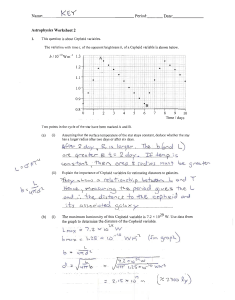
Foundation 1 - Discovering Astronomy
... – H2 (mostly), CO, H2O, NH3, H2CO – Most is concentrated in giant molecular clouds ...
... – H2 (mostly), CO, H2O, NH3, H2CO – Most is concentrated in giant molecular clouds ...
Basic Information about the Solar System Handout
... Our whole solar system, along with all the local stars you can see on a clear dark night, reside in one of our galaxy's spiral arms, known as the Orion arm, as they orbit the supermassive black hole in the dense star cluster at the center of our galaxy some 26,000 (± 1400) light-years distant from u ...
... Our whole solar system, along with all the local stars you can see on a clear dark night, reside in one of our galaxy's spiral arms, known as the Orion arm, as they orbit the supermassive black hole in the dense star cluster at the center of our galaxy some 26,000 (± 1400) light-years distant from u ...
Astronomers Find Extremely Large Planet
... young forming stars. The fact that the FLAMINGOS survey only found silhouette disks in clusters and not peppered thoughout the immense volume of the molecular clouds supports the point of view that such clusters of stars are the birthplace for most of the stars in our galaxy. “It’s surprising that t ...
... young forming stars. The fact that the FLAMINGOS survey only found silhouette disks in clusters and not peppered thoughout the immense volume of the molecular clouds supports the point of view that such clusters of stars are the birthplace for most of the stars in our galaxy. “It’s surprising that t ...
The Prospective Aspect of the Cosmogonic Models in Laozi and T
... • Dynamics of the Primitive Nebula:The spiral harmonizing force which initially arises in each spiral harmony system is the gravity center of each emergent system, and it is the sun in a solar system. At this point in the solar system’s center and at its periphery there is a vast aggregation of high ...
... • Dynamics of the Primitive Nebula:The spiral harmonizing force which initially arises in each spiral harmony system is the gravity center of each emergent system, and it is the sun in a solar system. At this point in the solar system’s center and at its periphery there is a vast aggregation of high ...
ET: Astronomy 230 Outline Important Caveat
... layers– e.g. early sea life. • Maybe planets being formed now, with less supernovae, would not have enough radioactivity to support continental drifts and volcanoes. (Idea of Peter Ward and Donald Brownlee.) ...
... layers– e.g. early sea life. • Maybe planets being formed now, with less supernovae, would not have enough radioactivity to support continental drifts and volcanoes. (Idea of Peter Ward and Donald Brownlee.) ...
The Solar System - Gordon College English Center
... The Solar System is the name that was given to the collection of celestial bodies that contains the Sun (which is a star by definition) and eight planets (which Earth is one of them) that orbit the sun regularly. In ancient times, people gazed at the night sky. They observed thousands of spots of li ...
... The Solar System is the name that was given to the collection of celestial bodies that contains the Sun (which is a star by definition) and eight planets (which Earth is one of them) that orbit the sun regularly. In ancient times, people gazed at the night sky. They observed thousands of spots of li ...
High Contrast - University of Arizona
... Current theories of disk/planet evolution suggest a presumed epoch of planet-building via the formation and agglomerative growth of embryonic bodies, and the subsequent accretion of gaseous atmospheres onto hot giant planets, is attendant with a significant decline in the gas-to-dust ratios in the r ...
... Current theories of disk/planet evolution suggest a presumed epoch of planet-building via the formation and agglomerative growth of embryonic bodies, and the subsequent accretion of gaseous atmospheres onto hot giant planets, is attendant with a significant decline in the gas-to-dust ratios in the r ...
Advances in Environmental Biology Approach Mahin Shahrivar and
... phenomenon of the resurrection day; in other words,the moon will be lightless and the sun will be also gathered up; as we know the light of the moon is coming from the sun; when the sun gets dark, the moon is also getting dark and as a consequence the earth gets into a dreadful darkness; for the rea ...
... phenomenon of the resurrection day; in other words,the moon will be lightless and the sun will be also gathered up; as we know the light of the moon is coming from the sun; when the sun gets dark, the moon is also getting dark and as a consequence the earth gets into a dreadful darkness; for the rea ...
question - UW Canvas
... 23. How is it that the core of a massive star is able to fuse heavier and heavier elements without any of these stages resulting in degeneracy or any flashes like the helium flash that occurs in solar-type stars? a. The cores of massive stars are so hot, have such high densities and pressures, that ...
... 23. How is it that the core of a massive star is able to fuse heavier and heavier elements without any of these stages resulting in degeneracy or any flashes like the helium flash that occurs in solar-type stars? a. The cores of massive stars are so hot, have such high densities and pressures, that ...
