McCance: Pathophysiology, 6th Edition
... 9. Bilirubin is a pigment liberated by the lysis of aged red blood cells in the liver and spleen. Unconjugated bilirubin is fat soluble and can cross cell membranes. Unconjugated bilirubin is converted to water-soluble, conjugated bilirubin by hepatocytes and is secreted with bile. 10. Fats are synt ...
... 9. Bilirubin is a pigment liberated by the lysis of aged red blood cells in the liver and spleen. Unconjugated bilirubin is fat soluble and can cross cell membranes. Unconjugated bilirubin is converted to water-soluble, conjugated bilirubin by hepatocytes and is secreted with bile. 10. Fats are synt ...
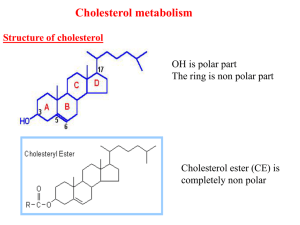
Lec4 Cholesterol met..
... 2- Drug inhibition: Statins such as atorvastatin (by Pfizer), lovastatin and simvastatin are drugs with a side chain structurally similar to HMG-CoA so competitively inhibit HMG-CoA reductase. They are used to decrease cholesterol levels in patients with hypercholesterolemia. 3- Diet: its activity a ...
... 2- Drug inhibition: Statins such as atorvastatin (by Pfizer), lovastatin and simvastatin are drugs with a side chain structurally similar to HMG-CoA so competitively inhibit HMG-CoA reductase. They are used to decrease cholesterol levels in patients with hypercholesterolemia. 3- Diet: its activity a ...
B vitamins
... B Vitamins are water soluble and play a crucial role in cell metabolisms as they form part of coenzymes that help enzymes release energy from foods. ...
... B Vitamins are water soluble and play a crucial role in cell metabolisms as they form part of coenzymes that help enzymes release energy from foods. ...
Document
... In ureotelic organisms the urea cycle disposes of approximately 90% of surplus nitrogen. Urea is formed from ammonia, CO2, and aspartate in a cyclic pathway referred to as the urea cycle. The urea cycle is a mechanism designed to convert NH4+ to urea, a less toxic molecule. Note that citrulline is t ...
... In ureotelic organisms the urea cycle disposes of approximately 90% of surplus nitrogen. Urea is formed from ammonia, CO2, and aspartate in a cyclic pathway referred to as the urea cycle. The urea cycle is a mechanism designed to convert NH4+ to urea, a less toxic molecule. Note that citrulline is t ...
SUBJECT OUTLINE Chemistry and Biochemistry BIOB111
... The first part of this subject introduces the student to Basic and Organic Chemistry and explores the nature and reactivity of matter. This provides the foundation for the second part – Biochemistry — which examines the relationship between the structure and function of complex biomolecules. Student ...
... The first part of this subject introduces the student to Basic and Organic Chemistry and explores the nature and reactivity of matter. This provides the foundation for the second part – Biochemistry — which examines the relationship between the structure and function of complex biomolecules. Student ...
A: Objective type questions: Choose the correct answers Most
... Low ATP stimulates the enzyme, but fructose-2,6-bisphosphate inhibits b. High ATP stimulates the enzyme, and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate activates c. High ATP stimulates the enzyme, but fructose-2,6-bisphosphate inhibits d. Low ATP stimulates the enzyme, and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate activates e. ATP ...
... Low ATP stimulates the enzyme, but fructose-2,6-bisphosphate inhibits b. High ATP stimulates the enzyme, and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate activates c. High ATP stimulates the enzyme, but fructose-2,6-bisphosphate inhibits d. Low ATP stimulates the enzyme, and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate activates e. ATP ...
Lecture 1 - Columbus Labs
... CHM441, Biological Chemistry I, introduces the components of biological macromolecules and the principles behind their observed structures. The structure, properties, and functions of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates will be the focus of the course with an additional emphasis on la ...
... CHM441, Biological Chemistry I, introduces the components of biological macromolecules and the principles behind their observed structures. The structure, properties, and functions of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates will be the focus of the course with an additional emphasis on la ...
