chapt07_lecture - Globe
... • The energy for living is obtained by breaking down the organic molecules originally produced in plants the energy invested in building the organic molecules is retrieved by stripping away electrons and using them to make ATP this process is called cellular respiration What About Fat Cells? A ...
... • The energy for living is obtained by breaking down the organic molecules originally produced in plants the energy invested in building the organic molecules is retrieved by stripping away electrons and using them to make ATP this process is called cellular respiration What About Fat Cells? A ...
Chem 562 - SDSU Chemistry
... Biochemistry and Protein Modification), that complete an advanced undergraduate education in biochemistry. Metabolism refers to the complete set of chemical reactions that sustain life. Metabolism begins with the extraction of energy from environmental sources such as sunlight and reduced organic co ...
... Biochemistry and Protein Modification), that complete an advanced undergraduate education in biochemistry. Metabolism refers to the complete set of chemical reactions that sustain life. Metabolism begins with the extraction of energy from environmental sources such as sunlight and reduced organic co ...
1 1) What kinds of molecules pass through a cell membrane most
... A) has an increased chemical reactivity; it is primed to do cellular work. B) has a decreased chemical reactivity; it is less likely to provide energy for cellular work. C) has been oxidized as a result of a redox reaction involving the gain of an inorganic phosphate. D) has been reduced as a result ...
... A) has an increased chemical reactivity; it is primed to do cellular work. B) has a decreased chemical reactivity; it is less likely to provide energy for cellular work. C) has been oxidized as a result of a redox reaction involving the gain of an inorganic phosphate. D) has been reduced as a result ...
2 H
... electron acceptor, oxygen • An artifcial e- donor, phenylenediamine, is used to reduce the cytochrome oxidase • If the enzyme is present, the colorless reagent (reduced state) will turn blue (oxidized state) ...
... electron acceptor, oxygen • An artifcial e- donor, phenylenediamine, is used to reduce the cytochrome oxidase • If the enzyme is present, the colorless reagent (reduced state) will turn blue (oxidized state) ...
Glycolipids and Glyc..
... mediate protein-protein interaction of several membrane proteins that act together in the signaling mechanism. Palmitoylation is acquired post-translationally in the cytoplasm and does not make use of the ER secretory pathway. Instead, palmitoylated proteins appear to be routed directly to the inner ...
... mediate protein-protein interaction of several membrane proteins that act together in the signaling mechanism. Palmitoylation is acquired post-translationally in the cytoplasm and does not make use of the ER secretory pathway. Instead, palmitoylated proteins appear to be routed directly to the inner ...
Review - Columbus Labs
... 3. Initiation. The initiating codon in eukaryotes is always AUG. Eukaryotes, in contrast with prokaryotes, do not use a specific purinerich sequence (RBS) on the 5′ side to distinguish initiator AUGs from internal ones. Instead, the AUG nearest the 5′ end of mRNA is usually selected as the start sit ...
... 3. Initiation. The initiating codon in eukaryotes is always AUG. Eukaryotes, in contrast with prokaryotes, do not use a specific purinerich sequence (RBS) on the 5′ side to distinguish initiator AUGs from internal ones. Instead, the AUG nearest the 5′ end of mRNA is usually selected as the start sit ...
My name is La`Cheyla Blount. I am a senior and an undergraduate
... this gene creates a sexual dimorphic response to hepatic iron overload. Iron overload caused by hepcidin dysregulation or other factors can result in diseases such as hemochromatosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. βcatenin plays various roles in liver homeostasis, and aberrant signaling contributes t ...
... this gene creates a sexual dimorphic response to hepatic iron overload. Iron overload caused by hepcidin dysregulation or other factors can result in diseases such as hemochromatosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. βcatenin plays various roles in liver homeostasis, and aberrant signaling contributes t ...
Metabolism of bilirubin and bile salts synthesis (uronic acid pathway
... About 1 gram of cholesterol is eliminated from the body per day. Approximately half is excreted in the feces after conversion to bile acids. The remainder is excreted as cholesterol. The primary bile acids are synthesized in the liver from cholesterol. These are cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid ...
... About 1 gram of cholesterol is eliminated from the body per day. Approximately half is excreted in the feces after conversion to bile acids. The remainder is excreted as cholesterol. The primary bile acids are synthesized in the liver from cholesterol. These are cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid ...
06_Metabolism of lipid
... acetoacetate by 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase. Acetoacetate also undergoes a slow, ...
... acetoacetate by 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase. Acetoacetate also undergoes a slow, ...
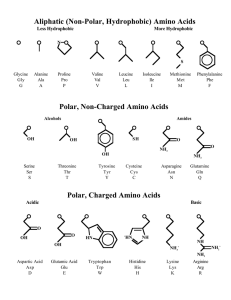
Amino Acids - Sehr Gut Web
... In these structures, the top circle represents the amino acid backbone (H2N—CH—COOH), with the R group depicted. In the case of proline, which is and alpha imino acid, rather than an amino acid, the circle represents the —CH—COOH group, the imino nitrogen being depicted as an element in the proline ...
