GET WORKSHEETS FROM MY ASSIGNMENTS PAGE Mrs
... 4.The most likely star color to have a planet with life would be ____ because: a. b. Consider Life Span and Life Zone size ...
... 4.The most likely star color to have a planet with life would be ____ because: a. b. Consider Life Span and Life Zone size ...
Lecture 9a: More on Star formation and evolution 10/22
... classes (O B A F G K M)… – Spectral classes are correlated with temperature, that is determined from the peak wavelength of “blackbody” ...
... classes (O B A F G K M)… – Spectral classes are correlated with temperature, that is determined from the peak wavelength of “blackbody” ...
FCAT 2.0 Science Review Big Idea 1: The Practice of Science THE
... • Hottest surface of any planet. MARS • Atmosphere = more than 95% carbon dioxide. • Reddish color as result of iron-rich rocks , leaving a rusty residue • Temperatures on surface range from -140 C to 20 C • Thin atmosphere • Has 2 moons • Has volcanoes; Olympus Mons= largest volcano is solar system ...
... • Hottest surface of any planet. MARS • Atmosphere = more than 95% carbon dioxide. • Reddish color as result of iron-rich rocks , leaving a rusty residue • Temperatures on surface range from -140 C to 20 C • Thin atmosphere • Has 2 moons • Has volcanoes; Olympus Mons= largest volcano is solar system ...
The Bigger Picture
... stars is based on the principle of Trigonometric Parallax • The parallax effect is the apparent motion of a nearby object compared to distant background objects because of a change in viewing angle. • Put a finger in front of your nose and watch it move with respect to the back of the room as you lo ...
... stars is based on the principle of Trigonometric Parallax • The parallax effect is the apparent motion of a nearby object compared to distant background objects because of a change in viewing angle. • Put a finger in front of your nose and watch it move with respect to the back of the room as you lo ...
CHAPTER REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. In which
... mostly iron, which is thought to be similar to the composition of Earth’s core. One of the most remarkable recent meteor events happened in Peekskill, New York, in 1992. As 18-year-old Michelle Knapp was watching television at about eight o’clock in the evening, she heard a loud noise outside her ho ...
... mostly iron, which is thought to be similar to the composition of Earth’s core. One of the most remarkable recent meteor events happened in Peekskill, New York, in 1992. As 18-year-old Michelle Knapp was watching television at about eight o’clock in the evening, she heard a loud noise outside her ho ...
Astronomy - Surfin` Through the Solar System
... they are located in the solar system. 4. The students will label the gas giants on their planet model to show where they are located in the solar system. Reference should be noted that Pluto is not one of the two types of planets. 5. If time allows, The Magic School Bus: Lost in the Solar System may ...
... they are located in the solar system. 4. The students will label the gas giants on their planet model to show where they are located in the solar system. Reference should be noted that Pluto is not one of the two types of planets. 5. If time allows, The Magic School Bus: Lost in the Solar System may ...
April 2006 Newsletter PDF - Cowichan Valley Starfinders Society
... explosions which blow huge bubbles of gas above the disk like smoke rising from chimneys. Shock Wave in Stephan's Quintet Galaxy Sun, 05 Mar 2006 - This photograph, taken by the Spitzer space telescope and a ground-based telescope in Spain, shows the Stephan's Quintet galaxy cluster, with one of the ...
... explosions which blow huge bubbles of gas above the disk like smoke rising from chimneys. Shock Wave in Stephan's Quintet Galaxy Sun, 05 Mar 2006 - This photograph, taken by the Spitzer space telescope and a ground-based telescope in Spain, shows the Stephan's Quintet galaxy cluster, with one of the ...
Lecture 30
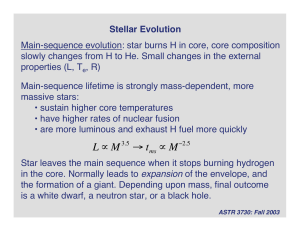
... Evolution of the core is controlled by the need for increasingly higher temperatures for nuclear burning of heavier elements: • Initially, burn hydrogen in the core • Once hydrogen is exhausted, too cool to burn helium • Core contracts, heats up • Helium burning stars • If star is massive enough, s ...
... Evolution of the core is controlled by the need for increasingly higher temperatures for nuclear burning of heavier elements: • Initially, burn hydrogen in the core • Once hydrogen is exhausted, too cool to burn helium • Core contracts, heats up • Helium burning stars • If star is massive enough, s ...
“Mystery of the Missing Seasons” Available in
... The aliens decide they need to go back to a bigger view--of the planets in space. They look again at what their planets are doing. First, they look at theirs. It spins or rotates--that's what makes the sun seem to travel across the sky during the day as they watch from the ground; as their planet sp ...
... The aliens decide they need to go back to a bigger view--of the planets in space. They look again at what their planets are doing. First, they look at theirs. It spins or rotates--that's what makes the sun seem to travel across the sky during the day as they watch from the ground; as their planet sp ...
STELLAR STRUCTURE AND EVOLUTION
... stellar surface, Rs the stellar radius. Energy may also be lost in the form of neutrinos or by direct mass loss (generally unobservable). Astronomers measure: f = (Rs/D)2 F ...
... stellar surface, Rs the stellar radius. Energy may also be lost in the form of neutrinos or by direct mass loss (generally unobservable). Astronomers measure: f = (Rs/D)2 F ...
Designing Curriculum and Instruction in Elementary School
... through the text; for example, a chunk called “Basic facts about OUR solar system.” Some facts may in one paragraph of the materials, and other facts in different paragraphs. So, when you make chunks, list WHERE the information is in the text. “Some facts are in paragraph 6; also see paragraph 12.” ...
