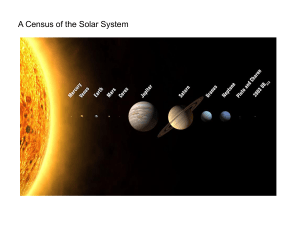
Summary from last lecture
... What is a planet? (solar system only for now!) (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a shape under hydrostatic equilibrium => must be “round” (and not potato-shaped!) An irregular solid body will deform under self-gravity to hydrostatic equili ...
... What is a planet? (solar system only for now!) (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a shape under hydrostatic equilibrium => must be “round” (and not potato-shaped!) An irregular solid body will deform under self-gravity to hydrostatic equili ...
A Census of the Solar System
... 1. Planets and their satellites all lie in the same plane - the ecliptic – to within a few degrees 2. Sun’s rotational equator aligned with ecliptic 3. Planetary orbits are nearly circular ellipses 4. Planets all revolve in same W -> E direction 5. Sun and planets all rotate on axes in same W –E dir ...
... 1. Planets and their satellites all lie in the same plane - the ecliptic – to within a few degrees 2. Sun’s rotational equator aligned with ecliptic 3. Planetary orbits are nearly circular ellipses 4. Planets all revolve in same W -> E direction 5. Sun and planets all rotate on axes in same W –E dir ...
Astro 1050 HW #2
... 23. T/F: Comets are made of mostly rocky material from the asteroid belt. 24. Discuss similarities and differences in the way terrestrial planets and giant planets formed in our Solar System. 25. Many of the giant exoplanets are quite close to their parent stars. If they initially formed farther out ...
... 23. T/F: Comets are made of mostly rocky material from the asteroid belt. 24. Discuss similarities and differences in the way terrestrial planets and giant planets formed in our Solar System. 25. Many of the giant exoplanets are quite close to their parent stars. If they initially formed farther out ...
Our Universe - Etiwanda E
... A piece of rock made up of material similar to a planet. Most asteroids are between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter captured by gravity. Some asteroids are the moons of planets. ...
... A piece of rock made up of material similar to a planet. Most asteroids are between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter captured by gravity. Some asteroids are the moons of planets. ...
Planets - WordPress.com
... 6. It has the most complex ring system of any planet in our solar system. 7. It is the least dense planet in the solar system with a density less than water. 8. Like Jupiter, it probably has an inner rocky core, an outer liquid metallic hydrogen core, and a dense hydrogen/helium atmosphere. 9. Like ...
... 6. It has the most complex ring system of any planet in our solar system. 7. It is the least dense planet in the solar system with a density less than water. 8. Like Jupiter, it probably has an inner rocky core, an outer liquid metallic hydrogen core, and a dense hydrogen/helium atmosphere. 9. Like ...
supplementary notes for space
... planets and other bodies in space (e.g. comets) orbit the Sun in predictable pathways – elliptical orbits… because we can use math to understand the pathways we can make accurate predictions about the position of bodies in space and about events such as solar eclipses (Moon moves between Earth and S ...
... planets and other bodies in space (e.g. comets) orbit the Sun in predictable pathways – elliptical orbits… because we can use math to understand the pathways we can make accurate predictions about the position of bodies in space and about events such as solar eclipses (Moon moves between Earth and S ...
Name____________________________________________
... __3__ Our Solar System __2___ The Milky Way __1__ The Universe 3. What is a galaxy? A huge group of single stars, star systems, star clusters, dust, and gas bound together by gravity. 4. What does an elliptical galaxy look like? Round or flattened ball; smashed circle 5. The Milky Way Galaxy is just ...
... __3__ Our Solar System __2___ The Milky Way __1__ The Universe 3. What is a galaxy? A huge group of single stars, star systems, star clusters, dust, and gas bound together by gravity. 4. What does an elliptical galaxy look like? Round or flattened ball; smashed circle 5. The Milky Way Galaxy is just ...
Chapter 29 Our Solar System
... All of the planets (& former planets) and their satellites orbit the Sun in the same direction, and all their orbits, except Pluto's lie near the same plane. ...
... All of the planets (& former planets) and their satellites orbit the Sun in the same direction, and all their orbits, except Pluto's lie near the same plane. ...
ASTRONOMY 1001 FALL SEMESTER 2004
... Comets, ion and dust tails, structure, nucleus, origin, behavior in orbit Origin of solar system, patterns of motion, centrifugal force, conservation of angular momentum, interstellar clouds, gravitational contraction, accretion, planetesimals, protoplanets, collisions, solar wind 3) Sun: Structure, ...
... Comets, ion and dust tails, structure, nucleus, origin, behavior in orbit Origin of solar system, patterns of motion, centrifugal force, conservation of angular momentum, interstellar clouds, gravitational contraction, accretion, planetesimals, protoplanets, collisions, solar wind 3) Sun: Structure, ...
Lecture11 - UCSB Physics
... • C) The gas in the nebular disk would have to be clumpy rather than smooth • D) The gas in the nebular disk would have to be mostly methane and ammonia rather than hydrogen and helium ...
... • C) The gas in the nebular disk would have to be clumpy rather than smooth • D) The gas in the nebular disk would have to be mostly methane and ammonia rather than hydrogen and helium ...
geocentric - Hewlett
... Earth is at the center of the Universe. So the Sun, Moon, Stars and Planets are all revolving around Earth. In the Geocentric Model, Earth does not move, it doesn’t even rotate. Who was the first scientist to say that the Earth is not the center of the Solar System, but the Sun? Copernicus was fir ...
