PLANETS
... H and He: The majority of its mass is in the form of the gaseous hydrogen and helium, with traces of water, methane, ammonia, and other hydrogen compounds. B. Terrestrial planets • Prototypes: Earth, Venus, Mars • Primarily composed of silicate rocks (carbon/diamond planets?) • In the Solar System ( ...
... H and He: The majority of its mass is in the form of the gaseous hydrogen and helium, with traces of water, methane, ammonia, and other hydrogen compounds. B. Terrestrial planets • Prototypes: Earth, Venus, Mars • Primarily composed of silicate rocks (carbon/diamond planets?) • In the Solar System ( ...
The Rocket Science of Launching Stellar Disks
... – Driven by line-scattering of star’s radiation – Rotation can lead to Wind Compressed Disk (WCD) – But still lacks angular momentum for orbit ...
... – Driven by line-scattering of star’s radiation – Rotation can lead to Wind Compressed Disk (WCD) – But still lacks angular momentum for orbit ...
environmental ethics gaia ppt
... and the presence of compounds of nutrient elements have been, for immense periods, just those optimal for surface life. Rather . . . energy is expended by the biota to actively maintain these optima. philosophicalinvestigations.co.uk ...
... and the presence of compounds of nutrient elements have been, for immense periods, just those optimal for surface life. Rather . . . energy is expended by the biota to actively maintain these optima. philosophicalinvestigations.co.uk ...
Grade 5 ELA Life on a New Planet
... are alike in some ways. Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars are all about the same size. They are all solid and made of rock. But there are also differences that keep Mercury, Venus, and Mars from being good places to live. Mercury is very close to the Sun, which makes it extremely hot. Regular temperat ...
... are alike in some ways. Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars are all about the same size. They are all solid and made of rock. But there are also differences that keep Mercury, Venus, and Mars from being good places to live. Mercury is very close to the Sun, which makes it extremely hot. Regular temperat ...
study guide
... • Conservation of angular momentum caused flattening into disk • Planetesimals condensed and collided to form planets ...
... • Conservation of angular momentum caused flattening into disk • Planetesimals condensed and collided to form planets ...
Ch 28 Class Notes
... A small star grouping, or sub-grouping of a constellation is called an _____________________. We are familiar with the constellation known as Ursa Major (the Great Bear). Within _____________________________ is the Big Dipper. The Big Dipper is an asterism in the shape of a dipper and handle. The tw ...
... A small star grouping, or sub-grouping of a constellation is called an _____________________. We are familiar with the constellation known as Ursa Major (the Great Bear). Within _____________________________ is the Big Dipper. The Big Dipper is an asterism in the shape of a dipper and handle. The tw ...
Cosmochemistry from Nanometers to Light- Years A Written by
... Cosmochemistry has always been an interdisciplinary field, and cosmochemists have always paid attention to discoveries by astronomers and imaginative theories conjured up by astrophysicists. Nevertheless, cosmochemistry and astronomy never meshed seamlessly. That seems to be changing as observations ...
... Cosmochemistry has always been an interdisciplinary field, and cosmochemists have always paid attention to discoveries by astronomers and imaginative theories conjured up by astrophysicists. Nevertheless, cosmochemistry and astronomy never meshed seamlessly. That seems to be changing as observations ...
Stellar Physics - Craigie High School
... Sun revolved around the Earth because that is what it seems to do! Similarly most people were sure that the Earth was flat until there was definite proof from sailors who had ventured round the world and not fallen off! It may prove useful therefore to give a brief historical introduction so that we ...
... Sun revolved around the Earth because that is what it seems to do! Similarly most people were sure that the Earth was flat until there was definite proof from sailors who had ventured round the world and not fallen off! It may prove useful therefore to give a brief historical introduction so that we ...
The Motion of Celestial Bodies
... motions in orbits which are conic sections (see Figure 1). During the next 200 years this field was dominated by mathematicians and astronomers like L. Euler (1707-1783), J. L. Lagrange (1736-1812), P. S. Laplace (1749-1827), U. J. Leverrier (1811-1877), F. Tisserand (1845-1896) and H. Poincaré (185 ...
... motions in orbits which are conic sections (see Figure 1). During the next 200 years this field was dominated by mathematicians and astronomers like L. Euler (1707-1783), J. L. Lagrange (1736-1812), P. S. Laplace (1749-1827), U. J. Leverrier (1811-1877), F. Tisserand (1845-1896) and H. Poincaré (185 ...
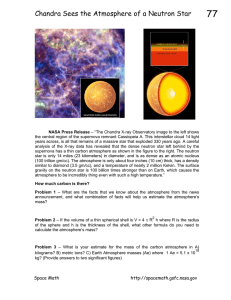
Chandra Sees the Atmosphere of a Neutron Star - Chandra X
... the central region of the supernova remnant Cassiopeia A. This interstellar cloud 14 light years across, is all that remains of a massive star that exploded 330 years ago. A careful analysis of the X-ray data has revealed that the dense neutron star left behind by the supernova has a thin carbon atm ...
... the central region of the supernova remnant Cassiopeia A. This interstellar cloud 14 light years across, is all that remains of a massive star that exploded 330 years ago. A careful analysis of the X-ray data has revealed that the dense neutron star left behind by the supernova has a thin carbon atm ...
Complete the “Assess Your Understanding” including
... was compressed into an extremely small volume. About 14 billion years ago, a sudden event called “the big bang” sent all of the matter and energy outward in all directions. As the universe expanded, some of the matter gathered into clumps because of gravity that evolved into galaxies. Today, the uni ...
