Fermentations
... Pasteur's usage, that "fermentation" means "life without air" required revision after the discovery of anaerobic respiration. The current definition of fermentation, intended to distinguish fermentation from anaerobic respiration, is that it is a chemoorganotrophic metabolism in which the electrons ...
... Pasteur's usage, that "fermentation" means "life without air" required revision after the discovery of anaerobic respiration. The current definition of fermentation, intended to distinguish fermentation from anaerobic respiration, is that it is a chemoorganotrophic metabolism in which the electrons ...
Lecture 4
... amino acids or to the group of uncharged ones, depending on the local pH. Lysine is classified as a charged residue because its terminal amino group is ionized under most physiological conditions, but its sidechain also contains a hydrophobic segment of four methylene groups. Likewise, the arginine ...
... amino acids or to the group of uncharged ones, depending on the local pH. Lysine is classified as a charged residue because its terminal amino group is ionized under most physiological conditions, but its sidechain also contains a hydrophobic segment of four methylene groups. Likewise, the arginine ...
Cellular Respiration
... • 1 glucose 2 ATP and 2 pyruvate • Glucose oxidized to pyruvate (loses electron) • NAD+ reduced to NADH (gains electron) ...
... • 1 glucose 2 ATP and 2 pyruvate • Glucose oxidized to pyruvate (loses electron) • NAD+ reduced to NADH (gains electron) ...
Chapter 9
... • 1 glucose 2 ATP and 2 pyruvate • Glucose oxidized to pyruvate (loses electron) • NAD+ reduced to NADH (gains electron) ...
... • 1 glucose 2 ATP and 2 pyruvate • Glucose oxidized to pyruvate (loses electron) • NAD+ reduced to NADH (gains electron) ...
SOURCES OF OUR OBJECTIONS Series A
... high phosphate content of the casein family allows it to associate with calcium and form calcium phosphate salts. The abundance of phosphate allows milk to contain much more calcium than would be possible if all the calcium were dissolved in solution, thus casein proteins provide a good source of ca ...
... high phosphate content of the casein family allows it to associate with calcium and form calcium phosphate salts. The abundance of phosphate allows milk to contain much more calcium than would be possible if all the calcium were dissolved in solution, thus casein proteins provide a good source of ca ...
Nutreval Interpretation Guide
... vi) A high ratio of phenylalanine to tyrosine (Nonessential Protein Amino Acids) suggests low tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), which would be consistent with low intracellular folates. This suggests a partial methylation ...
... vi) A high ratio of phenylalanine to tyrosine (Nonessential Protein Amino Acids) suggests low tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), which would be consistent with low intracellular folates. This suggests a partial methylation ...
Cells part 2 - fog.ccsf.edu
... • Overworked muscles can become anoxic • In low oxygen environments, pyruvate is converted to lactate to regenerate NAD+ • Lactic acid causes great suffering ...
... • Overworked muscles can become anoxic • In low oxygen environments, pyruvate is converted to lactate to regenerate NAD+ • Lactic acid causes great suffering ...
Gluconeogenesis
... starvation is mainly amino acid catabolism. Some amino acids are catabolized to pyruvate, oxaloacetate, or precursors of these. Muscle proteins may break down to supply amino acids. These are transported to liver where they are deaminated and converted to gluconeogenesis inputs. Glycerol, derived fr ...
... starvation is mainly amino acid catabolism. Some amino acids are catabolized to pyruvate, oxaloacetate, or precursors of these. Muscle proteins may break down to supply amino acids. These are transported to liver where they are deaminated and converted to gluconeogenesis inputs. Glycerol, derived fr ...
Separation and analysis of amino acids
... molecules, for example: • Tryptophan is a precursor of the neurotransmitter seretonin. • Glycine is a precursor of porphyrins such as heme. • Arginine is a precursor of nitric oxide. • Carnitine, made in the body from the amino acids lysine and methionine, is used in lipid transport within a cell. • ...
... molecules, for example: • Tryptophan is a precursor of the neurotransmitter seretonin. • Glycine is a precursor of porphyrins such as heme. • Arginine is a precursor of nitric oxide. • Carnitine, made in the body from the amino acids lysine and methionine, is used in lipid transport within a cell. • ...
Document
... • Transport of fatty acids into mitochondria • Beta-Oxidation proper in the mitochondrial matrix • Fatty acids are oxidized by most of the tissues in the body. • Brain, erythrocytes and adrenal medulla cannot utilize fatty acids for energy requirement. ...
... • Transport of fatty acids into mitochondria • Beta-Oxidation proper in the mitochondrial matrix • Fatty acids are oxidized by most of the tissues in the body. • Brain, erythrocytes and adrenal medulla cannot utilize fatty acids for energy requirement. ...
Gluconeogenesis
... starvation is mainly amino acid catabolism. Some amino acids are catabolized to pyruvate, oxaloacetate, or precursors of these. Muscle proteins may break down to supply amino acids. These are transported to liver where they are deaminated and converted to gluconeogenesis inputs. Glycerol, derived fr ...
... starvation is mainly amino acid catabolism. Some amino acids are catabolized to pyruvate, oxaloacetate, or precursors of these. Muscle proteins may break down to supply amino acids. These are transported to liver where they are deaminated and converted to gluconeogenesis inputs. Glycerol, derived fr ...
Chapter 15
... of the keto in pyruvate to a hydroxyl, yielding lactate, as NADH is oxidized to NAD+. Lactate, in addition to being an end-product of fermentation, serves as a mobile form of nutrient energy, & possibly as a signal molecule in mammalian organisms. Cell membranes contain carrier proteins that facilit ...