When muscular work starts, the adrenal medulla secretes a
... This ends the preparatory phase of glycolysis. Two molecules of ATP must be invested to activate or prime the glucose molecule for its cleavage into two three carbon pieces; later there will be a good return on this investment. The energy gain comes in the payoff phase of glycolysis. Each molecule o ...
... This ends the preparatory phase of glycolysis. Two molecules of ATP must be invested to activate or prime the glucose molecule for its cleavage into two three carbon pieces; later there will be a good return on this investment. The energy gain comes in the payoff phase of glycolysis. Each molecule o ...
The Chemistry of the cell
... amino (-NH2) groups - recur repeatedly in biological molecules. • The small organic molecules of the cell have molecular weights in the range 100 to 1000 and contain up to 30 or so carbon atoms. • They are usually found free in solution, where some of them form a pool of intermediates from which lar ...
... amino (-NH2) groups - recur repeatedly in biological molecules. • The small organic molecules of the cell have molecular weights in the range 100 to 1000 and contain up to 30 or so carbon atoms. • They are usually found free in solution, where some of them form a pool of intermediates from which lar ...
acetyl CoA
... Inside the mitochondrion (before the citric acid cycle can begin), pyruvate (3C) must be decarboxylated into acetate (2C), then oxidized and joined to a molecule of Coenzyme A, and so converted to acetyl CoA, which links the cycle to glycolysis. During the transformation process of pyruvate into ac ...
... Inside the mitochondrion (before the citric acid cycle can begin), pyruvate (3C) must be decarboxylated into acetate (2C), then oxidized and joined to a molecule of Coenzyme A, and so converted to acetyl CoA, which links the cycle to glycolysis. During the transformation process of pyruvate into ac ...
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Worksheets
... Exothermic reactions in organisms are called catabolic reactions. These reactions break down molecules into smaller units and release energy. An example of a catabolic reaction is the breakdown of glucose, which releases energy that cells need to carry out life processes. Endothermic reactions in or ...
... Exothermic reactions in organisms are called catabolic reactions. These reactions break down molecules into smaller units and release energy. An example of a catabolic reaction is the breakdown of glucose, which releases energy that cells need to carry out life processes. Endothermic reactions in or ...
Mitochondrial Shuttles and Transporters - Rose
... you will note that the malate-aspartate shuttle results only in the movement of the electrons from NADH from the outside to the inside, with no net movement of carbon or nitrogen. This conserves all of the energy in the NADH electrons, and allows the synthesis of three ATP (under optimum conditions) ...
... you will note that the malate-aspartate shuttle results only in the movement of the electrons from NADH from the outside to the inside, with no net movement of carbon or nitrogen. This conserves all of the energy in the NADH electrons, and allows the synthesis of three ATP (under optimum conditions) ...
THE CITRIC ACID CYCLE
... combine with O2 deliberately taken into the cell, to form H2O. The citric acid cycle, in which much of the reduction of NAD+ and FAD occurs, is a part of this process. ...
... combine with O2 deliberately taken into the cell, to form H2O. The citric acid cycle, in which much of the reduction of NAD+ and FAD occurs, is a part of this process. ...
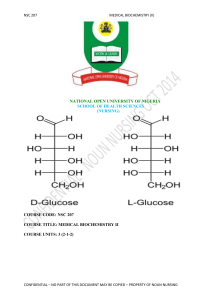
NSC 207 - National Open University of Nigeria
... 3. A lot of energy is derived aerobically by means of TCA cycle and electron transport chain. The entry point to this oxidative pathway is acetyl coenzyme A (Acetyl CoA), which is formed inside mitochondria by the oxidative decarboxylation of Pyruvate: Pyruvate + NAD + + CoA AcetylcoA + CO 2 + NADH ...
... 3. A lot of energy is derived aerobically by means of TCA cycle and electron transport chain. The entry point to this oxidative pathway is acetyl coenzyme A (Acetyl CoA), which is formed inside mitochondria by the oxidative decarboxylation of Pyruvate: Pyruvate + NAD + + CoA AcetylcoA + CO 2 + NADH ...
