protein digest.99
... • amino acids enter cells by binding to specific a.a. transport proteins and riding down Na+ gradient • Na+ pump requires ATP and is essential for a.a. transport ...
... • amino acids enter cells by binding to specific a.a. transport proteins and riding down Na+ gradient • Na+ pump requires ATP and is essential for a.a. transport ...
Introduction to Carbohydrates
... • Low levels of free fatty acids occur in all tissues, but substantial amounts can sometimes be found in the plasma, particularly during fasting. • Plasma free fatty acids (transported by serum albumin) are in route from their point of origin (triacylglycerol of adipose tissue or circulating lipopro ...
... • Low levels of free fatty acids occur in all tissues, but substantial amounts can sometimes be found in the plasma, particularly during fasting. • Plasma free fatty acids (transported by serum albumin) are in route from their point of origin (triacylglycerol of adipose tissue or circulating lipopro ...
18 Pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA to Krebs Cycle A/P
... lactic acid in bacteria and man when oxygen is in short supply or not available. The build up of lactic acid causes some interesting effects. 1.) Lactic acid build up is a way to temporarily store a high-energy hydrogen proton and electron in lactic acid by oxidizing NADH NAD+. This allows the use o ...
... lactic acid in bacteria and man when oxygen is in short supply or not available. The build up of lactic acid causes some interesting effects. 1.) Lactic acid build up is a way to temporarily store a high-energy hydrogen proton and electron in lactic acid by oxidizing NADH NAD+. This allows the use o ...
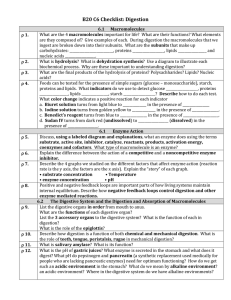
B20 C6 Checklist
... pepsin, chymotrypsin, trypsin, The pancreatic enzymes digest ______________, ________________, __________________and _________________. Carbohydrates are stored in the liver and muscle as _____________________ (the storage form of carbohydrates in animals) which is made of _______________ molecules. ...
... pepsin, chymotrypsin, trypsin, The pancreatic enzymes digest ______________, ________________, __________________and _________________. Carbohydrates are stored in the liver and muscle as _____________________ (the storage form of carbohydrates in animals) which is made of _______________ molecules. ...
ascendant cerebral 5-hydroxytryptamine
... slice preparations. The metabolic effects in vivo, like those of barbiturates, can be attributed to the general damping down ofelectrical activity, thus diminishing ionic fluxes induced by action potentials and by the release of excitatory transmitters. However, a direct effect of the inhibitory ami ...
... slice preparations. The metabolic effects in vivo, like those of barbiturates, can be attributed to the general damping down ofelectrical activity, thus diminishing ionic fluxes induced by action potentials and by the release of excitatory transmitters. However, a direct effect of the inhibitory ami ...
Exam 4
... a. Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase is one of the enzymes of the pathway. b. It is an exothermic process. c. It results in net synthesis of ATP. d. It results in synthesis of NADH. e. all of the above. 25. During strenuous exercise, the NADH formed in the glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase reaction ...
... a. Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase is one of the enzymes of the pathway. b. It is an exothermic process. c. It results in net synthesis of ATP. d. It results in synthesis of NADH. e. all of the above. 25. During strenuous exercise, the NADH formed in the glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase reaction ...
Book Problems Chapter 2
... (a) ATP + H2O → ADP + Pi The transporter must include a cytosolic nucleotide binding site that changes its conformation when its bound ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP. This conformational change must be communicated to the membrane-spanning portion of the protein, where the transported substrate binds. (b) ...
... (a) ATP + H2O → ADP + Pi The transporter must include a cytosolic nucleotide binding site that changes its conformation when its bound ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP. This conformational change must be communicated to the membrane-spanning portion of the protein, where the transported substrate binds. (b) ...
Metabolism: the Degradation and Synthesis of Living Cells
... strategies of metabolism. • Studies on enzymes. • Observation of metabolic processes in intact living organisms (e.g., in the brains under various states) • Metabolism differences among various organisms or various states of the same organism (for diagnosing and treating such diseases as cancer, inf ...
