Amino acids
... The simplest amino acid is Glycine, which has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. Alanine, Valine, Leucine and Isoleucine have saturated hydrocarbon R groups (i.e. they only have hydrogen and carbon linked by single covalent bonds). Leucine and Isoleucine are isomers of each other. ...
... The simplest amino acid is Glycine, which has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. Alanine, Valine, Leucine and Isoleucine have saturated hydrocarbon R groups (i.e. they only have hydrogen and carbon linked by single covalent bonds). Leucine and Isoleucine are isomers of each other. ...
amino acids
... The simplest amino acid is Glycine, which has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. Alanine, Valine, Leucine and Isoleucine have saturated hydrocarbon R groups (i.e. they only have hydrogen and carbon linked by single covalent bonds). Leucine and Isoleucine are isomers of each other. ...
... The simplest amino acid is Glycine, which has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. Alanine, Valine, Leucine and Isoleucine have saturated hydrocarbon R groups (i.e. they only have hydrogen and carbon linked by single covalent bonds). Leucine and Isoleucine are isomers of each other. ...
File - Ryan Younkerman
... a. Made in the pancreas and digests fats into fatty acids in the gall bladder b. Made in the liver and breaks fat droplets into small particles in the intestine c. Made in the liver and digests proteins into amino acids in the intestine d. Made in the gall bladder and digests fats into fatty acids i ...
... a. Made in the pancreas and digests fats into fatty acids in the gall bladder b. Made in the liver and breaks fat droplets into small particles in the intestine c. Made in the liver and digests proteins into amino acids in the intestine d. Made in the gall bladder and digests fats into fatty acids i ...
amino acid , peptide and protein metabolism
... 1) Catabolism (protein, amino acid degradation) Excess AA excreted(Carbon skeleton, amino group) (2)Regulation of amino acid catabolism 3) Amino acid synthesis (Anabolism). essential and non essential amino acid. 4) Errors of protein metabolism and clinical significance ...
... 1) Catabolism (protein, amino acid degradation) Excess AA excreted(Carbon skeleton, amino group) (2)Regulation of amino acid catabolism 3) Amino acid synthesis (Anabolism). essential and non essential amino acid. 4) Errors of protein metabolism and clinical significance ...
chapter7_Sections 5
... • Fermentation pathways start with glycolysis • Substances other than oxygen accept electrons at the end of the pathways • Compared with aerobic respiration, the net yield of ATP from fermentation is small ...
... • Fermentation pathways start with glycolysis • Substances other than oxygen accept electrons at the end of the pathways • Compared with aerobic respiration, the net yield of ATP from fermentation is small ...
insulin resistance
... glycogen (glycogenesis), to pyruvic acid (glycolysis), suppresses gluconeogenesis. Also promotes synthesis of nucleic acid, fatty acids and protein. Net effect of reducing blood glucose • Hypothesized increase in glucagon secretion and activity: stimulates glucose production (glygenolysis, gluconeog ...
... glycogen (glycogenesis), to pyruvic acid (glycolysis), suppresses gluconeogenesis. Also promotes synthesis of nucleic acid, fatty acids and protein. Net effect of reducing blood glucose • Hypothesized increase in glucagon secretion and activity: stimulates glucose production (glygenolysis, gluconeog ...
lipids: saponification
... maintaining the hydrophobic core of the micelle. This is the way soaps work. Your textbook contains some good illustrations of soap micelles. In “hard” water, divalent and trivalent cations (such as Mg+2, Ca+2 and Fe+3) will precipitate out the fatty acid salts as insoluble precipitates. That is wh ...
... maintaining the hydrophobic core of the micelle. This is the way soaps work. Your textbook contains some good illustrations of soap micelles. In “hard” water, divalent and trivalent cations (such as Mg+2, Ca+2 and Fe+3) will precipitate out the fatty acid salts as insoluble precipitates. That is wh ...
Digestion
... fats – break down large fat globules to smaller ones Then pancreatic lipase digests fats into fatty acids Which are absorbed ...
... fats – break down large fat globules to smaller ones Then pancreatic lipase digests fats into fatty acids Which are absorbed ...
