Disaccharides
... Dietary disaccharides, as well as degradation products of starch, need to be broken down to monosaccharides in order to be absorbed. This final hydrolysis is accomplished by hydrolases enzymes attached to the intestinal membrane brush-border, referred to as ...
... Dietary disaccharides, as well as degradation products of starch, need to be broken down to monosaccharides in order to be absorbed. This final hydrolysis is accomplished by hydrolases enzymes attached to the intestinal membrane brush-border, referred to as ...
Document
... activated trypsin which may find its way into the ducts, by forming a complex with it Enzyme Y is also exhibiting a protective function, which is activated by traces of active trypsin degrades zymogen The alkaline pH (8.0-9.5) and low Ca2+ concentration in pancreatic secretions promote the degradati ...
... activated trypsin which may find its way into the ducts, by forming a complex with it Enzyme Y is also exhibiting a protective function, which is activated by traces of active trypsin degrades zymogen The alkaline pH (8.0-9.5) and low Ca2+ concentration in pancreatic secretions promote the degradati ...
Ch03Test_File+heikka
... electric charges. That makes this region of the molecule a. hydrophobic. b. hydrophilic. c. nonpolar. d. unsaturated. e. saturated. Answer: b 16. In a biological membrane, the phospholipids are arranged with the fatty acid chains facing the interior of the membrane. As a result, the interior of the ...
... electric charges. That makes this region of the molecule a. hydrophobic. b. hydrophilic. c. nonpolar. d. unsaturated. e. saturated. Answer: b 16. In a biological membrane, the phospholipids are arranged with the fatty acid chains facing the interior of the membrane. As a result, the interior of the ...
ppt
... Nucleotides can be synthesized from carbohydrates and amino acids, or reused following nucleic acid breakdown. Ribose-5-phosphate is starting point for nucleotide synthesis. Different pathways for synthesis of purine and pyrimidine. ...
... Nucleotides can be synthesized from carbohydrates and amino acids, or reused following nucleic acid breakdown. Ribose-5-phosphate is starting point for nucleotide synthesis. Different pathways for synthesis of purine and pyrimidine. ...
Lecture Resource ()
... In each of these transformations, one of the bonds to the a-carbon of the amino acid substrate is broken in the first step of the reaction ...
... In each of these transformations, one of the bonds to the a-carbon of the amino acid substrate is broken in the first step of the reaction ...
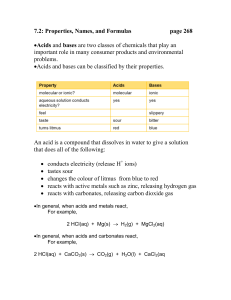
7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas page 268 •Acids and bases
... 7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas ...
... 7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas ...
Proteins are polymers of amino acids, Polypeptides (cofactors
... 3- Conditionally essential amino acid. – Meaning they are not normally required in the diet but can become essential and must be supplied exogenously in certain physiologic conditions in populations that do not synthesize it in adequate amounts. – Example: Tyrosine becomes essential in people with “ ...
... 3- Conditionally essential amino acid. – Meaning they are not normally required in the diet but can become essential and must be supplied exogenously in certain physiologic conditions in populations that do not synthesize it in adequate amounts. – Example: Tyrosine becomes essential in people with “ ...
KREBS CYCLE Definition Krebs cycle (aka tricarboxylic acid cycle
... 5. Second oxidative-decarboxylation takes place. α-ketoglutarate is converted to succinyl-CoA. CO2 and NADH are produced. ...
... 5. Second oxidative-decarboxylation takes place. α-ketoglutarate is converted to succinyl-CoA. CO2 and NADH are produced. ...
i. introduction to metabolism and catabolism
... b) Heterotrophs remove these electrons and give them to more electronegative molecules, releasing the stored energy B. CATABOLISM 1. The energy released during catabolism must be stored so that it is available for anabolism (energy currency) a) High energy bonds, such as ATP b) Reducing equivalents, ...
... b) Heterotrophs remove these electrons and give them to more electronegative molecules, releasing the stored energy B. CATABOLISM 1. The energy released during catabolism must be stored so that it is available for anabolism (energy currency) a) High energy bonds, such as ATP b) Reducing equivalents, ...
Biochem lectures
... Hierarchical nature of hormonal control Hormonal regulation of some physiological activities involves a hierarchy of cell types acting on each other either to stimulate or to modulate the release and action of a particular hormone. The secretion of hormones from successive levels of endocrine cells ...
... Hierarchical nature of hormonal control Hormonal regulation of some physiological activities involves a hierarchy of cell types acting on each other either to stimulate or to modulate the release and action of a particular hormone. The secretion of hormones from successive levels of endocrine cells ...
Chapter 26
... • Fat has glucose-sparing and protein-sparing effects when used for energy needs – Glucose is spared for consumption by cells that cannot use fat, like neurons – Protein not catabolized for fuel ...
... • Fat has glucose-sparing and protein-sparing effects when used for energy needs – Glucose is spared for consumption by cells that cannot use fat, like neurons – Protein not catabolized for fuel ...
U4L26 Nitrogen - The University of Sydney
... • Non-toxic – Can be present in blood at mM levels – Cleared by kidneys ...
... • Non-toxic – Can be present in blood at mM levels – Cleared by kidneys ...
Section 3 - Carbon Compounds
... include galactose, which is a component of milk, and fructose, which is found in many fruits. The large macromolecules formed from monosaccharides are known as polysaccharides. Many animals store excess sugar in a polysaccharide called glycogen, or animal starch. When the level of glucose in your bl ...
