Chapter 13 Carbohydrate Metabolism
... • The rate at which the citric acid cycle operates is precisely adjusted to meet cellular needs for ATP. – Citrate synthetase (Step 1) is an allosteric enzyme that is inhibited by ATP and NADH and activated by ADP. – Isocitrate dehydrogenase (Step 3) is an allosteric enzyme that is inhibited by NADH ...
... • The rate at which the citric acid cycle operates is precisely adjusted to meet cellular needs for ATP. – Citrate synthetase (Step 1) is an allosteric enzyme that is inhibited by ATP and NADH and activated by ADP. – Isocitrate dehydrogenase (Step 3) is an allosteric enzyme that is inhibited by NADH ...
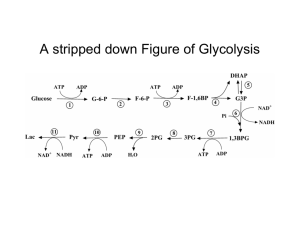
Figure 17-3 Degradation of glucose via the glycolytic pathway.
... which must be generated in the mitochondria. OAA cannot be transported out so it must be converted to PEP or malate (or Asp but lets ...
... which must be generated in the mitochondria. OAA cannot be transported out so it must be converted to PEP or malate (or Asp but lets ...
12ppt - UCSD Course Websites
... The Biochemical Bottom Line: Krebs Acetyl-CoA + 3 NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi + 2 H2O ...
... The Biochemical Bottom Line: Krebs Acetyl-CoA + 3 NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi + 2 H2O ...
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 1 The Human Digestive
... against infection and invasion of body tissues by bacteria. They are formed in the plasma cells found in lymphoid tissue. The liver contains a very large amount of lymphoid tissue, lymph nodes, and lymph. Damage may severely impair the immune process of the body. 1-16. THE PANCREAS The other accesso ...
... against infection and invasion of body tissues by bacteria. They are formed in the plasma cells found in lymphoid tissue. The liver contains a very large amount of lymphoid tissue, lymph nodes, and lymph. Damage may severely impair the immune process of the body. 1-16. THE PANCREAS The other accesso ...
Name - Phillips Scientific Methods
... This is called the ___________________________ gradient. Click this link. 8. What passes through the proton channel? ____________________ 9. Is this by diffusion or active transport? __________________ 10. What is produced by this special protein channel as H+ ions continue to pass through it? _____ ...
... This is called the ___________________________ gradient. Click this link. 8. What passes through the proton channel? ____________________ 9. Is this by diffusion or active transport? __________________ 10. What is produced by this special protein channel as H+ ions continue to pass through it? _____ ...
AA lecture 2 urea cycle
... • Hexameric glutamate dehydrogenase is is controlled allosterically. – High energy levels inhibit (ATP and GTP). – Low energy levels activate (ADP and GDP). • NADP+ can replace NAD+. • NH4+ , which is toxic to humans, is produced in the mitochondria and used to make carbamoyl phosphate. ...
... • Hexameric glutamate dehydrogenase is is controlled allosterically. – High energy levels inhibit (ATP and GTP). – Low energy levels activate (ADP and GDP). • NADP+ can replace NAD+. • NH4+ , which is toxic to humans, is produced in the mitochondria and used to make carbamoyl phosphate. ...
Fatty Acid Synthesis in Protozoan Parasites: Unusual Pathways and
... ~ 35% of fatty acid synthesis activity and appear normal as adults, 60-70% of heterozygotes progeny die in utero. The fate of the developing embryos is unaffected by the fatty acid content of the parental diet, indicating that de novo fatty acid synthesis is an absolute requirement for mammalian dev ...
... ~ 35% of fatty acid synthesis activity and appear normal as adults, 60-70% of heterozygotes progeny die in utero. The fate of the developing embryos is unaffected by the fatty acid content of the parental diet, indicating that de novo fatty acid synthesis is an absolute requirement for mammalian dev ...
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration and Fermentation - Biology E
... In the third stage of respiration, the electron transport chain accepts electrons from the breakdown products of the first two stages (most often via NADH) and passes these electrons from one molecule to another. At the end of the chain, the electrons are combined with molecular oxygen and hydrogen ...
... In the third stage of respiration, the electron transport chain accepts electrons from the breakdown products of the first two stages (most often via NADH) and passes these electrons from one molecule to another. At the end of the chain, the electrons are combined with molecular oxygen and hydrogen ...
Chapter 7
... DG = -686kcal/mol of glucose DG can be even higher than this in a cell This large amount of energy must be released in small steps rather than all at once. ...
... DG = -686kcal/mol of glucose DG can be even higher than this in a cell This large amount of energy must be released in small steps rather than all at once. ...
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
... All are -amino acids - the amino and carboxyl are connected to the same C They differ by the other substituent attached to the carbon, called the side chain, with H as the fourth substituent Proline is a five-membered secondary amine, with N and the C part of a five-membered ring See table 26.1 ...