... of the keto in pyruvate to a hydroxyl, yielding lactate, as NADH is oxidized to NAD+. Lactate, in addition to being an end-product of fermentation, serves as a mobile form of nutrient energy, & possibly as a signal molecule in mammalian organisms. Cell membranes contain carrier proteins that facilit ...
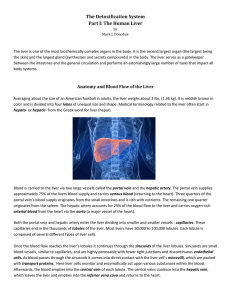
The Detoxification System Part I: The Human Liver
... Because glucose is very hydrophilic (water loving), this results in co-storage of large amounts of water. This form of energy storage takes up too much weight and volume to be efficient. Therefore surplus glucose is metabolized into fatty acids, via a process called lipogenesis, which are subsequent ...
... Because glucose is very hydrophilic (water loving), this results in co-storage of large amounts of water. This form of energy storage takes up too much weight and volume to be efficient. Therefore surplus glucose is metabolized into fatty acids, via a process called lipogenesis, which are subsequent ...
How to Assess Patient Biochemical and Nutritional Metametrix Clinical Laboratory
... Mitochondria function is also evaluated by measuring Krebs or Citric Acid Cycle intermediates. Utilization of energy from food components is demonstrated by the ability of the body to make basic molecules to support organ function. Measurement allows for evaluation of an individual from the cellular ...
... Mitochondria function is also evaluated by measuring Krebs or Citric Acid Cycle intermediates. Utilization of energy from food components is demonstrated by the ability of the body to make basic molecules to support organ function. Measurement allows for evaluation of an individual from the cellular ...
2 Practical Nutrition
... Energy Producer - The body doesn't like to use these at all or for a last resort because they are expensive. 1 gram = 4 Kcal energy. They are consumed as complete (has all the essential amino acids in them - usually animal source) or incomplete (missing at least 1 essential amino acid - usually pl ...
... Energy Producer - The body doesn't like to use these at all or for a last resort because they are expensive. 1 gram = 4 Kcal energy. They are consumed as complete (has all the essential amino acids in them - usually animal source) or incomplete (missing at least 1 essential amino acid - usually pl ...
1. The table below refers to some disaccharides, their constituent
... Describe one way in which the physical properties of a triglyceride composed of fatty acids of type B will differ from a triglyceride of similar molecular size composed of fatty acids of type A. ...
... Describe one way in which the physical properties of a triglyceride composed of fatty acids of type B will differ from a triglyceride of similar molecular size composed of fatty acids of type A. ...
Foods I - PRE-ASSESSMENT / FINAL REVIEW Directions: Match
... A. packing and leveling it off in a dry measuring cup. B. melting it first and pouring it into the recipe. C. using the water displacement method. D. both A and C. 41. When measuring brown sugar, it is important to: A. add a little bit of extra brown sugar to the recipe. B. under-measure a little be ...
... A. packing and leveling it off in a dry measuring cup. B. melting it first and pouring it into the recipe. C. using the water displacement method. D. both A and C. 41. When measuring brown sugar, it is important to: A. add a little bit of extra brown sugar to the recipe. B. under-measure a little be ...
2 Organic Acidemias
... acidemias is urine organic acid analysis by GC/MS, utilizing a capillary column. Organic acids can be measured in any physiologic fluid. However, it is most effective to use urine to identify the organic acids that signal these disorders, as semiquantitative methods may not identify the important co ...
... acidemias is urine organic acid analysis by GC/MS, utilizing a capillary column. Organic acids can be measured in any physiologic fluid. However, it is most effective to use urine to identify the organic acids that signal these disorders, as semiquantitative methods may not identify the important co ...
A1983RT00700001
... hibitor studies are used as evidence for the Beevers in Santa Cruz, California. P.J. Lea joined the department after spending three operation of the glutamate synthase cycle. years working with Sir Leslie Fowden at Uni[The SCI® indicates that this paper has been cited in over 220 publications since ...
... hibitor studies are used as evidence for the Beevers in Santa Cruz, California. P.J. Lea joined the department after spending three operation of the glutamate synthase cycle. years working with Sir Leslie Fowden at Uni[The SCI® indicates that this paper has been cited in over 220 publications since ...
1. glucose is broken down to pyruvate in the cytoplasm;
... glucose converted to pyruvate (two molecules); by glycolysis; pyruvate enters the mitochondria; pyruvate converted to acetyl CoA / ethyl CoA; by oxidative decarboxylation / NADH and CO2 formed; fatty acids / lipids converted to acetyl CoA; acetyl groups enter the Krebs cycle (accept acetyl CoA); FAD ...
... glucose converted to pyruvate (two molecules); by glycolysis; pyruvate enters the mitochondria; pyruvate converted to acetyl CoA / ethyl CoA; by oxidative decarboxylation / NADH and CO2 formed; fatty acids / lipids converted to acetyl CoA; acetyl groups enter the Krebs cycle (accept acetyl CoA); FAD ...
amino acid 1
... 1. In peripheral tissues,the a-amino groups of the amino acids are transferred to glutamate by a transamination reaction, as in the liver. 2. However, rather than oxidatively deaminating glutamate to form ammonium ion, the a-amino group is transferred to pyruvate to form alanine. 3. The liver takes ...
... 1. In peripheral tissues,the a-amino groups of the amino acids are transferred to glutamate by a transamination reaction, as in the liver. 2. However, rather than oxidatively deaminating glutamate to form ammonium ion, the a-amino group is transferred to pyruvate to form alanine. 3. The liver takes ...