Cell Metabolism
... suggesting that they are unable to efficiently mobilize stored fat for energy. Microarray studies support this model, indicating reduced expression of genes that control lipid catabolism and b-oxidation. A GAL4dHNF4;UAS-lacZ ligand sensor can be activated by starvation or exogenous long-chain fatty ...
... suggesting that they are unable to efficiently mobilize stored fat for energy. Microarray studies support this model, indicating reduced expression of genes that control lipid catabolism and b-oxidation. A GAL4dHNF4;UAS-lacZ ligand sensor can be activated by starvation or exogenous long-chain fatty ...
The Digestive System
... Chemical digestion by Mechanical digestion by bile pancreatic lipase (breaks (bile crystallizes into bile salts down lipids) and aid in lipid breakdown) ...
... Chemical digestion by Mechanical digestion by bile pancreatic lipase (breaks (bile crystallizes into bile salts down lipids) and aid in lipid breakdown) ...
File
... • Tyrosine evolves by adding an –OH group to the para position on the phenyl ring of phenylalanine ...
... • Tyrosine evolves by adding an –OH group to the para position on the phenyl ring of phenylalanine ...
... 5. (12 pts). Please answer one of the following four choices. Please indicate your choice. Choice A: The South Beach diet suggests that the dieter completely eliminate carbohydrates from their diet. Should athletes with high energy demands, such a sprinters, go on this diet? Why or why not? Choice B ...
Digestion Absorption and Alcohol
... levels of blood glucose. Large quantities of glucose reach the liver from the alimentary canal via the hepatic portal vein. ...
... levels of blood glucose. Large quantities of glucose reach the liver from the alimentary canal via the hepatic portal vein. ...
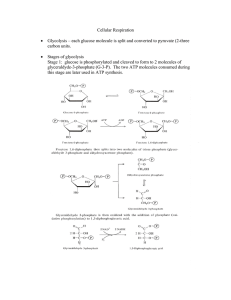
Cellular Respiration - Seattle Central College
... glucose and the conversion of Fructose-6-phosphate to Fructose-1,6-diphosphate. The net production of ATP per glucose is 2. ...
... glucose and the conversion of Fructose-6-phosphate to Fructose-1,6-diphosphate. The net production of ATP per glucose is 2. ...
lec33_2013 - Andrew.cmu.edu
... How the motor works: Every time three proton move through the complex, the subunit rotates 120°. The rotation of subunit changes the conformation of the β-subunits such that the Gibbs energy of the bound ADP + Pi becomes higher than the energy of ATP, thus ATP forms spontaneously from the bo ...
... How the motor works: Every time three proton move through the complex, the subunit rotates 120°. The rotation of subunit changes the conformation of the β-subunits such that the Gibbs energy of the bound ADP + Pi becomes higher than the energy of ATP, thus ATP forms spontaneously from the bo ...
BIOLOGY 311C - Brand Spring 2009
... a. function rapidly over a narrow range of temperatures. b. function rapidly over a broad range of pH values. c. contain an adaptable binding site so it can react with many different kinds of substrate. d. be a fibrous protein. ...
... a. function rapidly over a narrow range of temperatures. b. function rapidly over a broad range of pH values. c. contain an adaptable binding site so it can react with many different kinds of substrate. d. be a fibrous protein. ...
PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
... - Mitochondria have a TWO membrane system • Outer Membrane: Permeable to small molecules • Inner Membrane: NOT permeable – Has specific integral membrane protein transporters • Region between the two membranes = intermembrane space • Inner membrane is highly folded and forms boundary to fluid filled ...
... - Mitochondria have a TWO membrane system • Outer Membrane: Permeable to small molecules • Inner Membrane: NOT permeable – Has specific integral membrane protein transporters • Region between the two membranes = intermembrane space • Inner membrane is highly folded and forms boundary to fluid filled ...
Sentinel™ Performance LS Formula
... minerals, trace minerals and vitamins help build, strengthen and maintain all body tissues including bone and muscle. These nutrients also help regulate metabolic activities and help support the immune system to sustain overall health. The more biologically available chelated forms of zinc, copper a ...
... minerals, trace minerals and vitamins help build, strengthen and maintain all body tissues including bone and muscle. These nutrients also help regulate metabolic activities and help support the immune system to sustain overall health. The more biologically available chelated forms of zinc, copper a ...
8 Aerobic Respiration
... The NADH and FADH2 give off their electron, which powers each protein channel in sequence.* The NAD+ and FAD+ then return to pick up another electron *REMEMBER: If we can’t do this step, then the cell has to do fermentation instead. ...
... The NADH and FADH2 give off their electron, which powers each protein channel in sequence.* The NAD+ and FAD+ then return to pick up another electron *REMEMBER: If we can’t do this step, then the cell has to do fermentation instead. ...
PHM 381M Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I
... In addition, there will be audio and visual recordings of the lectures and all that is shown on the doc cam. This class takes part in lecture capturing (now called lectures online). The audio and visual materials presented in class will be recorded and made available to you for review via Canvas. It ...
... In addition, there will be audio and visual recordings of the lectures and all that is shown on the doc cam. This class takes part in lecture capturing (now called lectures online). The audio and visual materials presented in class will be recorded and made available to you for review via Canvas. It ...