... All are -amino acids - the amino and carboxyl are connected to the same C They differ by the other substituent attached to the carbon, called the side chain, with H as the fourth substituent Proline is a five-membered secondary amine, with N and the C part of a five-membered ring See table 26.1 ...
BY 123 Mock Exam #2 Answer Key Chapters 8,9,10,12,13 Catabolic
... d. Use allosteric enzymes that can bind to activators or inhibitors e. Use the energy from anabolic pathways to drive catabolic pathways 5) An endergonic reaction could be described as one that: a. Proceeds spontaneously with the addition of activation energy b. Produces products with more free ener ...
... d. Use allosteric enzymes that can bind to activators or inhibitors e. Use the energy from anabolic pathways to drive catabolic pathways 5) An endergonic reaction could be described as one that: a. Proceeds spontaneously with the addition of activation energy b. Produces products with more free ener ...
Practice Test - IHS AP Biology
... 5) The immediate energy source that drives ATP synthesis by ATP synthase during oxidative phosphorylation is A) the flow of electrons down the electron transport chain. B) the oxidation of glucose and other organic compounds. C) the H+ concentration gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane. ...
... 5) The immediate energy source that drives ATP synthesis by ATP synthase during oxidative phosphorylation is A) the flow of electrons down the electron transport chain. B) the oxidation of glucose and other organic compounds. C) the H+ concentration gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane. ...
CHAPTER 17: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
... Monosaccharides are absorbed by facilitated diffusion (and active transport). They are carried away by submucosal blood capillaries into the bloodstream (i.e. mesenteric vein to hepatic portal vein to liver). Amino acids are absorbed by active transport. They are carried away by submucosal blood cap ...
... Monosaccharides are absorbed by facilitated diffusion (and active transport). They are carried away by submucosal blood capillaries into the bloodstream (i.e. mesenteric vein to hepatic portal vein to liver). Amino acids are absorbed by active transport. They are carried away by submucosal blood cap ...
BHS 150.2 Biochemistry Date: 01/25/13, 1st hour Notetaker: Laurel
... glycogen metabolism One function of liver: supply body with glucose Brain needs glucose constantly, works under insulin-independent mechanism >3-4 days, brain can use other fuel sources of glucose (starvation) RBCs need glucose supply for protection/ prevent damage After ingesting a meal, BG levels ...
... glycogen metabolism One function of liver: supply body with glucose Brain needs glucose constantly, works under insulin-independent mechanism >3-4 days, brain can use other fuel sources of glucose (starvation) RBCs need glucose supply for protection/ prevent damage After ingesting a meal, BG levels ...
A 3-month old female infant seemed normal until she developed
... transported to the TCA cycle where is gets converted to glucose. Pyruvate carboxylase ensures that there is a constant supply of oxaloacetate for the TCA cycle by forming oxaloacetate directly from pyruvate by the addition of carbon, this addition of carbon dioxide happens due to ATP and biotin. Pyr ...
... transported to the TCA cycle where is gets converted to glucose. Pyruvate carboxylase ensures that there is a constant supply of oxaloacetate for the TCA cycle by forming oxaloacetate directly from pyruvate by the addition of carbon, this addition of carbon dioxide happens due to ATP and biotin. Pyr ...
Life: The Science of Biology, 10e
... • DNA sequences can be copied into RNA (transcription). The RNA can specify a sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide (translation). ...
... • DNA sequences can be copied into RNA (transcription). The RNA can specify a sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide (translation). ...
Amino Acids
... Disruption of the disulfide bonds may change the three-dimensional structure of the proteins so that they lose their bioactivity (such as trypsin inhibition activity or potential ...
... Disruption of the disulfide bonds may change the three-dimensional structure of the proteins so that they lose their bioactivity (such as trypsin inhibition activity or potential ...
Journal of Bacteriology 186:
... (P < 0.05), in the excimerization rate constant of the opaque variants compared with that of the transparent variants was observed, indicating higher microviscosity of the membrane of bacterial cells in the opaque variants. Liposomes prepared from phospholipids of the opaque phenotype showed an even ...
... (P < 0.05), in the excimerization rate constant of the opaque variants compared with that of the transparent variants was observed, indicating higher microviscosity of the membrane of bacterial cells in the opaque variants. Liposomes prepared from phospholipids of the opaque phenotype showed an even ...
Life and Cell
... In the Watson-Crick model of DNA structure: A) both strands run in the same direction, 3' to 5'; they are parallel. B) phosphate groups project toward the middle of the helix, where they are protected from interaction with water. C) T can form three hydrogen bonds with either G or C in the opposite ...
... In the Watson-Crick model of DNA structure: A) both strands run in the same direction, 3' to 5'; they are parallel. B) phosphate groups project toward the middle of the helix, where they are protected from interaction with water. C) T can form three hydrogen bonds with either G or C in the opposite ...
Amino Acid
... Standard amino acids share a common structure but differ in their side chains—the so-called R group ...
... Standard amino acids share a common structure but differ in their side chains—the so-called R group ...