Biology First Semester Study Questions
... 5. Which carbohydrates are found in animals? 6. Which carbohydrates are found in plants? 7. What are the four types of lipids? 8. What are the functions of each lipid? 9. Which lipids are found in animals? 10. Which lipids are found in plants? 11. What are the two types of nucleic acids? 12. What ar ...
... 5. Which carbohydrates are found in animals? 6. Which carbohydrates are found in plants? 7. What are the four types of lipids? 8. What are the functions of each lipid? 9. Which lipids are found in animals? 10. Which lipids are found in plants? 11. What are the two types of nucleic acids? 12. What ar ...
ppt
... Lipid content of cell membranes varies (Table 1). Mammalian plasma membranes: mostly 4 major phospholipids • Animal cells also contain glycolipids and cholesterol • Organelle membranes have different composition • Even different lipids on inner, outer surface membrane ...
... Lipid content of cell membranes varies (Table 1). Mammalian plasma membranes: mostly 4 major phospholipids • Animal cells also contain glycolipids and cholesterol • Organelle membranes have different composition • Even different lipids on inner, outer surface membrane ...
18. Metabolism of lipids 1
... • two lipoproteins — apo B-100 and apo E • the main transport form of TGs synthesized in the organism (liver) • deliver the TGs from liver to peripheral tissue (muscle for energy, adipose for storage) • bind to membrane-bound lipoprotein lipases (triacylglycerols are again degraded into free fatty a ...
... • two lipoproteins — apo B-100 and apo E • the main transport form of TGs synthesized in the organism (liver) • deliver the TGs from liver to peripheral tissue (muscle for energy, adipose for storage) • bind to membrane-bound lipoprotein lipases (triacylglycerols are again degraded into free fatty a ...
Fatty acid
... four fused rings that are oriented in a planar manner. Cholesterol is an amphipathic molecule with a polar hydroxyl head group and a non-polar steroid nucleus and hydrocarbon side chain. In addition to having a structural role in membranes, sterols are precursors for several products such as steroid ...
... four fused rings that are oriented in a planar manner. Cholesterol is an amphipathic molecule with a polar hydroxyl head group and a non-polar steroid nucleus and hydrocarbon side chain. In addition to having a structural role in membranes, sterols are precursors for several products such as steroid ...
Respiration - Biology Innovation
... Fats and proteins can also be used to respire. When fats are about to be respired they are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol. The glycerol is converted into triose phosphate and enters the glycolysis stage. The fatty acids are broken down into two carbon fragments and entered into the Krebs ...
... Fats and proteins can also be used to respire. When fats are about to be respired they are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol. The glycerol is converted into triose phosphate and enters the glycolysis stage. The fatty acids are broken down into two carbon fragments and entered into the Krebs ...
Ch. 2 – Bio Chem
... http://www.whitetigernaturalmedicine.com/wpcontent/uploads/2012/02/amino-acid-structure.jpg ...
... http://www.whitetigernaturalmedicine.com/wpcontent/uploads/2012/02/amino-acid-structure.jpg ...
Lecture 7
... • Produces only small amounts of ATP (one or two ATP molecules for each molecule of starting material) • ATP molecules are produced by substratelevel phosphorylation. ...
... • Produces only small amounts of ATP (one or two ATP molecules for each molecule of starting material) • ATP molecules are produced by substratelevel phosphorylation. ...
Both DRIs and RDAs refer to long-term average daily nutrient intake
... • Proteins consumed in excess of the body's needs is deaminated and the resulting carbon skeleton metabolized to provide: 1- energy or 2- acetyl CoA for fatty acid synthesis If carbohydrates intake is less than 130 g/day ,, Therefore, carbohydrate is considered to be protein-sparing,as it allows ami ...
... • Proteins consumed in excess of the body's needs is deaminated and the resulting carbon skeleton metabolized to provide: 1- energy or 2- acetyl CoA for fatty acid synthesis If carbohydrates intake is less than 130 g/day ,, Therefore, carbohydrate is considered to be protein-sparing,as it allows ami ...
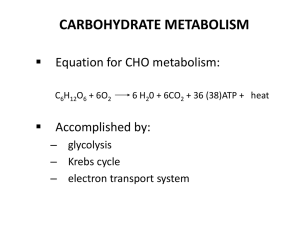
The bridge between glycolysis and the citric acid (Krebs) cycle
... • Support by biochemical analysis (of the vitamins) showed for the first time that, at the molecular level, the same structures and functions are found in all living beings; that the whole living world is constructed out of the same materials • Thus there emerged a new aspect, a hidden face of the e ...
... • Support by biochemical analysis (of the vitamins) showed for the first time that, at the molecular level, the same structures and functions are found in all living beings; that the whole living world is constructed out of the same materials • Thus there emerged a new aspect, a hidden face of the e ...
The Chemistry of Biology
... A. Triglycerides B. Monosaccharides C. Polypeptides D. Polysaccharides E. ATP 36. All of the following are polysaccharides except A. Dextran in some bacterial slime layers B. Agar used to make solid culture media C. A cell's glycocalyx D. Cellulose in certain cell walls E. Prostaglandins in inflamma ...