... strategies of metabolism. • Studies on enzymes. • Observation of metabolic processes in intact living organisms (e.g., in the brains under various states) • Metabolism differences among various organisms or various states of the same organism (for diagnosing and treating such diseases as cancer, inf ...
Chapter 12 Pathways to biomolecules
... A fatty acid molecule consists of a hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl (–COOH) group at one end. A fat, or triglyceride, is the product of a condensation reaction between three fatty acid molecules and a glycerol molecule. The fatty acid groups that make up a saturated fat contain only single carbon– ...
... A fatty acid molecule consists of a hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl (–COOH) group at one end. A fat, or triglyceride, is the product of a condensation reaction between three fatty acid molecules and a glycerol molecule. The fatty acid groups that make up a saturated fat contain only single carbon– ...
LAB-AIDS^ #505-12 Molecules ot Lite Kit Student
... Carbohydrates, fats, proteins and nucleic acid's are the four major groups of organic molecules found in living organisms. This Lab-Aids kit deals with the important class of organic molecules known as proteins. They are the main structural and growth components of cells in tissues such as skin, hai ...
... Carbohydrates, fats, proteins and nucleic acid's are the four major groups of organic molecules found in living organisms. This Lab-Aids kit deals with the important class of organic molecules known as proteins. They are the main structural and growth components of cells in tissues such as skin, hai ...
amino acid
... dehydration synthesis, hydrolysis, digestion, photosynthesis________________________________ Energy for chemical reactions comes from _living things (plants & animals)_________. Plants: _ trap and store energy from sunlight in energyrich compounds, carbs (by performing photosynthesis) ...
... dehydration synthesis, hydrolysis, digestion, photosynthesis________________________________ Energy for chemical reactions comes from _living things (plants & animals)_________. Plants: _ trap and store energy from sunlight in energyrich compounds, carbs (by performing photosynthesis) ...
Digestive system notes http://www
... involvement of the endocrine system (ie hormones) insulin hormone - lowers blood glucose glucagon - raises blood glucose pancreas islets/ ß-cells/alpha-cells produce these hormones liver & muscles convert glucose (with insulin); to glycogen and vice versa (with glucagon) ...
... involvement of the endocrine system (ie hormones) insulin hormone - lowers blood glucose glucagon - raises blood glucose pancreas islets/ ß-cells/alpha-cells produce these hormones liver & muscles convert glucose (with insulin); to glycogen and vice versa (with glucagon) ...
intermediary metabolism
... Metabolic control is exerted at a second level in higher organisms by hormonal regulation. Hormones are chemical menagers secreted by different endocrine glands and carried by blood to other tissues or organs, where they may stimulate or inhibit some specific metabolic activity. For e.g. the hormone ...
... Metabolic control is exerted at a second level in higher organisms by hormonal regulation. Hormones are chemical menagers secreted by different endocrine glands and carried by blood to other tissues or organs, where they may stimulate or inhibit some specific metabolic activity. For e.g. the hormone ...
Textbook of Biochemistry - OSU Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
... 6.1.1 ATP links energy producing and utilization. 6.2 Thermodynamic Relationships and Energy Rich Components 6.2.1 Free energy is energy that is available for useful work. 6.2.2 The caloric value of dietary substances is shown in Tale 6.2. 6.2.3 Compounds are classified on the basis of energy releas ...
... 6.1.1 ATP links energy producing and utilization. 6.2 Thermodynamic Relationships and Energy Rich Components 6.2.1 Free energy is energy that is available for useful work. 6.2.2 The caloric value of dietary substances is shown in Tale 6.2. 6.2.3 Compounds are classified on the basis of energy releas ...
Document
... – Glycerol + two fatty acids and a phosphorus (P) containing group • “Head” and “tail” regions have different properties • Important in cell membrane structure “Typical” structure of a phospholipid molecule Two fatty acid chains and a phosphorus-containing group are attached to the glycerol backbone ...