Part 2
... 2. Hormonal control (via enzyme phosphorylation) 3. Substrate level control 4. Covalent modification (phosphorylation via the kinase cascade) ...
... 2. Hormonal control (via enzyme phosphorylation) 3. Substrate level control 4. Covalent modification (phosphorylation via the kinase cascade) ...
Amino Acid Exporter: A Tool for the Next
... [9]. The existence of amino acid exporters raises an important question of why bacterial cells possess these transporters to export L-amino acids J Biotechnol Biomater ISSN:2155-952X JBTBM an open access journal ...
... [9]. The existence of amino acid exporters raises an important question of why bacterial cells possess these transporters to export L-amino acids J Biotechnol Biomater ISSN:2155-952X JBTBM an open access journal ...
Biology 112/111
... thylakoid space, how many H+’s and electrons are picked up by NADP+, what are 2 H2O broken into?) 12. What products of the light-dependent reactions are used in the Calvin cycle? 13. What does the Calvin cycle require from the atmosphere? 14. What does the Calvin cycle produce? LEVEL 1: Describe the ...
... thylakoid space, how many H+’s and electrons are picked up by NADP+, what are 2 H2O broken into?) 12. What products of the light-dependent reactions are used in the Calvin cycle? 13. What does the Calvin cycle require from the atmosphere? 14. What does the Calvin cycle produce? LEVEL 1: Describe the ...
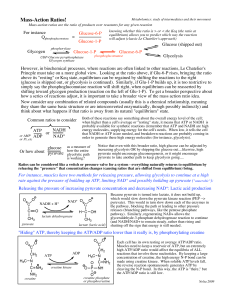
Mass-Action Ratios!
... Each cell has its own resting or average ATP/ADP ratio. Muscles need to keep a reservoir of ATP, but an extremely high ATP/ADP ratio would affect the equilibria of ALL reactions that involve these nucleotides. By keeping a large concentration of creatine, the high energy N-P bond can be made using c ...
... Each cell has its own resting or average ATP/ADP ratio. Muscles need to keep a reservoir of ATP, but an extremely high ATP/ADP ratio would affect the equilibria of ALL reactions that involve these nucleotides. By keeping a large concentration of creatine, the high energy N-P bond can be made using c ...
Slide 1
... (most medicines, alcohol, harmful substances from the body) 1. Production of blood clotting factors 2. Storage of glycogen 3. Storage of vitamins and minerals 4. Destruction of old non-functional red blood cells 5. Removal of hormones 6. Removal of ammonia from the body (urea formation) 7. Formation ...
... (most medicines, alcohol, harmful substances from the body) 1. Production of blood clotting factors 2. Storage of glycogen 3. Storage of vitamins and minerals 4. Destruction of old non-functional red blood cells 5. Removal of hormones 6. Removal of ammonia from the body (urea formation) 7. Formation ...
Digestive Physiology
... • Synthesis of bile salts: bile salts are used in the small intestine for the emulsification and absorption of lipids, cholesterol, phospholipids, and lipoproteins. • Storage: stores glycogen, vitamins and minerals. • Phagocytosis: Kupffer cells phagocytize RBCs, WBCs, bacteria, and toxins. ...
... • Synthesis of bile salts: bile salts are used in the small intestine for the emulsification and absorption of lipids, cholesterol, phospholipids, and lipoproteins. • Storage: stores glycogen, vitamins and minerals. • Phagocytosis: Kupffer cells phagocytize RBCs, WBCs, bacteria, and toxins. ...
Animal Physiology, Chapter 4
... • Rumen – first chamber/fermentation occurs • Regurgitate fermenting materials from the rumen into mouth • Further grinding and reswallow • From rumen reticulum omasum abomasum (true stomach) ...
... • Rumen – first chamber/fermentation occurs • Regurgitate fermenting materials from the rumen into mouth • Further grinding and reswallow • From rumen reticulum omasum abomasum (true stomach) ...