Astronomy Webquest Part 1: Life of Stars: Go to http://www.odec.ca
... 3. Near the end of the main sequence, when there is not enough hydrogen gas to support the star, the outer layers will ______________ in an attempt to ______________________________. 4. This forms a ____________. Click on next. 5. After the core collapses due to lack of hydrogen, the red giant will ...
... 3. Near the end of the main sequence, when there is not enough hydrogen gas to support the star, the outer layers will ______________ in an attempt to ______________________________. 4. This forms a ____________. Click on next. 5. After the core collapses due to lack of hydrogen, the red giant will ...
Volume 1 (Issue 6), June 2012
... and to contribute their observation to a collective experiment to measure the sun’s distance. To have extended utility, the phone app will serve before, during, and after the transit. Prior to the transit, one can practice timing the interior contacts using a simulation of the transit. Additionally, ...
... and to contribute their observation to a collective experiment to measure the sun’s distance. To have extended utility, the phone app will serve before, during, and after the transit. Prior to the transit, one can practice timing the interior contacts using a simulation of the transit. Additionally, ...
PHYS101 Sec 001 Hour Exam No. 3 Preview 2 Page: 1 1 It
... of the hydrogen that we need from sea water. Which of the following comments about the energy needed to separate the hydrogen and oxygen in water is correct? a. It is the greater than the energy released when the hydrogen is burned, so we get a net loss of energy. b. It is the same as the energy rel ...
... of the hydrogen that we need from sea water. Which of the following comments about the energy needed to separate the hydrogen and oxygen in water is correct? a. It is the greater than the energy released when the hydrogen is burned, so we get a net loss of energy. b. It is the same as the energy rel ...
Coordinates - Naval Postgraduate School
... The sea is not "flat", that is it is not an ellipsoid. The true gravity field of the earth is lumpy. Just as the up direction is perpendicular to the ellipsoid in the homogeneous earth case, for the real earth up is perpendicular to the geoid. This causes small variations in the "up" defined by the ...
... The sea is not "flat", that is it is not an ellipsoid. The true gravity field of the earth is lumpy. Just as the up direction is perpendicular to the ellipsoid in the homogeneous earth case, for the real earth up is perpendicular to the geoid. This causes small variations in the "up" defined by the ...
+(J - cloudfront.net
... spectrum and temperature of a certain star are used to determine its luminosity to be approximately 5.0 x 1031 W. The '!Pparent brightness of the star is 1.4 x 10-9 W m-2. These data can be used to detennine the distance ofihe'staifromEarth~------""----..-.--..---- - - ..(i) ...
... spectrum and temperature of a certain star are used to determine its luminosity to be approximately 5.0 x 1031 W. The '!Pparent brightness of the star is 1.4 x 10-9 W m-2. These data can be used to detennine the distance ofihe'staifromEarth~------""----..-.--..---- - - ..(i) ...
Astronomy - Test 3
... E) Measuring the “turnoff point” where stars leave the main sequence 2. Why is it that hot plasma ejected from the Sun generally follows looping shapes? A) It is simply feeling the effects of gravity B) It is following magnetic field lines C) It is passing through holes drilled in the corona previou ...
... E) Measuring the “turnoff point” where stars leave the main sequence 2. Why is it that hot plasma ejected from the Sun generally follows looping shapes? A) It is simply feeling the effects of gravity B) It is following magnetic field lines C) It is passing through holes drilled in the corona previou ...
The ExOoS Mission - Extraterrestrial Octopus on Steroids
... Astrobiology is one of the fields with the fastest development in the last years (Harrison et al. 2013; Seager et al. 2012). Advances in molecular techniques and technology have allowed the detection and the study of living organisms and their traces in environments traditionally unconceivable to ho ...
... Astrobiology is one of the fields with the fastest development in the last years (Harrison et al. 2013; Seager et al. 2012). Advances in molecular techniques and technology have allowed the detection and the study of living organisms and their traces in environments traditionally unconceivable to ho ...
Rare Earth hypothesis

In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth Hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligence) required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances. The hypothesis argues that complex extraterrestrial life is a very improbable phenomenon and likely to be extremely rare. The term ""Rare Earth"" originates from Rare Earth: Why Complex Life Is Uncommon in the Universe (2000), a book by Peter Ward, a geologist and paleontologist, and Donald E. Brownlee, an astronomer and astrobiologist, both faculty members at the University of Washington.An alternative view point was argued by Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, among others. It holds that Earth is a typical rocky planet in a typical planetary system, located in a non-exceptional region of a common barred-spiral galaxy. Given the principle of mediocrity (also called the Copernican principle), it is probable that the universe teems with complex life. Ward and Brownlee argue to the contrary: that planets, planetary systems, and galactic regions that are as friendly to complex life as are the Earth, the Solar System, and our region of the Milky Way are very rare.