... was compressed into an extremely small volume. About 14 billion years ago, a sudden event called “the big bang” sent all of the matter and energy outward in all directions. As the universe expanded, some of the matter gathered into clumps because of gravity that evolved into galaxies. Today, the uni ...
Physical Setting/Earth Science
... Directions (51–65): Record your answers in the spaces provided in your answer booklet. Some questions may require the use of the 2010 Edition Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Earth Science. Base your answers to questions 51 through 54 on the passage below. Earth’s Early Atmosphere Early in Eart ...
... Directions (51–65): Record your answers in the spaces provided in your answer booklet. Some questions may require the use of the 2010 Edition Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Earth Science. Base your answers to questions 51 through 54 on the passage below. Earth’s Early Atmosphere Early in Eart ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... • Stars with masses similar to the sun evolve in essentially the same way as low-mass stars. • During their collapse from red giants to white dwarfs, medium-mass stars are thought to cast off their bloated outer layer, creating an expanding round cloud of gas called planetary nebula. ...
... • Stars with masses similar to the sun evolve in essentially the same way as low-mass stars. • During their collapse from red giants to white dwarfs, medium-mass stars are thought to cast off their bloated outer layer, creating an expanding round cloud of gas called planetary nebula. ...
1_ The Earth - St. Raymond High School for Boys
... move a little, tracing a very small arc in the night sky, around which the other visible stars make wider circles. **** At the North Pole, the North Star appears directly overhead. At the Equator, the North Star is seen on the horizon; south of the Equator it cannot be seen at all. At any point in t ...
... move a little, tracing a very small arc in the night sky, around which the other visible stars make wider circles. **** At the North Pole, the North Star appears directly overhead. At the Equator, the North Star is seen on the horizon; south of the Equator it cannot be seen at all. At any point in t ...
The gorilla connection
... relatively faint star passing in front of a distant bright star acts as a gravitational lens, focusing light from the distant object, magnifying it and causing it to brighten and fade with a characteristic ‘light curve’ over a period of weeks (Fig. 1a). If the nearer star possesses a planet, it too ...
... relatively faint star passing in front of a distant bright star acts as a gravitational lens, focusing light from the distant object, magnifying it and causing it to brighten and fade with a characteristic ‘light curve’ over a period of weeks (Fig. 1a). If the nearer star possesses a planet, it too ...
Vocabulary - El Camino College
... degrees in a complete circle. Degrees can be approximately measured by knowing that the fist subtends an angle of 10 degrees when the arm is outstretched. The pinky fingernail subtends about 1 degree. Each degree is subdivided into 60 equal parts, called arcminutes. (There are 60 arcminutes in one d ...
... degrees in a complete circle. Degrees can be approximately measured by knowing that the fist subtends an angle of 10 degrees when the arm is outstretched. The pinky fingernail subtends about 1 degree. Each degree is subdivided into 60 equal parts, called arcminutes. (There are 60 arcminutes in one d ...
Probeseiten 2 PDF
... conclusion: were Ceres and Pallas perhaps fragments of a former planet? Could that explain why they were so small? And were there other fragments waiting to be discovered in this part of the solar system? It was indeed curious that, even in the most powerful of telescopes, the new celestial objects ...
... conclusion: were Ceres and Pallas perhaps fragments of a former planet? Could that explain why they were so small? And were there other fragments waiting to be discovered in this part of the solar system? It was indeed curious that, even in the most powerful of telescopes, the new celestial objects ...
Neutron Stars
... If initial star mass < 8 MSun or so. (and remember: Maximum WD mass is 1.4 MSun , radius is about that of the Earth) ...
... If initial star mass < 8 MSun or so. (and remember: Maximum WD mass is 1.4 MSun , radius is about that of the Earth) ...
NAME: CLASS: 1 Solar System Formation: PowerPoint Notes Sheet
... Which planets rotate faster? gaseous Which type of planets have many moons? Gaseous Slide 4: What is special about Pluto? Inclined orbit (18 degrees) and oval shape - not circular Slide 5: List the planets in order of increasing tilt angle: Mercury, (0), Jupiter (3) Earth (23) Mars (25) Saturn (27), ...
... Which planets rotate faster? gaseous Which type of planets have many moons? Gaseous Slide 4: What is special about Pluto? Inclined orbit (18 degrees) and oval shape - not circular Slide 5: List the planets in order of increasing tilt angle: Mercury, (0), Jupiter (3) Earth (23) Mars (25) Saturn (27), ...
Rare Earth hypothesis

In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth Hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligence) required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances. The hypothesis argues that complex extraterrestrial life is a very improbable phenomenon and likely to be extremely rare. The term ""Rare Earth"" originates from Rare Earth: Why Complex Life Is Uncommon in the Universe (2000), a book by Peter Ward, a geologist and paleontologist, and Donald E. Brownlee, an astronomer and astrobiologist, both faculty members at the University of Washington.An alternative view point was argued by Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, among others. It holds that Earth is a typical rocky planet in a typical planetary system, located in a non-exceptional region of a common barred-spiral galaxy. Given the principle of mediocrity (also called the Copernican principle), it is probable that the universe teems with complex life. Ward and Brownlee argue to the contrary: that planets, planetary systems, and galactic regions that are as friendly to complex life as are the Earth, the Solar System, and our region of the Milky Way are very rare.