The Chemical Building Blocks of Life
... 2. Disulfide linkages (S-S) 3.3 Carbohydrates A. Characteristics 1. Most abundant biological molecule 2. Major chemical fuel energy for cells 3. Stored as starch in plants 4. Stored as glycogen in animals 5. Chains of carbohydrates can form structural components (e.g., cellulose). B. C, H, O—1:2:1 r ...
... 2. Disulfide linkages (S-S) 3.3 Carbohydrates A. Characteristics 1. Most abundant biological molecule 2. Major chemical fuel energy for cells 3. Stored as starch in plants 4. Stored as glycogen in animals 5. Chains of carbohydrates can form structural components (e.g., cellulose). B. C, H, O—1:2:1 r ...
GI I and II
... 33. Define amphipathic and give examples of amphipathic compounds that affect lipid digestion. a. Amphipathic compounds are molecules with both hydrophilic and hydrophobic portions. i. Examples: lecithin, fatty acids, monoglycerides, some proteins 34. Describe the roles of emulsification and micelle ...
... 33. Define amphipathic and give examples of amphipathic compounds that affect lipid digestion. a. Amphipathic compounds are molecules with both hydrophilic and hydrophobic portions. i. Examples: lecithin, fatty acids, monoglycerides, some proteins 34. Describe the roles of emulsification and micelle ...
Aerobic Respiration
... hexose phosphate, then splitting into 2 x 3C triose phosphate molecules which are oxidised to form 2 x pyruvate, yielding a little ATP and reduced NAD. In cytoplasm. • Link reaction - pyruvate is decarboxylated and hydrogenated. The remaining 2C unit is added to CoA to form AcetylCoA. This occurs tw ...
... hexose phosphate, then splitting into 2 x 3C triose phosphate molecules which are oxidised to form 2 x pyruvate, yielding a little ATP and reduced NAD. In cytoplasm. • Link reaction - pyruvate is decarboxylated and hydrogenated. The remaining 2C unit is added to CoA to form AcetylCoA. This occurs tw ...
statins i
... → increase of bile acids synthesis from CH (activation of 7-αhydroxylasis) → increase of liver LDL uptake (up-regulation of LDL-receptor) → cholesterol tissue mobilization and uptake from plasma to liver ...
... → increase of bile acids synthesis from CH (activation of 7-αhydroxylasis) → increase of liver LDL uptake (up-regulation of LDL-receptor) → cholesterol tissue mobilization and uptake from plasma to liver ...
Test 1
... E) supply pentoses and NADPH. 4. Which one of the following types of mechanisms is not known to play a role in the reversible alteration of enzyme activity? A) Activation by cleavage of an inactive zymogen B) Allosteric response to a regulatory molecule C) Alteration of the synthesis or degradation ...
... E) supply pentoses and NADPH. 4. Which one of the following types of mechanisms is not known to play a role in the reversible alteration of enzyme activity? A) Activation by cleavage of an inactive zymogen B) Allosteric response to a regulatory molecule C) Alteration of the synthesis or degradation ...
Solution
... b. Ethanolic and lactic acid fermentation are two pathways that enable the glycolysis to occur in the absence of oxygen through the regeneration of NADH. ...
... b. Ethanolic and lactic acid fermentation are two pathways that enable the glycolysis to occur in the absence of oxygen through the regeneration of NADH. ...
Principles of Biology Exam
... B. Prefers to give up 3 electrons to form ions. C. Has 2 electrons in its outer shell so it forms 2 chemical bonds. D. Is never found in inorganic molecules but always found in organic molecules. ...
... B. Prefers to give up 3 electrons to form ions. C. Has 2 electrons in its outer shell so it forms 2 chemical bonds. D. Is never found in inorganic molecules but always found in organic molecules. ...
Protein Synthesis Translation
... Ribosome assembles at the start codon of mRNA ◦ Start codon: AUG ◦ Codes for amino acid: Methionine ...
... Ribosome assembles at the start codon of mRNA ◦ Start codon: AUG ◦ Codes for amino acid: Methionine ...
Chapter 14 Proteins
... ◦ Peptide: A short polymer of amino acids joined by peptide bonds; they are classified by the number of amino acids in the chain. ◦ Dipeptide: A molecule containing two amino acids joined by a peptide bond. ◦ Tripeptide: A molecule containing three amino acids joined by peptide bonds. ◦ Polypeptide: ...
... ◦ Peptide: A short polymer of amino acids joined by peptide bonds; they are classified by the number of amino acids in the chain. ◦ Dipeptide: A molecule containing two amino acids joined by a peptide bond. ◦ Tripeptide: A molecule containing three amino acids joined by peptide bonds. ◦ Polypeptide: ...
View PDF - OMICS International
... Proteins are vital for health. They act like saviour of each cell by participating in all anabolic as well catabolic processes in the body. They are known to build the muscle mass and repair the damaged cells. However, the human body has limited capacity to store excess protein hence need regular su ...
... Proteins are vital for health. They act like saviour of each cell by participating in all anabolic as well catabolic processes in the body. They are known to build the muscle mass and repair the damaged cells. However, the human body has limited capacity to store excess protein hence need regular su ...
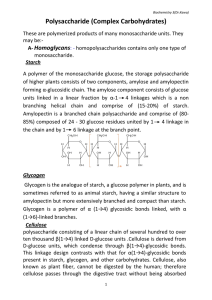
Biochemistry 3(Dr.Kawa) Polysaccharide (Complex Carbohydrates
... polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to over ten thousand β(1→4) linked D-glucose units .Cellulose is derived from D-glucose units, which condense through β(1→4)-glycosidic bonds. This linkage design contrasts with that for α(1→4)-glycosidic bonds present in starch, glycoge ...
... polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to over ten thousand β(1→4) linked D-glucose units .Cellulose is derived from D-glucose units, which condense through β(1→4)-glycosidic bonds. This linkage design contrasts with that for α(1→4)-glycosidic bonds present in starch, glycoge ...
Unit 3-7 Digestive System Notes File
... Changing PCO2 levels are monitored by chemoreceptors of the brain stem Carbon dioxide in the blood diffuses into the cerebrospinal fluid where it is hydrated Resulting carbonic acid dissociates, releasing hydrogen ions PCO2 levels rise (hypercapnia) resulting in increased depth and rate of breathing ...
... Changing PCO2 levels are monitored by chemoreceptors of the brain stem Carbon dioxide in the blood diffuses into the cerebrospinal fluid where it is hydrated Resulting carbonic acid dissociates, releasing hydrogen ions PCO2 levels rise (hypercapnia) resulting in increased depth and rate of breathing ...
2. Microbial Growth Kinetics
... 1. Nutritional characteristics of the organism when grown on a cheap medium 2. Optimum temp of the organism 3. Reaction of the organism with the equipment and suitability for the type of process 4. Stability of the organism and its amenability for genetic ...
... 1. Nutritional characteristics of the organism when grown on a cheap medium 2. Optimum temp of the organism 3. Reaction of the organism with the equipment and suitability for the type of process 4. Stability of the organism and its amenability for genetic ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... metabolized to lactate or to CO2 and alcohol (it is species specific)…result can be net gain of only 2 ATP per molecule verses 32 – 34 under normal cycle just described ...
... metabolized to lactate or to CO2 and alcohol (it is species specific)…result can be net gain of only 2 ATP per molecule verses 32 – 34 under normal cycle just described ...
Tricarboxylic acid cycle
... Is the final common oxidative pathway for carbohydrates, fats and amino acids Along with energy, cycle supplies many intermediates required for the synthesis of amino acids, glucose, heme etc Site: mitochondrial matrix Oxidation of acetyl CoA Co2 + H2O Occurs in a cyclic manner, generate ATP ...
... Is the final common oxidative pathway for carbohydrates, fats and amino acids Along with energy, cycle supplies many intermediates required for the synthesis of amino acids, glucose, heme etc Site: mitochondrial matrix Oxidation of acetyl CoA Co2 + H2O Occurs in a cyclic manner, generate ATP ...
Cellular Energy and Mitochondrial ATP Production: A
... Lactic acid fermentation takes place in some fungi and some bacteria like Lactobacillus acidophilus (yogurt). In humans, lactic acid fermentation takes place in the muscles during times of strenuous exercise or great exertion. Under these conditions the oxygen supplied by the lungs and blood system ...
... Lactic acid fermentation takes place in some fungi and some bacteria like Lactobacillus acidophilus (yogurt). In humans, lactic acid fermentation takes place in the muscles during times of strenuous exercise or great exertion. Under these conditions the oxygen supplied by the lungs and blood system ...
Cell Respiration Take Home Test 1. When cells break down food
... a. is released all at once. b. is released entirely as body heat into the environment. c. is temporarily stored in ATP molecules while some is released as body heat. d. causes excitation of electrons in chlorophyll molecules. 2. The process of aerobic cellular respiration a. is performed only by org ...
... a. is released all at once. b. is released entirely as body heat into the environment. c. is temporarily stored in ATP molecules while some is released as body heat. d. causes excitation of electrons in chlorophyll molecules. 2. The process of aerobic cellular respiration a. is performed only by org ...
Chapter 19 - Evangel University
... • Seeds are rich in lipids, which contain fatty acids • During germination, plants use the acetyl-CoA produced in fatty acid oxidation to produce oxaloacetate and other intermediates for carbohydrate synthesis • Once plants begin photosynthesis and can fix CO2, glyoxysomes disappear ...
... • Seeds are rich in lipids, which contain fatty acids • During germination, plants use the acetyl-CoA produced in fatty acid oxidation to produce oxaloacetate and other intermediates for carbohydrate synthesis • Once plants begin photosynthesis and can fix CO2, glyoxysomes disappear ...
lecture6
... oxaloacetate for the formation of citrate, but the concentration of oxaloacetate is lowered if carbohydrate is unavailable or improperly utilized. Recall that oxaloacetate is normally formed from pyruvate, the product of glycolysis, by pyruvate carboxylase (Section 16.3.1). This is the molecular bas ...
... oxaloacetate for the formation of citrate, but the concentration of oxaloacetate is lowered if carbohydrate is unavailable or improperly utilized. Recall that oxaloacetate is normally formed from pyruvate, the product of glycolysis, by pyruvate carboxylase (Section 16.3.1). This is the molecular bas ...
Dietary Fat and Cholesterol - OSU Fact Sheets
... and milk or dairy products, make choices that are lean, low-fat, or fat-free. • Limit intake of fats and oils high in saturated and/or trans fatty acids, and choose products low in such fats and oils. ...
... and milk or dairy products, make choices that are lean, low-fat, or fat-free. • Limit intake of fats and oils high in saturated and/or trans fatty acids, and choose products low in such fats and oils. ...
ACID - SchoolNotes
... in your hair, nails, cell membranes, and other parts of you body consist of amino acids. • Enzymes that catalyze reactions in your body are composed of amino acids. • Hydrochloric acid is in your stomach to aid in the digestion of food. • Organic bases are major components of DNA and products of the ...
... in your hair, nails, cell membranes, and other parts of you body consist of amino acids. • Enzymes that catalyze reactions in your body are composed of amino acids. • Hydrochloric acid is in your stomach to aid in the digestion of food. • Organic bases are major components of DNA and products of the ...