... through the text; for example, a chunk called “Basic facts about OUR solar system.” Some facts may in one paragraph of the materials, and other facts in different paragraphs. So, when you make chunks, list WHERE the information is in the text. “Some facts are in paragraph 6; also see paragraph 12.” ...
colour
... stellar surface, Rs the stellar radius. Energy may also be lost in the form of neutrinos or by direct mass loss (generally unobservable). Astronomers measure: f = (Rs/D)2 F ...
... stellar surface, Rs the stellar radius. Energy may also be lost in the form of neutrinos or by direct mass loss (generally unobservable). Astronomers measure: f = (Rs/D)2 F ...
geography chapter – 1 the earth in the solar system previous
... Ques.1 why does the time of a place not depend on its latitude? Ans. To see the position of a place it is necessary to know latitude of a place. For example that Tonga Island (Pacific Ocean) and Mauritius island (in the Indian ocean) are situated on the same latitude (i.e. 200s). Now in order to loc ...
... Ques.1 why does the time of a place not depend on its latitude? Ans. To see the position of a place it is necessary to know latitude of a place. For example that Tonga Island (Pacific Ocean) and Mauritius island (in the Indian ocean) are situated on the same latitude (i.e. 200s). Now in order to loc ...
Chapter 2
... Complete the following concept map by correctly adding the connecting phrases or terms provided to the appropriate locations. Some items may be used more than once; others may not be applicable to this diagram. 1. converts simple elements such as 2. present in 3. for example 4. extrasolar planets su ...
... Complete the following concept map by correctly adding the connecting phrases or terms provided to the appropriate locations. Some items may be used more than once; others may not be applicable to this diagram. 1. converts simple elements such as 2. present in 3. for example 4. extrasolar planets su ...
Stellar Evolution
... and Carbon • “White dwarf” cools but does not contract because core is degenerate • No energy from fusion, no energy from gravitational contraction • White dwarf slowly fades away… ...
... and Carbon • “White dwarf” cools but does not contract because core is degenerate • No energy from fusion, no energy from gravitational contraction • White dwarf slowly fades away… ...
ET: Astronomy 230 Outline Important Caveat
... • About 2/3 of all stars are in multiple systems. – Is this good or bad? • Disks around stars are very common, even most binary systems have them. • Hard to think of a formation scenario without a disk at some point– single or binary system. • Disk formation matches our solar system parameters. • We ...
... • About 2/3 of all stars are in multiple systems. – Is this good or bad? • Disks around stars are very common, even most binary systems have them. • Hard to think of a formation scenario without a disk at some point– single or binary system. • Disk formation matches our solar system parameters. • We ...
Answer
... happening within the core of the star to cause the sudden changes in luminosity and temperature? The dominant type of fusion has changed. The core of the star has collapsed under gravity as there is no longer an outward pressure from the radiation to create balanced forces. This collapse causes the ...
... happening within the core of the star to cause the sudden changes in luminosity and temperature? The dominant type of fusion has changed. The core of the star has collapsed under gravity as there is no longer an outward pressure from the radiation to create balanced forces. This collapse causes the ...
an Educator`s GuidE
... observing the effects they have on their parent stars. These effects, driven by gravity and line-of-sight, are visible to us as either periodic dimming (called “transits”) or shifting wavelengths within the electromagnetic spectrum (referred to as a “wobble”). To find a world capable of supporting l ...
... observing the effects they have on their parent stars. These effects, driven by gravity and line-of-sight, are visible to us as either periodic dimming (called “transits”) or shifting wavelengths within the electromagnetic spectrum (referred to as a “wobble”). To find a world capable of supporting l ...
Rachel and the TreeSchoolers Theme Song
... Gravity is pulling me down Gravity is pulling me down Gravity is pulling me down Gravity is pulling me down ...
... Gravity is pulling me down Gravity is pulling me down Gravity is pulling me down Gravity is pulling me down ...
Terrestrial planet formation in exoplanetary systems with a giant
... in an orbit that remains confined to the habitable zone. However, these simulations focus on the orbital stability problem, and do not investigate the possibility that such terrestrial planets can actually f orm in these systems. The process of planetesimal accumulation into planets depends on the c ...
... in an orbit that remains confined to the habitable zone. However, these simulations focus on the orbital stability problem, and do not investigate the possibility that such terrestrial planets can actually f orm in these systems. The process of planetesimal accumulation into planets depends on the c ...
the planet venus – the prophets
... There are almost no references in Scripture to planets or their meanings. An important exception is Venus. Peter writes: “And we have the prophetic word confirmed, which you will do well to heed as a light that shines in a dark place, until the day dawns and the morning star rises in your hearts.” ( ...
... There are almost no references in Scripture to planets or their meanings. An important exception is Venus. Peter writes: “And we have the prophetic word confirmed, which you will do well to heed as a light that shines in a dark place, until the day dawns and the morning star rises in your hearts.” ( ...
Lecture 10: Stellar Evolution
... 1044 erg s-1 - thus supernova same as energy radiated by the entire galaxy in 9 years. ...
... 1044 erg s-1 - thus supernova same as energy radiated by the entire galaxy in 9 years. ...
Red Dwarf Stars: Ages, Rotation, Magnetic
... pre-main sequence stars and close binaries in the sample. Also in this study, we exclude spectral types later than ∼M7 because they appear to have Age-Rotation-Activity relations quite different to earlier spectral types. From a limited sample of M7–9 V stars, it appears that they do not undergo mag ...
... pre-main sequence stars and close binaries in the sample. Also in this study, we exclude spectral types later than ∼M7 because they appear to have Age-Rotation-Activity relations quite different to earlier spectral types. From a limited sample of M7–9 V stars, it appears that they do not undergo mag ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.