... – Glycerol + two fatty acids and a phosphorus (P) containing group • “Head” and “tail” regions have different properties • Important in cell membrane structure “Typical” structure of a phospholipid molecule Two fatty acid chains and a phosphorus-containing group are attached to the glycerol backbone ...
What Are the Functions of Amylase, Protease and Lipase Digestive
... Although amylase, protease and lipase are the three main enzymes your body uses to digest food, many other specialized enzymes also help in the process. Cells that line your intestines make enzymes called maltase, sucrase and lactase, each able to convert a specific type of sugar into glucose. Simil ...
... Although amylase, protease and lipase are the three main enzymes your body uses to digest food, many other specialized enzymes also help in the process. Cells that line your intestines make enzymes called maltase, sucrase and lactase, each able to convert a specific type of sugar into glucose. Simil ...
Biochemistry Unit Homework (Chapters 5 and 8)
... 2. Make a chart to contrast a system with high free energy versus a system with low free energy for the following factors: work capacity, equilibrium, spontaneity, and stability. 3. Contrast and compare exergonic reactions versus endergonic reactions. Which reaction type matches with catabolic react ...
... 2. Make a chart to contrast a system with high free energy versus a system with low free energy for the following factors: work capacity, equilibrium, spontaneity, and stability. 3. Contrast and compare exergonic reactions versus endergonic reactions. Which reaction type matches with catabolic react ...
here - Biology 100
... Which of the following is/are true concerning metabolic pathways? a. The products of a metabolic reaction will always contain more energy than did the reactants. b. They occur in an orderly series of chemical reactions. c. They may cause the formation or breakdown of molecules. d. They are able to s ...
... Which of the following is/are true concerning metabolic pathways? a. The products of a metabolic reaction will always contain more energy than did the reactants. b. They occur in an orderly series of chemical reactions. c. They may cause the formation or breakdown of molecules. d. They are able to s ...
(a) Small intestine
... Oxygen-using events take place within the cell to create ATP from ADP Carbon leaves cells as carbon dioxide (CO2) Hydrogen atoms are combined with oxygen to form water Energy produced by these reactions adds a phosphorus to ADP to produce ATP ATP can be broken down to release energy for cellular u ...
... Oxygen-using events take place within the cell to create ATP from ADP Carbon leaves cells as carbon dioxide (CO2) Hydrogen atoms are combined with oxygen to form water Energy produced by these reactions adds a phosphorus to ADP to produce ATP ATP can be broken down to release energy for cellular u ...
colon cleanse colon cleanse advanced
... Discussion Colon Cleanse Advanced of high-quality, easy-to-digest protein with the addition of amino acids, micronutrients, essential fatty acids, and metabolic cofactors makes ...
... Discussion Colon Cleanse Advanced of high-quality, easy-to-digest protein with the addition of amino acids, micronutrients, essential fatty acids, and metabolic cofactors makes ...
Renal Physiology 9 (Acid Base 1)
... Acid – Base balance (a.k.a. pH HOMEOSTASIS) one of the essential functions of the body. When discussing acid - base balance, we are normally concerned with regulation of H+ ion balance (although HCO3- plays a vital role in this balance). ...
... Acid – Base balance (a.k.a. pH HOMEOSTASIS) one of the essential functions of the body. When discussing acid - base balance, we are normally concerned with regulation of H+ ion balance (although HCO3- plays a vital role in this balance). ...
Coomes CELLULAR RESPIRATION: PRACTICE QUESTIONS PRE
... 7. A drug is tested in the laboratory and is found to create holes in both mitochondrial membranes. Scientists suspect that the drug will be harmful to human cells because it will inhibit A) the citric acid cycle. B) oxidative phosphorylation. C) glycolysis. D) the formation of alcohol. E) the citri ...
... 7. A drug is tested in the laboratory and is found to create holes in both mitochondrial membranes. Scientists suspect that the drug will be harmful to human cells because it will inhibit A) the citric acid cycle. B) oxidative phosphorylation. C) glycolysis. D) the formation of alcohol. E) the citri ...