Problem Set 5 (Due February 25th) 1. Show how glucose can be
... d. How was enzyme activity monitored? Monitoring the reduction of NAD+ to NADH spectrophotometrically – I noticed that the experimental section refers to another paper, so I apologize if this gave you a headache. e. Figure 5 has a lot of important information. i. What does this figure tell us about ...
... d. How was enzyme activity monitored? Monitoring the reduction of NAD+ to NADH spectrophotometrically – I noticed that the experimental section refers to another paper, so I apologize if this gave you a headache. e. Figure 5 has a lot of important information. i. What does this figure tell us about ...
respiration
... Occurs continuously in all living things Is a series of enzyme controlled reactions May or may not use oxygen Involves the exchange of gases between the organism and the environment The energy in glucose is released when bonds are broken The energy is stored in molecules of ATP ...
... Occurs continuously in all living things Is a series of enzyme controlled reactions May or may not use oxygen Involves the exchange of gases between the organism and the environment The energy in glucose is released when bonds are broken The energy is stored in molecules of ATP ...
Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy
... glucose and generate energy-containing products. • Fermentation reactions anaerobically oxidize the NADH + H+ produced in glycolysis. ...
... glucose and generate energy-containing products. • Fermentation reactions anaerobically oxidize the NADH + H+ produced in glycolysis. ...
Lecture #10 – 9/26 – Dr. Hirsh
... Photons absorbed, E is transferred to other molecules to do work. Pigments = planar molecules that can absorb photons at different wavelengths Chlorophyll a and b absorb near infra-red and blue. Other visible wavelengths captured by the other photopigments except for green (500 nm). Photopigments tr ...
... Photons absorbed, E is transferred to other molecules to do work. Pigments = planar molecules that can absorb photons at different wavelengths Chlorophyll a and b absorb near infra-red and blue. Other visible wavelengths captured by the other photopigments except for green (500 nm). Photopigments tr ...
No Slide Title
... •PPARs are members of nuclear hormone receptor family •PPARs bind as heterodimer with RXR to PPRE •PPARs are activated by fatty acid (PUFA) ligands •Three forms in mammals, a, b/d and g ...
... •PPARs are members of nuclear hormone receptor family •PPARs bind as heterodimer with RXR to PPRE •PPARs are activated by fatty acid (PUFA) ligands •Three forms in mammals, a, b/d and g ...
Cell Respiration Teacher Notes
... Does not require oxygen (anaerobic). Main energy source for prokaryotes http://www.science.smith.edu/departments/Biology/Bio231/gly colysis.html ...
... Does not require oxygen (anaerobic). Main energy source for prokaryotes http://www.science.smith.edu/departments/Biology/Bio231/gly colysis.html ...
Exam Name___________________________________
... B) D-glucose and D-gulose C) D-glucose and D-fructose D) D-glucose and D-galactose E) D-glucose and D-allose ...
... B) D-glucose and D-gulose C) D-glucose and D-fructose D) D-glucose and D-galactose E) D-glucose and D-allose ...
Slides/AVS 504 Met Fri 2013 pt 2
... 1. Gastric hydrolysis of peptide linkages in the protein 2. Digestion of protein to smaller peptides by action of pancreatic proteases, which are secreted as zymogens and activated in the lumen of the small intestine 3. Hydrolysis of peptide linkages in oligopeptides by brushborder (apical) membrane ...
... 1. Gastric hydrolysis of peptide linkages in the protein 2. Digestion of protein to smaller peptides by action of pancreatic proteases, which are secreted as zymogens and activated in the lumen of the small intestine 3. Hydrolysis of peptide linkages in oligopeptides by brushborder (apical) membrane ...
Cell Respiration - Biology Junction
... 3) turns twice because two acetyl-CoA molecules enter the cycle per glucose molecule; 4) produces two immediate ATP molecules per glucose molecule. d. The electron transport chain: 1) is a series of carriers in the inner mitochondrial membrane that accept electrons from glucose--electrons are passed ...
... 3) turns twice because two acetyl-CoA molecules enter the cycle per glucose molecule; 4) produces two immediate ATP molecules per glucose molecule. d. The electron transport chain: 1) is a series of carriers in the inner mitochondrial membrane that accept electrons from glucose--electrons are passed ...
Energy Transfer
... • There is not enough stored ATP to fuel all of your body’s processes. • Your body must oxidize stored macronutrients so that mitochondria can synthesize more ATP. • ATP is synthesized by coupling of electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation in the electron transport chain. ...
... • There is not enough stored ATP to fuel all of your body’s processes. • Your body must oxidize stored macronutrients so that mitochondria can synthesize more ATP. • ATP is synthesized by coupling of electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation in the electron transport chain. ...
Homeostasis: Functions of the liver - mf011
... used for energy for cellular functions (more energy than glucose) Liver responsible for proper lipid concentrations in the blood. Lipids removed from blood by liver cells or transported to fat storage areas in the form of adipose tissue or lipoproteins for brain and nerve tissue synthesis Chol ...
... used for energy for cellular functions (more energy than glucose) Liver responsible for proper lipid concentrations in the blood. Lipids removed from blood by liver cells or transported to fat storage areas in the form of adipose tissue or lipoproteins for brain and nerve tissue synthesis Chol ...