Citric Acid Cycle Overview
... • Why is the activation of pyruvate carboxylase by acetyl‐CoA a good regulatory strategy? ...
... • Why is the activation of pyruvate carboxylase by acetyl‐CoA a good regulatory strategy? ...
Making basic science clinically relevant for learners: the biochemistry example Eric Niederhoffer
... • How does nervous tissue (neurons and glial cells) produce ATP (carbohydrates, fatty acids, ketone bodies, branched-chain amino acids)? • How do glial cells (astrocytes) assist neurons? • What are some key clinical features (history, physical, laboratory test results) associated with defects in met ...
... • How does nervous tissue (neurons and glial cells) produce ATP (carbohydrates, fatty acids, ketone bodies, branched-chain amino acids)? • How do glial cells (astrocytes) assist neurons? • What are some key clinical features (history, physical, laboratory test results) associated with defects in met ...
3.5 What are the chemical structures and functions of nucleic acids?
... molecules called monomers. Macromolecules in living organisms include polysaccharides, proteins, and nucleic acids. Functional groups are small groups of atoms that are consistently found together in a variety of different macromolecules. Functional groups have particular chemical properties that th ...
... molecules called monomers. Macromolecules in living organisms include polysaccharides, proteins, and nucleic acids. Functional groups are small groups of atoms that are consistently found together in a variety of different macromolecules. Functional groups have particular chemical properties that th ...
Answer Key - Department of Chemistry ::: CALTECH
... was shorter because of the presence of a new enzyme catalyzing the reaction glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate + NAD+ 3-phosphoglycerate + NADH + H+. Would shortening the glycolytic pathway in this way benefit the cell? Explain. No. There would be no anaerobic productions of ATP; aerobic ATP production wo ...
... was shorter because of the presence of a new enzyme catalyzing the reaction glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate + NAD+ 3-phosphoglycerate + NADH + H+. Would shortening the glycolytic pathway in this way benefit the cell? Explain. No. There would be no anaerobic productions of ATP; aerobic ATP production wo ...
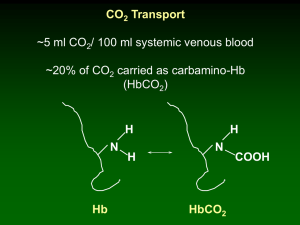
CO2 would move across a plasma membrane more quickly than
... Something is inhibiting his cells from using oxygen. Glycolysis occurs, but with no usable oxygen respiration cannot continue. ...
... Something is inhibiting his cells from using oxygen. Glycolysis occurs, but with no usable oxygen respiration cannot continue. ...
acetyl CoA - LSU School of Medicine
... ketone bodies (acetoacetate, b- (or 3-) hydroxybutyrate, acetone). B) Transported to other tissues, converted to acetyl CoA and metabolized by the citric acid cycle. C) Importance - water-soluble; produced in liver when excess acetyl CoA exceeds the oxidative capacity; can be used by skeletal and ca ...
... ketone bodies (acetoacetate, b- (or 3-) hydroxybutyrate, acetone). B) Transported to other tissues, converted to acetyl CoA and metabolized by the citric acid cycle. C) Importance - water-soluble; produced in liver when excess acetyl CoA exceeds the oxidative capacity; can be used by skeletal and ca ...
Metabolism PPT File
... glucose + oxygen —> water + carbon dioxide + energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 —> 6H2O + 6CO2 + energy Glucose is formed from the breakdown of ...
... glucose + oxygen —> water + carbon dioxide + energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 —> 6H2O + 6CO2 + energy Glucose is formed from the breakdown of ...
Lh6Ch18AAOxid
... Things to Know and Do Before Class 1. Amino acids from protein are an important energy source in carnivorous animals and during starvation. 2. The first step of AA catabolism is transfer of the NH3 via PLP-dependent aminotransferase usually to ketoglutarate to yield L-glutamate. 3. In most mammal ...
... Things to Know and Do Before Class 1. Amino acids from protein are an important energy source in carnivorous animals and during starvation. 2. The first step of AA catabolism is transfer of the NH3 via PLP-dependent aminotransferase usually to ketoglutarate to yield L-glutamate. 3. In most mammal ...
BioChem pg 635 to 641 ch 34 [4-20
... A. Conversion of cholesterol to Cholic Acid and Chenocholic Acid Bile salts are synthesized in the liver from cholesterol Rxns hydroxylate the steroid nucleus and cleave side chain In the first and rate-limiting reaction ...
... A. Conversion of cholesterol to Cholic Acid and Chenocholic Acid Bile salts are synthesized in the liver from cholesterol Rxns hydroxylate the steroid nucleus and cleave side chain In the first and rate-limiting reaction ...
Carbon-Based Molecules
... and butter. You know plant fats as oils, such as olive oil and peanut oil. The structures of fats and oils are similar. They both consist of a molecule called glycerol (glihs-uh-rawl) bonded to molecules called fatty acids. Fatty acids are chains of carbon atoms bonded to hydrogen atoms. Two differe ...
... and butter. You know plant fats as oils, such as olive oil and peanut oil. The structures of fats and oils are similar. They both consist of a molecule called glycerol (glihs-uh-rawl) bonded to molecules called fatty acids. Fatty acids are chains of carbon atoms bonded to hydrogen atoms. Two differe ...
ppt lecture
... • Diffusion: fatty acids • Lipids resynthesize into triglycerides, phospholipids (blood & lymph vessels), ...
