...
... M = R3 / T2 for R in AU, T in years, and M in solar masses. ...
Lecture 1
... surface is illuminated by the sun during this phase? 7. How much of the Moon’s illuminated surface is visible from Earth for this phase of the Moon? ...
... surface is illuminated by the sun during this phase? 7. How much of the Moon’s illuminated surface is visible from Earth for this phase of the Moon? ...
Question 1 The rings of Saturn are seen by Answer 1. reflected and
... . How far will Comet Halley be from the Sun when it reaches its farthest point from the Sun, or aphelion, if its sidereal period is 76 years? (Caution: This calculation needs Kepler's law and a little care. Assume that the comet's perihelion distance from the Sun is negligible.) Answer ...
... . How far will Comet Halley be from the Sun when it reaches its farthest point from the Sun, or aphelion, if its sidereal period is 76 years? (Caution: This calculation needs Kepler's law and a little care. Assume that the comet's perihelion distance from the Sun is negligible.) Answer ...
1 Marsbugs: The Electronic Astrobiology Newsletter, Volume 12
... with an outer disk would cause the orbits to change very slowly, and a strong interaction with a passing planet would cause the orbits to change very quickly compared to the 7,000-year time scale for the orbits to evolve," Ford said. "Because the two hypotheses make different predictions for the evo ...
... with an outer disk would cause the orbits to change very slowly, and a strong interaction with a passing planet would cause the orbits to change very quickly compared to the 7,000-year time scale for the orbits to evolve," Ford said. "Because the two hypotheses make different predictions for the evo ...
File
... Shoemaker), passed near asteroid 253 Mathilde and established orbit around 433 Eros. In 2001, NEAR Shoemaker “landed” on 433 Eros. Launched in 2003, the Japanese Hayabusa mission goal is to return a sample of Comet Itokawa. The craft made collection contact with the asteroid, and will return with po ...
... Shoemaker), passed near asteroid 253 Mathilde and established orbit around 433 Eros. In 2001, NEAR Shoemaker “landed” on 433 Eros. Launched in 2003, the Japanese Hayabusa mission goal is to return a sample of Comet Itokawa. The craft made collection contact with the asteroid, and will return with po ...
GET WORKSHEETS FROM MY ASSIGNMENTS PAGE Mrs
... Not too hot, not too cold- “Just right” 2. What is a LIFE SPAN? The time the star lasts ...
... Not too hot, not too cold- “Just right” 2. What is a LIFE SPAN? The time the star lasts ...
Kepler`s Third Law
... • Venus has phases like the moon, and they agree with the Copernican, not the Ptolemaic model. • He also found far more stars and clusters of stars than anyone had seen before, and he resolved the Milky Way, showing that it is a myriad of stars – but it was not yet clear that we, too, are part of th ...
... • Venus has phases like the moon, and they agree with the Copernican, not the Ptolemaic model. • He also found far more stars and clusters of stars than anyone had seen before, and he resolved the Milky Way, showing that it is a myriad of stars – but it was not yet clear that we, too, are part of th ...
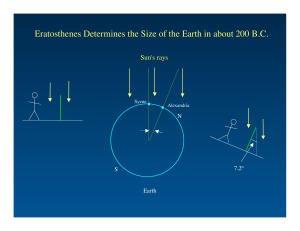
Eratosthenes Determines the Size of the Earth in about 200 B.C.
... • Stars: 88 Constellations, about 3000 stars visible (by eye) at any time • Sun: Does it appear to move? On the same path from day to day? • Moon: Does it always look the same? ...
... • Stars: 88 Constellations, about 3000 stars visible (by eye) at any time • Sun: Does it appear to move? On the same path from day to day? • Moon: Does it always look the same? ...
Moro_Martin`s Talk - CIERA
... Quick Tour to Star and Planet Formation Stars form in clouds of dust and gas. Local density increase occurs within these clouds that portion of the cloud contracts in on itself under its own gravitational pull a protostar is formed (no fusion yet). By conservation of angular momentum, what is left ...
... Quick Tour to Star and Planet Formation Stars form in clouds of dust and gas. Local density increase occurs within these clouds that portion of the cloud contracts in on itself under its own gravitational pull a protostar is formed (no fusion yet). By conservation of angular momentum, what is left ...
Rare Earth hypothesis

In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth Hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligence) required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances. The hypothesis argues that complex extraterrestrial life is a very improbable phenomenon and likely to be extremely rare. The term ""Rare Earth"" originates from Rare Earth: Why Complex Life Is Uncommon in the Universe (2000), a book by Peter Ward, a geologist and paleontologist, and Donald E. Brownlee, an astronomer and astrobiologist, both faculty members at the University of Washington.An alternative view point was argued by Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, among others. It holds that Earth is a typical rocky planet in a typical planetary system, located in a non-exceptional region of a common barred-spiral galaxy. Given the principle of mediocrity (also called the Copernican principle), it is probable that the universe teems with complex life. Ward and Brownlee argue to the contrary: that planets, planetary systems, and galactic regions that are as friendly to complex life as are the Earth, the Solar System, and our region of the Milky Way are very rare.