Understanding conserved amino acids in proteins
... Recent studies [2,4] identiCed positions in several common protein folds where amino acids are universally conserved within each family of proteins having that fold. Such positions are localized in structure, and their unusually strong conservatism may be due to functional reason (e.g. super-site), ...
... Recent studies [2,4] identiCed positions in several common protein folds where amino acids are universally conserved within each family of proteins having that fold. Such positions are localized in structure, and their unusually strong conservatism may be due to functional reason (e.g. super-site), ...
Dear Notetaker:
... Need to be able to use all the glucose that is coming in so it needs to work faster Once fructose 6 phosphate levels start to decline because glycolysis becomes more efficient PFK2 will no longer be active but fructose 2,6 biphosphotase will be active Fructose 2,6 biphosphate cannot be used fo ...
... Need to be able to use all the glucose that is coming in so it needs to work faster Once fructose 6 phosphate levels start to decline because glycolysis becomes more efficient PFK2 will no longer be active but fructose 2,6 biphosphotase will be active Fructose 2,6 biphosphate cannot be used fo ...
BC 367 Biochemistry of the Cell I
... Production of acetyl-CoA (e.g., during glycolysis and the bridging reaction) Oxidation of acetyl-CoA via the citric acid cycle Electon transport and oxidative phosphorylation to produce lots of ATP Fig 16-1 ...
... Production of acetyl-CoA (e.g., during glycolysis and the bridging reaction) Oxidation of acetyl-CoA via the citric acid cycle Electon transport and oxidative phosphorylation to produce lots of ATP Fig 16-1 ...
The rocky roots of the acetyl
... first living system with energy and reduced carbon compounds? Traditional views point to glycolytic-like fermentations as the source of carbon and energy [3], and pyrite formation coupled to a reverse citric acid cycle (a pathway of CO2 fixation in some prokaryotes), which has construable similariti ...
... first living system with energy and reduced carbon compounds? Traditional views point to glycolytic-like fermentations as the source of carbon and energy [3], and pyrite formation coupled to a reverse citric acid cycle (a pathway of CO2 fixation in some prokaryotes), which has construable similariti ...
Masterclass 1
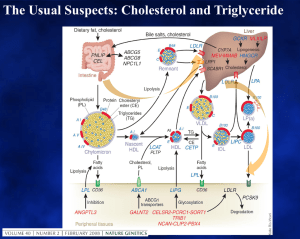
... How could you obtain an LDL-C result? The case for “d”, but “c” is misleading Lab Tests Online: “Direct LDL-C is ordered whenever calculation of LDL cholesterol will not be accurate because the person's triglyceridesare significantly elevated. It may be ordered by a doctor when prior test results h ...
... How could you obtain an LDL-C result? The case for “d”, but “c” is misleading Lab Tests Online: “Direct LDL-C is ordered whenever calculation of LDL cholesterol will not be accurate because the person's triglyceridesare significantly elevated. It may be ordered by a doctor when prior test results h ...
$doc.title
... Sucrose is a disaccharide made of a glucose bonded to a fructose. When a pure bacterial culture is incubated anaerobically in a validated (that is, base broth was run) PR sucrose, ...
... Sucrose is a disaccharide made of a glucose bonded to a fructose. When a pure bacterial culture is incubated anaerobically in a validated (that is, base broth was run) PR sucrose, ...
Chapter 9 Lecture Notes
... • Glucose can be synthesized from pyruvate and fatty acids from acetyl CoA. Glycolysis and the Krebs cycle function as metabolic interchanges that enable cells to convert one kind of molecule to another as needed. ...
... • Glucose can be synthesized from pyruvate and fatty acids from acetyl CoA. Glycolysis and the Krebs cycle function as metabolic interchanges that enable cells to convert one kind of molecule to another as needed. ...
Research on Hydrogenation of FAME to Fatty Alcohols
... velocity. Besides, the date in Table 4 and Figure 5 shows that the conversion rate of fatty acid methyl ester was above 99% with the condition of less than 4.0h-1 space velocity. While in terms of purpose products, it was more than 90%, and increased slightly with space velocity increased. Compared ...
... velocity. Besides, the date in Table 4 and Figure 5 shows that the conversion rate of fatty acid methyl ester was above 99% with the condition of less than 4.0h-1 space velocity. While in terms of purpose products, it was more than 90%, and increased slightly with space velocity increased. Compared ...
BMS 6204 MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY & GENETICS SPRING 2010
... 3.6 ATP: Do I really want that second serving of pasta? Let's do the math (anaerobic vs. aerobic) 3.7 Glucose Storage: glycogenesis/glycogenolysis Small groups (3.1) 3.8 Gluconeogenesis: Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Muscle Metabolism: Cori cycle 3.9 Urea Synthesis and Metabolism Q & A with L ...
... 3.6 ATP: Do I really want that second serving of pasta? Let's do the math (anaerobic vs. aerobic) 3.7 Glucose Storage: glycogenesis/glycogenolysis Small groups (3.1) 3.8 Gluconeogenesis: Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Muscle Metabolism: Cori cycle 3.9 Urea Synthesis and Metabolism Q & A with L ...