... Earth is at the center of the Universe. So the Sun, Moon, Stars and Planets are all revolving around Earth. In the Geocentric Model, Earth does not move, it doesn’t even rotate. Who was the first scientist to say that the Earth is not the center of the Solar System, but the Sun? Copernicus was fir ...
Moon Obs #1 Due!
... hard surfaces, but cloud formations in their atmospheres • Jovian planets are much larger then the terrestrials! ...
... hard surfaces, but cloud formations in their atmospheres • Jovian planets are much larger then the terrestrials! ...
File
... material (mostly H and He) within a spiral arm of the milky way galaxy began to contract and flatten into a rotating disk Disk rotated and most of the mass concentrated in the center Surrounding the central disk, the turbulent rotating nebula of interstellar gases began to cool and condense, forming ...
... material (mostly H and He) within a spiral arm of the milky way galaxy began to contract and flatten into a rotating disk Disk rotated and most of the mass concentrated in the center Surrounding the central disk, the turbulent rotating nebula of interstellar gases began to cool and condense, forming ...
Solar System Worksheet
... 6. Venus’s period of revolution lasts ____________ (compared to one earth year). 7. _____________ _ is the hottest planet due to a runaway greenhouse gas effect that traps heat with its thick CO2 atmosphere. 8. Earth is the only planet in the solar system known to have _____________ 9. Venus’s perio ...
... 6. Venus’s period of revolution lasts ____________ (compared to one earth year). 7. _____________ _ is the hottest planet due to a runaway greenhouse gas effect that traps heat with its thick CO2 atmosphere. 8. Earth is the only planet in the solar system known to have _____________ 9. Venus’s perio ...
Test#2
... c) in Casssini's division, d) they all move at the same speed 28. Why are no impact craters seen on Io? a) it does not have a solid surface, b) it has extensive volcanic activity c) it was very recently captured by the solar system, d) its icy surface heals very rapidly 29. The heat that keeps the i ...
... c) in Casssini's division, d) they all move at the same speed 28. Why are no impact craters seen on Io? a) it does not have a solid surface, b) it has extensive volcanic activity c) it was very recently captured by the solar system, d) its icy surface heals very rapidly 29. The heat that keeps the i ...
... A. A body that orbits the sun, is not a satellite of a planet, is massive enough to pull itself into a spherical shape but not massive enough to clear out other bodies in and near it’s orbit B. Pair of stars that orbit around their common center of mass. C. A form of hydrogen that is a good electric ...
small rocky planets
... is 11 times bigger than that of the Earth’s. Overall, Jupiter is about 318 times the size of Earth. Jupiter is composed almost entirely of hydrogen and helium. • Because Jupiter rotates so quickly, it’s clouds form belts (low-lying, relatively warm cloud layers) and zones (bright, high-altitude, coo ...
... is 11 times bigger than that of the Earth’s. Overall, Jupiter is about 318 times the size of Earth. Jupiter is composed almost entirely of hydrogen and helium. • Because Jupiter rotates so quickly, it’s clouds form belts (low-lying, relatively warm cloud layers) and zones (bright, high-altitude, coo ...
Astronomy 103
... Note: in only one second, light can circumnavigate the Earth more than seven times ...
... Note: in only one second, light can circumnavigate the Earth more than seven times ...
Astronomy Review - Cockeysville Middle
... Flying Rocks Made of rocky or metallic materials Seen because it reflects sunlight. Mainly found between Jupiter and Mars in the Asteroid Belt. ...
... Flying Rocks Made of rocky or metallic materials Seen because it reflects sunlight. Mainly found between Jupiter and Mars in the Asteroid Belt. ...
The Sun as We See It Lecture 10, September 17, 2003
... Further properties of the Sun • The chemical composition of the Sun: cosmic composition • The luminosity of the Sun = 3.85E+26 Watts • The age of the Sun (how could we know this?) • Comparison of other objects (M4, Arcturus) ...
... Further properties of the Sun • The chemical composition of the Sun: cosmic composition • The luminosity of the Sun = 3.85E+26 Watts • The age of the Sun (how could we know this?) • Comparison of other objects (M4, Arcturus) ...
Week 7 Revision Lecture
... • The system tries to achieve the lowest energy = highest stability. • As everything orbits, some resonances are stable (Pluto-Neptune; Io, Europa and Ganymede). Others are not stable (cleared gaps in Saturn’s rings). ...
... • The system tries to achieve the lowest energy = highest stability. • As everything orbits, some resonances are stable (Pluto-Neptune; Io, Europa and Ganymede). Others are not stable (cleared gaps in Saturn’s rings). ...
Chapter 8 Powerpoint
... Understanding the Solar System • By definition, there are eight planets which consist of four terrestrial planets which are closer to the Sun and four gaseous giant planets which are further away. The terrestrial and gas planets are separated by a belt of rocky debris known as the ...
... Understanding the Solar System • By definition, there are eight planets which consist of four terrestrial planets which are closer to the Sun and four gaseous giant planets which are further away. The terrestrial and gas planets are separated by a belt of rocky debris known as the ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.