... • Diffusion: fatty acids • Lipids resynthesize into triglycerides, phospholipids (blood & lymph vessels), ...
Digestion
... • Diffusion: fatty acids • Lipids resynthesize into triglycerides, phospholipids (blood & lymph vessels), ...
... • Diffusion: fatty acids • Lipids resynthesize into triglycerides, phospholipids (blood & lymph vessels), ...
3. CITRIC ACID CYCLE
... pyruvate is further converted to acetyl CoA by pyruvate dehydrogenase before entering into citric acid cycle. • During this process two more molecules of NADH are available for oxidation by the electron transport cycle reoxidation route to yield 6 ATP molecules. ...
... pyruvate is further converted to acetyl CoA by pyruvate dehydrogenase before entering into citric acid cycle. • During this process two more molecules of NADH are available for oxidation by the electron transport cycle reoxidation route to yield 6 ATP molecules. ...
2 Molecular - bloodhounds Incorporated
... chain on either side of the double bond are either both “up” or both “down,” such that both are on the same side of the molecule. • In trans bonds, the two pieces of the molecule are on opposite sides of the double bond, that is, one “up” and one “down” across from each other. • Naturally-occurring ...
... chain on either side of the double bond are either both “up” or both “down,” such that both are on the same side of the molecule. • In trans bonds, the two pieces of the molecule are on opposite sides of the double bond, that is, one “up” and one “down” across from each other. • Naturally-occurring ...
Biomolecules - Good Earth School
... An amino acid exists as a positive ion in acidic solution and as a negative ion in the basic solution. Therefore, on passing current, it will migrate towards the cathode in acidic solution and towards the anode in basic solution. Hence, at a particular pH of the solution, the amino acid molecule sho ...
... An amino acid exists as a positive ion in acidic solution and as a negative ion in the basic solution. Therefore, on passing current, it will migrate towards the cathode in acidic solution and towards the anode in basic solution. Hence, at a particular pH of the solution, the amino acid molecule sho ...
Basic_Chemistry___Biochemistry__Ch_2__S2
... Carbon can make four bonds with many types of atoms including itself; can form large molecules Result: many different types of organic molecules each with a unique structure and therefore function ...
... Carbon can make four bonds with many types of atoms including itself; can form large molecules Result: many different types of organic molecules each with a unique structure and therefore function ...
Mode-of-Action
... Sold with phenoxy herbicides and dicamba as PowerZone and SpeedZone Limited translocation Inhibits key enzyme in chlorophyll synthesis Causes buildup of phytotoxic compounds which damages cell membranes Cellular fluids leak, followed by cell death ...
... Sold with phenoxy herbicides and dicamba as PowerZone and SpeedZone Limited translocation Inhibits key enzyme in chlorophyll synthesis Causes buildup of phytotoxic compounds which damages cell membranes Cellular fluids leak, followed by cell death ...
Word
... During gluconeogenesis malate is moving into the cytoplasm It transports NADH from the cytosol to the matrix It is essentially irreversible It uses an -ketoglutarate-aspartate cotransporter to maintains carbon balance It maintain glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate dehydrogenase activity under anaerobic con ...
... During gluconeogenesis malate is moving into the cytoplasm It transports NADH from the cytosol to the matrix It is essentially irreversible It uses an -ketoglutarate-aspartate cotransporter to maintains carbon balance It maintain glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate dehydrogenase activity under anaerobic con ...
Lecture 8 - People Server at UNCW
... – Located in aortic and carotid bodies, medulla – Sample pO2 and pCO2 in blood ...
... – Located in aortic and carotid bodies, medulla – Sample pO2 and pCO2 in blood ...
1 acetyl CoA - WordPress.com
... citric acid cycle is used to harvest high energy electrons from carbon fuel. the central metabolic hub of the cell produces intermediates which are precursors for fatty acids, amino acids, nucleotide bases, and cholesterol The citric acid cycle may seem like an elaborate way to oxidize acetate into ...
... citric acid cycle is used to harvest high energy electrons from carbon fuel. the central metabolic hub of the cell produces intermediates which are precursors for fatty acids, amino acids, nucleotide bases, and cholesterol The citric acid cycle may seem like an elaborate way to oxidize acetate into ...
are PROTEINS!!!!!!
... • Carbohydrates are the major source of energy for most living things and include sugars, like glucose and sucrose, and starches. – Starches are long chains of sugars. ...
... • Carbohydrates are the major source of energy for most living things and include sugars, like glucose and sucrose, and starches. – Starches are long chains of sugars. ...
Chapter 3
... -speed up chemical reactions without becoming part of the reaction…thus, one enzyme can speed up thousands of chemical reactions. -called “catalysts” -lower the “activation energy” or the amount of energy that is needed to start a reaction. When a protein undergoes a shape change, it loses its abili ...
... -speed up chemical reactions without becoming part of the reaction…thus, one enzyme can speed up thousands of chemical reactions. -called “catalysts” -lower the “activation energy” or the amount of energy that is needed to start a reaction. When a protein undergoes a shape change, it loses its abili ...