... In these structures, the top circle represents the amino acid backbone (H2N—CH—COOH), with the R group depicted. In the case of proline, which is and alpha imino acid, rather than an amino acid, the circle represents the —CH—COOH group, the imino nitrogen being depicted as an element in the proline ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism Glucose Metabolism Oxidation of Glucose
... Citric Acid Cycle . ● When the blood glucose level is high (after meals ) the excess is converted to glycogen and stored (Glycogenesis ) .The body has limited capacity for storing glycogen and the remaining excess glucose is converted to fat and stored ...
... Citric Acid Cycle . ● When the blood glucose level is high (after meals ) the excess is converted to glycogen and stored (Glycogenesis ) .The body has limited capacity for storing glycogen and the remaining excess glucose is converted to fat and stored ...
Nonessential Amino Acid Metabolism in Healthy Adult Males Using
... 13CO2 oxidation values analyzed using repeated measures ANOVA (Graphpad PRISM) ...
... 13CO2 oxidation values analyzed using repeated measures ANOVA (Graphpad PRISM) ...
2b.-Citric-Acid-Cycle
... • ______ enzymes present in the _____ have acted on the substrate _____ and oxidised it. This rapid release of _____has reduced the resazurin dye and caused it to change colour. – Explain why the reaction in test tube B was slower than test tube A. • Test tube was slower than A because no glucose wa ...
... • ______ enzymes present in the _____ have acted on the substrate _____ and oxidised it. This rapid release of _____has reduced the resazurin dye and caused it to change colour. – Explain why the reaction in test tube B was slower than test tube A. • Test tube was slower than A because no glucose wa ...
Unit 4 - Digestive System
... Most food is digested rapidly, and the resulting molecules (including glucose) enter the blood stream. Without some control, the level of glucose (and other compounds) in the blood would be quite variable. The liver removes glucose from blood, converting it into glycogen. Glycogen is stored in both ...
... Most food is digested rapidly, and the resulting molecules (including glucose) enter the blood stream. Without some control, the level of glucose (and other compounds) in the blood would be quite variable. The liver removes glucose from blood, converting it into glycogen. Glycogen is stored in both ...
Ch. 5 - Macromolecules
... • The structure of phospholipids – Results in a bilayer arrangement found in cell membranes ...
... • The structure of phospholipids – Results in a bilayer arrangement found in cell membranes ...
Cellular Respiration CPB
... eukaryotes: series of proteins embedded in the inner membrane of mitochondrion prokaryotes: same chain in cell membrane H-E e- move from 1 carrier protein to the next E is used to move H ions across membrane (ATP synthase) every rotation of ATPase phosphate group is added to A-P-P A-P-P~ ...
... eukaryotes: series of proteins embedded in the inner membrane of mitochondrion prokaryotes: same chain in cell membrane H-E e- move from 1 carrier protein to the next E is used to move H ions across membrane (ATP synthase) every rotation of ATPase phosphate group is added to A-P-P A-P-P~ ...
Amino acids degradation and synthesis
... Amino acids whose catabolism yields pyruvate or one of the intermediates of the citric acid cycle are termed glucogenic or glycogenic Amino acids whose catabolism yields either acetoacetate or one of its precursor, (acetyl CoA or acetoacetyl CoA) are termed ketogenic. Some amino acids are both gluco ...
... Amino acids whose catabolism yields pyruvate or one of the intermediates of the citric acid cycle are termed glucogenic or glycogenic Amino acids whose catabolism yields either acetoacetate or one of its precursor, (acetyl CoA or acetoacetyl CoA) are termed ketogenic. Some amino acids are both gluco ...
prospect benecord
... wheat, etc. Policosanol has an inhibitor effect on the enzymes responsible for the endogenous synthesis of cholesterol in the liver. Clinical studies have proven a synergic effect between policosanol and the Omega 3 fatty acids found in fish oil, the beneficial effects on the cholesterol level and s ...
... wheat, etc. Policosanol has an inhibitor effect on the enzymes responsible for the endogenous synthesis of cholesterol in the liver. Clinical studies have proven a synergic effect between policosanol and the Omega 3 fatty acids found in fish oil, the beneficial effects on the cholesterol level and s ...
Proteins - Chavis Biology
... d. _______________________________ results from interactions among _________________________ _________________________ (for example, hemoglobin is composed of 4 polypeptide chains) 5. The folding of proteins is aided by other proteins called ___________________________ a. Act as ____________________ ...
... d. _______________________________ results from interactions among _________________________ _________________________ (for example, hemoglobin is composed of 4 polypeptide chains) 5. The folding of proteins is aided by other proteins called ___________________________ a. Act as ____________________ ...
powerpoint notes link
... • Bile is produced in the liver, and stored in the gall bladder. • When fat is detected in the duodenum, a hormone called CCK brings about the release of bile from the gall bladder and it is added to the duodenum. • Bile emulsifies fat (physically breaks it down into smaller droplets). • Bile can be ...
... • Bile is produced in the liver, and stored in the gall bladder. • When fat is detected in the duodenum, a hormone called CCK brings about the release of bile from the gall bladder and it is added to the duodenum. • Bile emulsifies fat (physically breaks it down into smaller droplets). • Bile can be ...