* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Our SOlar System
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
De revolutionibus orbium coelestium wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
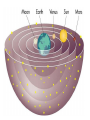
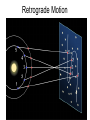
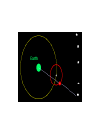
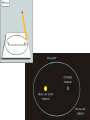
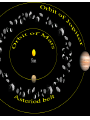
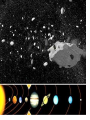
Our Solar System Models of the Solar System Objectives: Compare the models of the universe developed by Ptolemy & Copernicus Summarize Kepler’s 3 laws of planetary motion Aristotle (384-322 B.C.) • Promoted a GEOCENTRIC model of the universe • The universe revolves around ME • But doesn’t explain the RETROGRADE motion Retrograde Motion Ptolemy (87-150 A.D.) epicycles Copernicus (1500s A.D.) Proposed the HELIOCENTRIC model of the universe. The arguments against the Heliocentric Model 1) If the Earth actually spun on an axis -- as required in a heliocentric system to explain the diurnal motion (day/night)of the sky-- why didn't objects fly off the spinning Earth? 2) If the Earth was in motion around the sun, why didn't it leave behind the birds flying in the air? 3) If the Earth were actually on an orbit around the sun, why wasn't a parallax effect observed? That is, as illustrated in the adjacent figure, stars should appear to change their position with the respect to the other background stars as the Earth moved about its orbit, because of viewing them from a different perspective Copernicus Copernicus put the SUN in the middle of our solar system=> heliocentric model Galileo agreed with him & invented the first TELESCOPE just to prove that the Sun was in the center of our solar system. Kepler (1571-1630 AD) • First to explain the principles of how a telescope works • First to suggest that the Sun rotates about its axis Formulated the other’s ideas into Mathematical formulas creating Kepler’s 3 laws of Planetary Motion The First Law: Planets move in ellipses with the Sun at one focus. APHELION PERIHELION Astronomical Unit = 149 598 000 km The 2nd Law: A planet speeds up as it gets closer to the sun. So that the area of space covered is the same whether the earth is close to the sun or further away. The 3rd Law: the time it takes to orbit the sun is directly related to its distance from the sun. Sir Issac Newton (1642-1727) explained that the planets move in ellipses around the Sun because of GRAVITY Assignment: Kepler’s 3 Laws of Planetary Motion Handout Comets follow the Kuiper Belt. The Kuiper Belt follows past Neptune's orbit to the other side of the Sun. There is an "Oort" cloud that's a spherical region of Comets on the Kuiper Belt. What do you think this ghostly image is?