june 2011 - Holt Planetarium
... and mantle, leaving behind its core and not much else. This spectacular view of the crater Degas was obtained as a highresolution targeted observation (90 m/pixel). Impact melt coats its floor, and as the melt cooled and shrank, it formed the cracks observed across the crater. For context, Mariner 1 ...
... and mantle, leaving behind its core and not much else. This spectacular view of the crater Degas was obtained as a highresolution targeted observation (90 m/pixel). Impact melt coats its floor, and as the melt cooled and shrank, it formed the cracks observed across the crater. For context, Mariner 1 ...
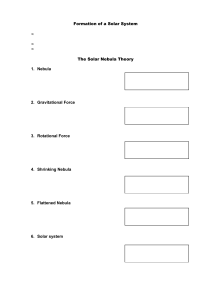
Formation of a Solar System • • • The Solar Nebula Theory 1. Nebula
... • The theory of how stars and planets form is called the solar nebula theory. • The Sun is calculated to be 5 billion years old • The Earth is calculated to be 4.6 billion years old The Solar Nebula Theory 1. Nebula Cloud of dust and gas ...
... • The theory of how stars and planets form is called the solar nebula theory. • The Sun is calculated to be 5 billion years old • The Earth is calculated to be 4.6 billion years old The Solar Nebula Theory 1. Nebula Cloud of dust and gas ...
Chapter 1 Question Set
... A hypothesis is a proposal or suggestion about how or why something happened (often put forth as a theory: “My theory is that the dog ran away because the children pulled her tail.”). A law is a rule or state of nature that exists everywhere. A theory explains why a law or state of nature is the way ...
... A hypothesis is a proposal or suggestion about how or why something happened (often put forth as a theory: “My theory is that the dog ran away because the children pulled her tail.”). A law is a rule or state of nature that exists everywhere. A theory explains why a law or state of nature is the way ...
Our SOlar System
... That is, as illustrated in the adjacent figure, stars should appear to change their position with the respect to the other background stars as the Earth moved about its orbit, because of viewing them from a different perspective ...
... That is, as illustrated in the adjacent figure, stars should appear to change their position with the respect to the other background stars as the Earth moved about its orbit, because of viewing them from a different perspective ...
Name Class Date Our Solar System The solar system consists of our
... (26%). Hot chemical reactions (known as thermonuclear reactions) inside the Sun release enormous amounts of energy, mostly as light and heat. These reactions occur when the hydrogen turns into helium. Earth’s Sun is an average-sized star. The Sun is more than a million times greater in volume than E ...
... (26%). Hot chemical reactions (known as thermonuclear reactions) inside the Sun release enormous amounts of energy, mostly as light and heat. These reactions occur when the hydrogen turns into helium. Earth’s Sun is an average-sized star. The Sun is more than a million times greater in volume than E ...
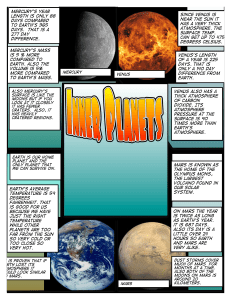
Mercury`s year length is only 88 days compared to
... because we have just the right temperature while other planets are too far from the sun so very cold or too close so very hot. ...
... because we have just the right temperature while other planets are too far from the sun so very cold or too close so very hot. ...
Formation of the Solar System The Solar System
... – Pluto-Charon: retrograde motion of system – Neptune-Triton: retrograde orbit of Triton – Retrograde rotation of large bodies • Uranus, Venus ...
... – Pluto-Charon: retrograde motion of system – Neptune-Triton: retrograde orbit of Triton – Retrograde rotation of large bodies • Uranus, Venus ...
Early history of astronomy
... • The motion of a body, such as a planet or moon, along a path around some point in space • Earth's orbit is elliptical • Earth is closest to the Sun (perihelion) in January • Earth is farthest from the Sun (aphelion) in July • The plane of the ecliptic is an imaginary plane that connects Earth's or ...
... • The motion of a body, such as a planet or moon, along a path around some point in space • Earth's orbit is elliptical • Earth is closest to the Sun (perihelion) in January • Earth is farthest from the Sun (aphelion) in July • The plane of the ecliptic is an imaginary plane that connects Earth's or ...
Solar System Live!
... Has an abundance of liquid water making life possible. Has increasing amounts of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere which may contribute to global warming, harm the environment, or threaten all life on the planet. Mars has surface features that include huge ridged gullies and trenches, indicating the ...
... Has an abundance of liquid water making life possible. Has increasing amounts of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere which may contribute to global warming, harm the environment, or threaten all life on the planet. Mars has surface features that include huge ridged gullies and trenches, indicating the ...
The Solar System 2015
... Apart from the eight planets in the Solar System, there is also known a few hundreds of extrasolar planets, which orbit foreign stars. Contemporary astronomical instruments do not allow to observe these distant planets directly, but their properties are calculated from photometric and astrometric m ...