... include galactose, which is a component of milk, and fructose, which is found in many fruits. The large macromolecules formed from monosaccharides are known as polysaccharides. Many animals store excess sugar in a polysaccharide called glycogen, or animal starch. When the level of glucose in your bl ...
Lecture 12: Enzymes of Metabolism: An Introduction Reference
... iv. Statins are competitive inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase 1. Bind with affinity to the HMG-CoA reducatase active site and block the active site so HMG-CoA cant bind for reaction 11. State in general terms the relationship between LDL particles, LDL receptors on cells and cholesterol production by ...
... iv. Statins are competitive inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase 1. Bind with affinity to the HMG-CoA reducatase active site and block the active site so HMG-CoA cant bind for reaction 11. State in general terms the relationship between LDL particles, LDL receptors on cells and cholesterol production by ...
word - My eCoach
... Cellulose and Chitin Cellulose and Chitin are polysaccharides that function to support and protect the organism. The cell walls of plants are composed of cellulose. The cell walls of fungi and the exoskeleton of arthropods are composed of chitin. Cellulose is composed of beta-glucose monomers; starc ...
... Cellulose and Chitin Cellulose and Chitin are polysaccharides that function to support and protect the organism. The cell walls of plants are composed of cellulose. The cell walls of fungi and the exoskeleton of arthropods are composed of chitin. Cellulose is composed of beta-glucose monomers; starc ...
Digestive System
... • Flatus: gas produced by bacteria Disorders: • Appendix: appendicitis • Constipation: slow movement, >> water absorption • Diarrhea: >>speed of movement; >> secretion, << water absorption ...
... • Flatus: gas produced by bacteria Disorders: • Appendix: appendicitis • Constipation: slow movement, >> water absorption • Diarrhea: >>speed of movement; >> secretion, << water absorption ...
Essential Amino Acids
... molecules, and any excess proteins you eat are broken down into their amino acids and used for energy or converted and stored as fat. Protein breakdown produces the waste urea, which is filtered from the blood by the kidneys. Urea is what gives your urine its yellow color. Why protein is needed Diet ...
... molecules, and any excess proteins you eat are broken down into their amino acids and used for energy or converted and stored as fat. Protein breakdown produces the waste urea, which is filtered from the blood by the kidneys. Urea is what gives your urine its yellow color. Why protein is needed Diet ...
Fractose and galactose Metabolism
... About 15% to 20% of the calories contained in the western diet are supplied by fructose (about 100g/day). The major source of fructose is Disacchariede sucrose (table sugar). Fructose is also found as a free monosaccharide in many fruits and vegetables and in honey. Entry of fructose into cells is n ...
... About 15% to 20% of the calories contained in the western diet are supplied by fructose (about 100g/day). The major source of fructose is Disacchariede sucrose (table sugar). Fructose is also found as a free monosaccharide in many fruits and vegetables and in honey. Entry of fructose into cells is n ...
Energy Systems
... Strong research evidence, that with consistent aerobic training, the body can convert type IIb fibres into type Iia -that is, fast twitch muscles fibres can become an intermediary fibre that acts as both fast twitch and ...
... Strong research evidence, that with consistent aerobic training, the body can convert type IIb fibres into type Iia -that is, fast twitch muscles fibres can become an intermediary fibre that acts as both fast twitch and ...
Biology Homework - Whitinsville Christian School
... 5. How is polymer broken down into its subunits (monomers)? ...
... 5. How is polymer broken down into its subunits (monomers)? ...
Chapter 26 Nutrition and Metabolism *Lecture PowerPoint
... • Fat has glucose-sparing and protein-sparing effects when used for energy needs – Glucose is spared for consumption by cells that cannot use fat, like neurons – Protein not catabolized for fuel ...
... • Fat has glucose-sparing and protein-sparing effects when used for energy needs – Glucose is spared for consumption by cells that cannot use fat, like neurons – Protein not catabolized for fuel ...
Biochemistry Ch 37 696-706 [4-20
... Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway – ubiquitin is a small and highly conserved protein; it targets intracellular proteins for degradation by covalently binding to E-amino group of lysine residues accomplished by a 3 enzyme system -target is often polyubiquitinylated, forming long ubiquitin tails -a protea ...
... Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway – ubiquitin is a small and highly conserved protein; it targets intracellular proteins for degradation by covalently binding to E-amino group of lysine residues accomplished by a 3 enzyme system -target is often polyubiquitinylated, forming long ubiquitin tails -a protea ...
Krebs cycle
... Stoichiometry of the Citric Acid Cycle Two carbon atoms enter the cycle in the form of acetyl CoA. Two carbon atoms leave the cycle in the form of CO2 . Four pairs of hydrogen atoms leave the cycle in four oxidation reactions (three molecules of NAD+ one molecule of FAD are reduced). One mo ...
... Stoichiometry of the Citric Acid Cycle Two carbon atoms enter the cycle in the form of acetyl CoA. Two carbon atoms leave the cycle in the form of CO2 . Four pairs of hydrogen atoms leave the cycle in four oxidation reactions (three molecules of NAD+ one molecule of FAD are reduced). One mo ...
Amino Acid Analysis Please follow the guidelines below for
... Please clearly label your tubes, and include printed information about your samples, including weights. We will keep the samples stored at -80o C prior to analysis For HAA, we have a method calibrated from 5pmol-50pmol of each of the following amino acids: Cya**, His, Ser, Arg, Gly, Asp, MetS02**, G ...
... Please clearly label your tubes, and include printed information about your samples, including weights. We will keep the samples stored at -80o C prior to analysis For HAA, we have a method calibrated from 5pmol-50pmol of each of the following amino acids: Cya**, His, Ser, Arg, Gly, Asp, MetS02**, G ...