... A. Triglycerides B. Monosaccharides C. Polypeptides D. Polysaccharides E. ATP 36. All of the following are polysaccharides except A. Dextran in some bacterial slime layers B. Agar used to make solid culture media C. A cell's glycocalyx D. Cellulose in certain cell walls E. Prostaglandins in inflamma ...
Midterm Exam Note: Before beginning, please scan the entire exam
... 45) What is the best explanation for the shape of line E after 50 minutes? A) Water is no longer leaving the bag. B) Water is no longer entering the bag. C) Water is leaving and entering the bag at the same rate. D) Water is entering the bag at the same rate that sucrose is leaving the bag. E) Sucro ...
... 45) What is the best explanation for the shape of line E after 50 minutes? A) Water is no longer leaving the bag. B) Water is no longer entering the bag. C) Water is leaving and entering the bag at the same rate. D) Water is entering the bag at the same rate that sucrose is leaving the bag. E) Sucro ...
Origin of Life: I Monomers to Polymers
... and intermediates (HCN, H2CO, HC3N) and aminoacetonitrile (glycine precursor)" ...
... and intermediates (HCN, H2CO, HC3N) and aminoacetonitrile (glycine precursor)" ...
Document
... H HH HH HH HH H H HH HH HH HH HH H H HH O H- C- C- C- C- C- C-C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C-O-H H HH HH HH HH H H HH HH HH HH HH H H HH (about 50% longer than long-chain FAs) ...
... H HH HH HH HH H H HH HH HH HH HH H H HH O H- C- C- C- C- C- C-C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C- C-O-H H HH HH HH HH H H HH HH HH HH HH H H HH (about 50% longer than long-chain FAs) ...
Chapter 5
... of hydrophobic molecules • Lipids are the one class of large biological molecules that do not form polymers • The unifying feature of lipids is having little or no affinity for water • Lipids are hydrophobic because they consist mostly of hydrocarbons, which form nonpolar covalent bonds • The most b ...
... of hydrophobic molecules • Lipids are the one class of large biological molecules that do not form polymers • The unifying feature of lipids is having little or no affinity for water • Lipids are hydrophobic because they consist mostly of hydrocarbons, which form nonpolar covalent bonds • The most b ...
Amino Acids as Protein Building Blocks [2]
... primary sequence of amino acids. The physical chemical properties of the amino acids contain the biological information required for folding and function. ...
... primary sequence of amino acids. The physical chemical properties of the amino acids contain the biological information required for folding and function. ...
Biologically Important Molecules - Proteins PPT
... Proteins represent an extremely diverse type of macromolecule, providing such functions as: ...
... Proteins represent an extremely diverse type of macromolecule, providing such functions as: ...
Student Handout 1 Key - 3D Molecular Designs
... The double bond in an unsaturated fatty acid may form one of two possible configurations: trans or cis. You may model the trans configuration by attaching the second piece of the tail to the first to produce a straighter chain. The cis configuration may be modeled by producing a kinked configuration ...
... The double bond in an unsaturated fatty acid may form one of two possible configurations: trans or cis. You may model the trans configuration by attaching the second piece of the tail to the first to produce a straighter chain. The cis configuration may be modeled by producing a kinked configuration ...
Chem*3560 Lecture 29: Membrane Transport and metabolism
... This occurs if [ADP] is low, so that TCA cycle oxidation reactions slow down. Export of citrate to the cytoplasm bypasses most of the oxidative reactions of the TCA cycle. Malate generated in the cytoplasm balances citrate export, ensuring that substrate to generate new citrate is maintained. ...
... This occurs if [ADP] is low, so that TCA cycle oxidation reactions slow down. Export of citrate to the cytoplasm bypasses most of the oxidative reactions of the TCA cycle. Malate generated in the cytoplasm balances citrate export, ensuring that substrate to generate new citrate is maintained. ...
Document
... Not a long term storage form of energy Consumed at a high rate : stock in the cell is very small As it is being used up, it has to be replenished: need energy Phototrophs (algae, plants, some bacteria) use solar energy: photosynthesis Chemotrophs ( eg; S-bacteria, nitrifying bacteria) use chemical e ...
... Not a long term storage form of energy Consumed at a high rate : stock in the cell is very small As it is being used up, it has to be replenished: need energy Phototrophs (algae, plants, some bacteria) use solar energy: photosynthesis Chemotrophs ( eg; S-bacteria, nitrifying bacteria) use chemical e ...
Chapter 1 - TeacherWeb
... Cellular respiration – name four phases, starting reactants/ending products of each phase, location of each process, general understanding of each process, number of ATP & product at each stage produced by 1 glucose molecule Role of NAD+, FAD, Coenzyme A Similarities and differences between aerobic ...
... Cellular respiration – name four phases, starting reactants/ending products of each phase, location of each process, general understanding of each process, number of ATP & product at each stage produced by 1 glucose molecule Role of NAD+, FAD, Coenzyme A Similarities and differences between aerobic ...

















![Amino Acids as Protein Building Blocks [2]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001231379_1-1c71e58dd2b4a4d156753bc870eff68b-300x300.png)