... Apart from the eight planets in the Solar System, there is also known a few hundreds of extrasolar planets, which orbit foreign stars. Contemporary astronomical instruments do not allow to observe these distant planets directly, but their properties are calculated from photometric and astrometric m ...
Where a limit?
... Life in the Universe can have the forms not similar to the terrestrial. Life occurrence in the interstellar environment where various organic molecules (оксида carbon, methyl spirit, formaldehyde are revealed many) is possible. In a space matter can be formed and more difficult molecules. Probably t ...
... Life in the Universe can have the forms not similar to the terrestrial. Life occurrence in the interstellar environment where various organic molecules (оксида carbon, methyl spirit, formaldehyde are revealed many) is possible. In a space matter can be formed and more difficult molecules. Probably t ...
Lesson plan on the solar system for Year 6
... The Earth’s axis is tilted at 23.5 to the plane of its rotation (anticlockwise). The Earth is held in orbit round Sun by the Sun’s gravitational pull. Earths moves at 30km/s The Sun is a star. All stars give out a large amount of heat, light and other forms of energy The Moon does not spin on its a ...
... The Earth’s axis is tilted at 23.5 to the plane of its rotation (anticlockwise). The Earth is held in orbit round Sun by the Sun’s gravitational pull. Earths moves at 30km/s The Sun is a star. All stars give out a large amount of heat, light and other forms of energy The Moon does not spin on its a ...
Lesson Plan
... The Earth’s axis is tilted at 23.5 to the plane of its rotation (anticlockwise). The Earth is held in orbit round Sun by the Sun’s gravitational pull. Earths moves at 30km/s The Sun is a star. All stars give out a large amount of heat, light and other forms of energy The Moon does not spin ...
... The Earth’s axis is tilted at 23.5 to the plane of its rotation (anticlockwise). The Earth is held in orbit round Sun by the Sun’s gravitational pull. Earths moves at 30km/s The Sun is a star. All stars give out a large amount of heat, light and other forms of energy The Moon does not spin ...
Unit E Space Exploration Section 1 Notnd Space has changed over
... Little light reaches this planet Fastest wind speed – 2500 ...
... Little light reaches this planet Fastest wind speed – 2500 ...
How was Earth formed?
... immense amount of energy released. Sun is formed Dust and gases cool and condense in defined orbits around the sun ...
... immense amount of energy released. Sun is formed Dust and gases cool and condense in defined orbits around the sun ...
Solar System and Inner Planets
... covered by craters caused by meteorites Venus-second planet from the sun covered with heavy clouds atmosphere is carbon dioxide winds blowing at high speeds it IS the hottest planet can be seen early in the morning or late in the evening called the “morning star” or “evening star” do ...
... covered by craters caused by meteorites Venus-second planet from the sun covered with heavy clouds atmosphere is carbon dioxide winds blowing at high speeds it IS the hottest planet can be seen early in the morning or late in the evening called the “morning star” or “evening star” do ...
What should I study for the Chapter 27 – Solar System Test
... 13. Methane gives URANUS/NEPTUNE its blue-green color. (two answers acceptable) 14. The spacecraft Magellan took the first radar images of VENUS’s surface since it is impossible to see. 15. Not discovered until 1930 because it is so far away from Earth. PLUTO 16. Because of its proximity to the sun, ...
... 13. Methane gives URANUS/NEPTUNE its blue-green color. (two answers acceptable) 14. The spacecraft Magellan took the first radar images of VENUS’s surface since it is impossible to see. 15. Not discovered until 1930 because it is so far away from Earth. PLUTO 16. Because of its proximity to the sun, ...
b 03 Other Obj in Sol System combo ppt
... • rich in minerals (like planetary moons) • largest asteroid is only about 100 km in diameter • about 91 Apollo asteroids have been identified – potential for colliding with Earth (theory for extinction of the dinosaurs) • called minor planets or planetoids • rocky leftover mass of the inner planets ...
... • rich in minerals (like planetary moons) • largest asteroid is only about 100 km in diameter • about 91 Apollo asteroids have been identified – potential for colliding with Earth (theory for extinction of the dinosaurs) • called minor planets or planetoids • rocky leftover mass of the inner planets ...
coSmoS in youR PockET
... If you can’t see it, try again another night until you see it and then draw a picture of the Moon. ...
... If you can’t see it, try again another night until you see it and then draw a picture of the Moon. ...
Sample multiple choice questions for Exam 3
... Multiple Choice: 26 questions, 3 points each. Select the best answer to each of the questions below. Place your answer on the computer answer sheet provided. 1) The approximate dimensions of the frozen nucleus of a typical comet is a) 1-2 millimeters (pinhead-sized) b) 1-20 km (city-sized) c) 300 – ...
... Multiple Choice: 26 questions, 3 points each. Select the best answer to each of the questions below. Place your answer on the computer answer sheet provided. 1) The approximate dimensions of the frozen nucleus of a typical comet is a) 1-2 millimeters (pinhead-sized) b) 1-20 km (city-sized) c) 300 – ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.