Neonatal Glucose Homeostasis
... Fetus can use alternate substrates if necessary, but depends entirely on maternal supply and placental transfer of glucose, amino acids, free fatty acids, ketones, and glycerol for energy needs. Normal lower limit of fetal glucose concentration remains around 3 mmol/L (54 mg/dL) over most of gestati ...
... Fetus can use alternate substrates if necessary, but depends entirely on maternal supply and placental transfer of glucose, amino acids, free fatty acids, ketones, and glycerol for energy needs. Normal lower limit of fetal glucose concentration remains around 3 mmol/L (54 mg/dL) over most of gestati ...
Enzymatic Action in Digestion
... The foods we eat are composed primarily of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. In foods, however, these building blocks are often not in their most usable form and therefore must be digested before they can be transformed into whatever substance the body may need. Digestion is the process of break ...
... The foods we eat are composed primarily of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. In foods, however, these building blocks are often not in their most usable form and therefore must be digested before they can be transformed into whatever substance the body may need. Digestion is the process of break ...
Cellular Respiration
... Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle) Occurs in the Matrix of the Mitochondria Everything in the Krebs Cycle happens twice because there are two pyruvates from glycolysis. ...
... Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle) Occurs in the Matrix of the Mitochondria Everything in the Krebs Cycle happens twice because there are two pyruvates from glycolysis. ...
GI System GI Physiology Functions: - Ingestion
... Not activated UNTIL they get into the small intestine - When they get there, trypsinogen is ACTIVATED into trypsin by an enzyme – enterokinase – secreted in duodenal secretions Trypsin then activates chymotrypsinogenchymotrypsin Procarboxypeptidase carboxypeptidase These are POWERFUL protein dige ...
... Not activated UNTIL they get into the small intestine - When they get there, trypsinogen is ACTIVATED into trypsin by an enzyme – enterokinase – secreted in duodenal secretions Trypsin then activates chymotrypsinogenchymotrypsin Procarboxypeptidase carboxypeptidase These are POWERFUL protein dige ...
AminoAcidMetabolismFIN2011
... 1. In peripheral tissues,the a-amino groups of the amino acids are transferred to glutamate by a transamination reaction, as in the liver. 2. However, rather than oxidatively deaminating glutamate to form ammonium ion, the a-amino group is transferred to pyruvate to form alanine. 3. The liver takes ...
... 1. In peripheral tissues,the a-amino groups of the amino acids are transferred to glutamate by a transamination reaction, as in the liver. 2. However, rather than oxidatively deaminating glutamate to form ammonium ion, the a-amino group is transferred to pyruvate to form alanine. 3. The liver takes ...
amino acids
... Complete proteins such as eggs, milk, meat, and fish contain all of the essential amino acids. Incomplete proteins from plants such as grains, beans, and nuts are deficient in one or more essential amino acids. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake ...
... Complete proteins such as eggs, milk, meat, and fish contain all of the essential amino acids. Incomplete proteins from plants such as grains, beans, and nuts are deficient in one or more essential amino acids. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake ...
Key enzymes in glycolysis
... 1- Provide energy in the form of ATP (main function) 2- Provide intermediates for other metabolic pathways. It occurs in cytosols of all tissues All sugars can be converted to glucose & thus can be metabolized by glycolysis. ...
... 1- Provide energy in the form of ATP (main function) 2- Provide intermediates for other metabolic pathways. It occurs in cytosols of all tissues All sugars can be converted to glucose & thus can be metabolized by glycolysis. ...
video slide
... the pancreas secretes insulin, a hormone, into the blood. 2 Insulin enhances the transport of glucose into body cells and stimulates the liver and muscle cells to store glucose as glycogen. As a result, blood glucose level ...
... the pancreas secretes insulin, a hormone, into the blood. 2 Insulin enhances the transport of glucose into body cells and stimulates the liver and muscle cells to store glucose as glycogen. As a result, blood glucose level ...
Glycogen
... • pancreas secretes insulin. • Glucose from the portal vein enters the liver cells (hepatocytes). • Insulin acts on the hepatocytes to stimulate the action of several enzymes, including glycogen synthase. • Glucose molecules are added to the chains of glycogen as long as both insulin and glucose rem ...
... • pancreas secretes insulin. • Glucose from the portal vein enters the liver cells (hepatocytes). • Insulin acts on the hepatocytes to stimulate the action of several enzymes, including glycogen synthase. • Glucose molecules are added to the chains of glycogen as long as both insulin and glucose rem ...
Artifact 1
... glucose, fructose is metabolized exclusively in the liver by fructokinase. ‐‐‐‐‐form fructose 1‐P‐‐use up inorganic phosphate,… impossible to make ATP by the liver‐‐‐‐‐↓ATP‐dependent pumps Glucose metabolism is regulated by the rate‐limiting enzyme phosphofructokinase, which is inhibited by ATP ...
... glucose, fructose is metabolized exclusively in the liver by fructokinase. ‐‐‐‐‐form fructose 1‐P‐‐use up inorganic phosphate,… impossible to make ATP by the liver‐‐‐‐‐↓ATP‐dependent pumps Glucose metabolism is regulated by the rate‐limiting enzyme phosphofructokinase, which is inhibited by ATP ...