Workshop3Cellsans
... Both substrate-level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation result in the formation of ATP by the addition of an inorganic phosphate to a molecule of ADP. Both reactions are catalyzed by enzymes that couple the formation of ATP to an exergonic reaction that provides the energy for the synthes ...
... Both substrate-level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation result in the formation of ATP by the addition of an inorganic phosphate to a molecule of ADP. Both reactions are catalyzed by enzymes that couple the formation of ATP to an exergonic reaction that provides the energy for the synthes ...
Digestion and Nutrition
... Intestinal glands at the bases of the villi secrete large amounts of watery fluid that carry digestive products into the villi. Epithelial cells of the mucosa have embedded digestive enzymes on their microvilli, including peptidases, sucrase, maltase, and lactase, and ...
... Intestinal glands at the bases of the villi secrete large amounts of watery fluid that carry digestive products into the villi. Epithelial cells of the mucosa have embedded digestive enzymes on their microvilli, including peptidases, sucrase, maltase, and lactase, and ...
short chain polypeptide test
... intestinal mucosa (lining) is in good shape, structurally and functionally, amino acids are readily absorbed, while peptides and proteins are mainly excluded. When digestion is impaired or there is increased intestinal permeability, then peptides, being relatively small molecules, are easily absorbe ...
... intestinal mucosa (lining) is in good shape, structurally and functionally, amino acids are readily absorbed, while peptides and proteins are mainly excluded. When digestion is impaired or there is increased intestinal permeability, then peptides, being relatively small molecules, are easily absorbe ...
Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
... All three isozymes of pyruvate kinase are allosterically inhibited by ATP, acetyl-CoA and long chain fatty acids (all signs of an abundant energy supply). The liver isoenzyme (L form), but not the muscle isoenzyme (M form) is further regulated by phosphorylation. When the glucose level in blood decr ...
... All three isozymes of pyruvate kinase are allosterically inhibited by ATP, acetyl-CoA and long chain fatty acids (all signs of an abundant energy supply). The liver isoenzyme (L form), but not the muscle isoenzyme (M form) is further regulated by phosphorylation. When the glucose level in blood decr ...
Ch. 25 D
... Mixes chyme with enzymes and bile Churns chyme to increase contact with mucosa for absorption and digestion Moves residue towards large intestine ...
... Mixes chyme with enzymes and bile Churns chyme to increase contact with mucosa for absorption and digestion Moves residue towards large intestine ...
Many people today are hooked on “fat free” or
... Both substrate-level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation result in the formation of ATP by the addition of an inorganic phosphate to a molecule of ADP. Both reactions are catalyzed by enzymes that couple the formation of ATP to an exergonic reaction that provides the energy for the synthes ...
... Both substrate-level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation result in the formation of ATP by the addition of an inorganic phosphate to a molecule of ADP. Both reactions are catalyzed by enzymes that couple the formation of ATP to an exergonic reaction that provides the energy for the synthes ...
Metabolic Pathways - University of California, Santa Barbara
... 10. Stage 4 of catabolism is _________________________ in which 1 molecule of NADH produces ___________ molecules of ATP and 1 molecule of FADH2 produces ____________ molecules of ATP. Therefore for each molecule of acetyl CoA that enters the citric acid cycle ____________ molecules of ATP are produ ...
... 10. Stage 4 of catabolism is _________________________ in which 1 molecule of NADH produces ___________ molecules of ATP and 1 molecule of FADH2 produces ____________ molecules of ATP. Therefore for each molecule of acetyl CoA that enters the citric acid cycle ____________ molecules of ATP are produ ...
File
... two G3P but 4 ATP are made while rearranging them into pyruvate; therefore, glycolysis has a net production of 2 ATP ...
... two G3P but 4 ATP are made while rearranging them into pyruvate; therefore, glycolysis has a net production of 2 ATP ...
Multiple choice questions
... Muscle and liver glycogen stores in a well nourished athlete would be sufficient to sustain approximately how many minutes of submaximal exercise (if this were the only energy source used)? The exercise is club level marathon pace. ...
... Muscle and liver glycogen stores in a well nourished athlete would be sufficient to sustain approximately how many minutes of submaximal exercise (if this were the only energy source used)? The exercise is club level marathon pace. ...
Cholesterol Metabolism_MJH
... Bile acids • fat digestion products are absorbed in the first 100 cm of small intestine • the primary and secondary bile acids are reabsorbed almost exclusively in the ileum returning to the liver by way of the portal circulation (98 to 99%) • this is known as the entero-hepatic circulation • less ...
... Bile acids • fat digestion products are absorbed in the first 100 cm of small intestine • the primary and secondary bile acids are reabsorbed almost exclusively in the ileum returning to the liver by way of the portal circulation (98 to 99%) • this is known as the entero-hepatic circulation • less ...
Unit 2: Digestion
... All absorbed molecules are taken to a variety of body cells by the circulatory system. Within the body cells, molecules may be used for energy (ex. Glucose) or may be used to help build larger molecules within the cell (ex. Amino acids) Assimilation is the process of bringing the nutrient molecule t ...
... All absorbed molecules are taken to a variety of body cells by the circulatory system. Within the body cells, molecules may be used for energy (ex. Glucose) or may be used to help build larger molecules within the cell (ex. Amino acids) Assimilation is the process of bringing the nutrient molecule t ...
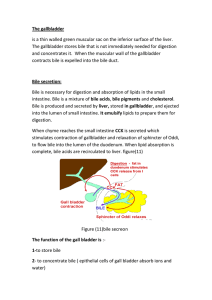
The gallbladder is a thin walled green muscular sac on the inferior
... into smaller glucose molecules where in the stomach it continues to be broken down further. *Upon entering the small intestine the pancreas releases the enzyme pancreatic amylase to help complete the hydrolysis of starch into smaller chains of glucose molecules – monosaccharide's, which is 1 molecul ...
... into smaller glucose molecules where in the stomach it continues to be broken down further. *Upon entering the small intestine the pancreas releases the enzyme pancreatic amylase to help complete the hydrolysis of starch into smaller chains of glucose molecules – monosaccharide's, which is 1 molecul ...
cellular respiration
... • if O2 is present then glycolysis enters the 2nd step of respiration; The Kreb’s cycle ...
... • if O2 is present then glycolysis enters the 2nd step of respiration; The Kreb’s cycle ...
1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 THE ARACHIDONIC ACID - diss.fu
... calcium for the translocation of the enzyme to membranes, however, the activity is calciumindependent (Watson and Doherty, 1994; Brinckmann et al., 1998; Hoffman et al., 1988). The 15-LOX activity is dependent on the hydroperoxide tone (Vanderhoek et al., 1982). The ‘threshold peroxide tone’ is depe ...
... calcium for the translocation of the enzyme to membranes, however, the activity is calciumindependent (Watson and Doherty, 1994; Brinckmann et al., 1998; Hoffman et al., 1988). The 15-LOX activity is dependent on the hydroperoxide tone (Vanderhoek et al., 1982). The ‘threshold peroxide tone’ is depe ...
Extracellular fluids
... HCO3- concentration is higher than in plasma Contains various enzymes participating in cleavage of high-molecular dietary constituents; many of these enzymes are secreted as zymogens: trypsinogen – activated to trypsin by enterokinase; then trypsin itself activates other zymogens: chymotrypsinog ...
... HCO3- concentration is higher than in plasma Contains various enzymes participating in cleavage of high-molecular dietary constituents; many of these enzymes are secreted as zymogens: trypsinogen – activated to trypsin by enterokinase; then trypsin itself activates other zymogens: chymotrypsinog ...
hanan abas
... We observe from these steps increase in hydrogen ions concentration when added to blood that comes from tissues and then increase in carbonic acid concentration and follow increase in soluble di oxide carbon concentration in blood, at results out the wast of CO2 by lungs . When prevent base effects ...
... We observe from these steps increase in hydrogen ions concentration when added to blood that comes from tissues and then increase in carbonic acid concentration and follow increase in soluble di oxide carbon concentration in blood, at results out the wast of CO2 by lungs . When prevent base effects ...